AI21 Jamba Model: 256K Context Window Architecture Guide
Deep dive into AI21 Jamba model's 256K token context window, Mamba-Transformer architecture, efficiency features, and enterprise applications.
Introduction
AI21 Labs released the Jamba model in 2024 as their first production-grade large language model, marking a significant advancement in AI language processing. This model combines two distinct architectures into a unified system, utilizing both Transformer layers and Mamba layers, a novel approach in AI model design. This hybrid is known as the Mamba-Transformer architecture. The most striking feature? A 256K token context window, enabling the processing of about 200,000 words in a single request, setting a new standard for AI model context lengths. Such models are essential for businesses needing to analyze long documents, maintain extended conversations, and handle large codebases without losing track, addressing a critical need in enterprise AI applications. The Jamba model focuses on developers working with RAG systems, enterprise applications managing legal documents, and companies necessitating effective processing of extensive text inputs, offering solutions to longstanding challenges in these sectors.
What is the AI21 Jamba Model
Jamba Hybrid Architecture Overview:
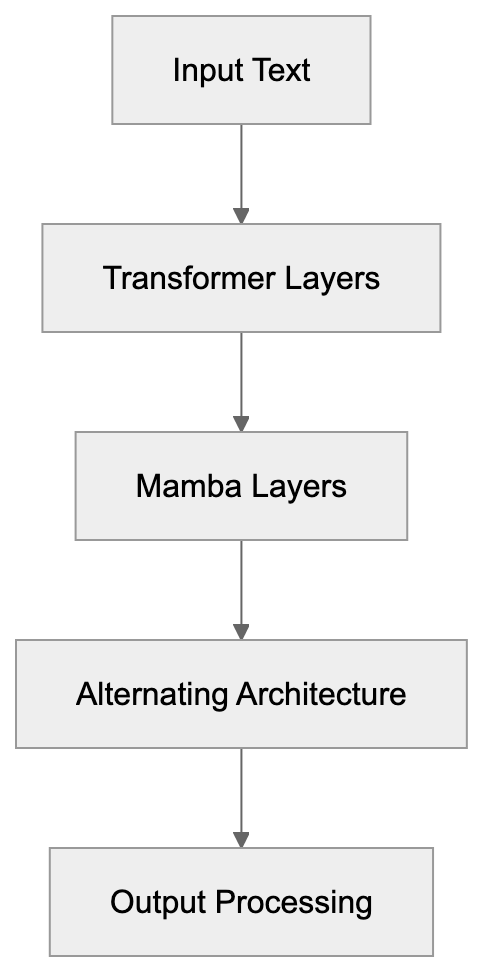
The Jamba model processes text using a hybrid architecture distinct from most AI models, which primarily use only Transformer blocks. Jamba integrates Mamba blocks, a new architecture type using state space models instead of attention mechanisms. This approach allows it to handle extremely long context windows without consuming exorbitant memory. Designed by AI21 Labs, Jamba can, in many cases, fit on a single GPU. The base version of the model varies in parameter count based on specific releases with a 256,000 token context window—approximately 16 times larger than GPT-3.5’s original 4K window. Transformer and Mamba layers alternate throughout its depth, balancing local patterns and long-range dependencies effectively.
Why Jamba Exists and Its Purpose
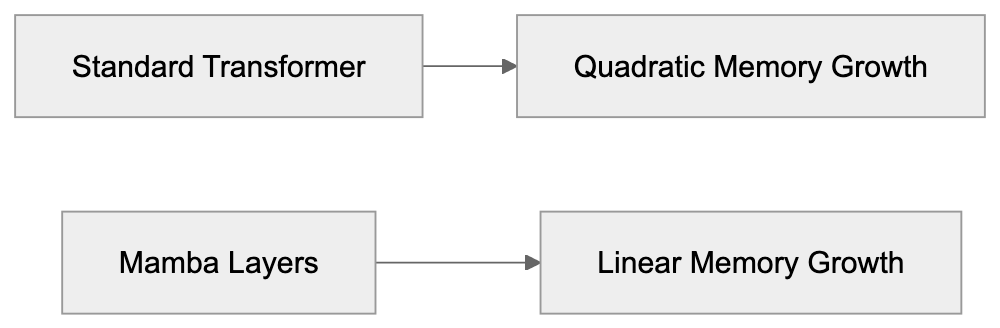
Long context windows address a significant issue. Standard models fail to retain information as conversations or documents surpass their token limits. Businesses analyzing contracts, legal briefs, research papers, or entire codebases require models that remember everything. Transformer architectures struggle here due to attention mechanisms that scale quadratically, meaning doubled context lengths quadruple memory requirements, leading to increased expenses. Mamba layers, however, scale linearly, maintaining a compressed state updated with new tokens. AI21 Labs designed Jamba to harness both strengths. Transformers excel at understanding word relationships, while Mamba maintains long-range information, creating a model that manages long contexts efficiently without requiring massive infrastructure.
Memory Scaling Comparison:
How Businesses and Developers Use Jamba
Developers integrate Jamba into applications necessitating long context understanding. Common applications include document analysis systems processing entire PDF files in a single pass, legal technologies reviewing lengthy contracts, and customer service platforms maintaining conversation history over multiple exchanges. Jamba functions well in RAG setups needing reference to extensive knowledge bases. Software development teams use it to analyze entire repositories, identifying architecture insights, bugs, or improvement opportunities. Enterprises access Jamba through AI21’s API, foregoing self-hosting. The API offers varied pricing tiers based on usage, and certain companies fine-tune Jamba with proprietary data for specialized tasks. The 256K context window reduces chunking and API calls, translating to cost savings for high-volume applications.
Technical Specifications and Performance
Common Jamba Use Cases:
The Jamba architecture leverages a specific ratio of Transformer to Mamba layers. AI21 Labs experimented with configurations before finalizing the production version. Some variants incorporate mixture-of-experts layers, activating only a subset of the model per token, thus reducing computational load. Notably memory-efficient, Jamba runs inference on contexts up to 256K tokens using considerably less GPU memory compared to similarly capacitated pure Transformer models. Processing speed varies with context length, yet remains competitive with other enterprise AI models. It supports standard sampling parameters like temperature, top-p, and frequency penalty, managing multiple languages, with English yielding the strongest results. Outcomes span JSON, code, structured data, and natural language based on input instructions, maintaining response quality across the full context window, albeit with slight degradation at maximum length.
Comparing Jamba to Alternative Models
Several models compete in the long context space, each employing distinct methods for extended inputs. Here’s a comparison:
| Model | Max Context | Architecture | Memory Efficiency | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI21 Jamba | 256K tokens | Mamba-Transformer hybrid | High | API, limited self-hosting |
| Anthropic Claude 3.5 Sonnet | 200K tokens | Transformer | Medium | API only |
| GPT-4o | 128K tokens | Transformer | Medium | API only |
| Google Gemini 1.5 Pro | 1M tokens | Transformer-based | Medium-High | API only |
| Mistral Large | 32K tokens | Transformer | Medium | API and self-hosting |
Jamba offers significant memory efficiency compared to pure Transformer models, ideal for self-hosting or latency-sensitive applications. While Gemini 1.5 Pro provides the longest context at 1M tokens, Jamba’s hybrid architecture strikes a balance between efficiency and context length.
Jamba Model Access and Pricing
AI21 Labs primarily offers access to Jamba through their API platform. Developers can register on AI21’s website for API keys, with a token-based pricing system that charges for input and output tokens separately. Prices generally remain competitive with other enterprise AI models. Service tiers include standard API access for most developers and specialized support for enterprises, offering dedicated assistance, custom rate limits, and potential private deployments. Some Jamba versions allow self-hosting under specific licensing for large enterprises with distinct data residency or security needs. API documentation provides integration examples for languages like Python and JavaScript, following standard REST API patterns. The monitoring dashboard tracks usage, costs, and performance metrics, with rate limits dictated by account tier.
Real-World Performance Considerations
Utilizing the full 256K context window presents trade-offs. Longer context lengths result in increased latency. Requests with 200K tokens take more time than those with 2K tokens, and cost scales with token count, making maximum requests costly. Most applications seldom constantly require such extended contexts. Savvy developers strategically chunk data, reserving the long context for essential cases. Jamba performs optimally with structured inputs; well-organized markdown, orderly code, and formatted documents yield superior outcomes compared to unstructured text. Prompt engineering is critical with long contexts to guide the model to relevant information. Certain techniques, such as placing key details near context start or end, help. The model occasionally loses track of details in overly extensive contexts, requiring applications to validate crucial information rather than relying on the model blindly.
Use Cases Where Jamba Excels
Jamba is particularly adept at document analysis, a primary domain of usage. Legal firms can upload entire case files to query specific clauses, precedents, or contradictions, processing everything in one pass. Financial analysts leverage Jamba for processing quarterly reports, 10-K filings, and analyst notes simultaneously. Research teams use Jamba to synthesize across multiple academic papers. In software development, code review tools benefit from analyzing whole repositories, identifying architecture patterns, and suggesting refactoring opportunities. Technical writing teams maintain consistency across extensive documentation sets using Jamba. Customer service platforms benefit from the extended conversation memory, enabling agents to access complete customer histories. Educational technologies employ Jamba for personalized tutoring that recalls all exchanges with a student, while content creation workflows maintain style and continuity in long-form pieces.
Limitations and Considerations
The Jamba model is not flawless in every scenario. Its hybrid architecture can present a learning curve compared to pure Transformer models. Fine-tuning is more constrained than with fully open-source alternatives, with hosting and maintenance relying on AI21 Labs if using the API. Model dependency means service outages or API changes affect applications. The model’s training data has a knowledge cutoff, resulting in missing information after that date. Bias in training data necessitates fairness reviews in outputs. Although impressive, the 256K context may not cover all use cases, with multi-million token scenarios still needing chunking. Cost management is crucial for high-volume applications, as continuous max-length contexts become expensive. Latency constraints could exclude Jamba from real-time applications demanding sub-second response times. The model functions best in English, with reduced performance in other languages.
The Future of Long Context Models
Current trends increasingly favor longer context windows. Models from 2020 usually offered 2K-4K tokens, whereas modern models range from 32K to 128K. Jamba’s 256K and Gemini’s 1M windows illustrate this evolution. Architectural innovations like Mamba-Transformer hybrids will likely proliferate as pure attention mechanisms face inherent scaling challenges. Hybrid approaches, state space models, and other alternatives show promise. Memory efficiency advancements are as crucial as raw context length, with models effectively managing 128K tokens surpassing those poorly handling 256K. Future developments will likely emphasize retrieval augmentation alongside long contexts, combining smart retrieval with extended memory for optimal solutions. Specialized models for specific domains, such as legal, medical, or financial AI, will increasingly demand expanded memory capabilities.
End
The AI21 Jamba model provides a unique solution to the long context challenge. Its 256K token window accommodates substantial documents, conversations, and codebases in single requests. The Mamba-Transformer hybrid architecture effectively delivers this capability with greater AI model efficiency than pure Transformer alternatives. Businesses employ Jamba for document analysis, code review, customer service, and research applications. Developers access it mainly via AI21’s API, although self-hosting options exist for specific enterprises. Competing with Claude 3.5 Sonnet, GPT-4o, Gemini 1.5 Pro, and others, each offers distinct trade-offs in context length, efficiency, and availability. Jamba thrives in scenarios necessitating extended memory without massive infrastructure demands, while limitations involve costs, latency at maximum contexts, and dependency on AI21’s infrastructure. The hybrid architecture signifies a meaningful evolution in transformer models, balancing capability with practical constraints.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the practical applications of the Jamba model for businesses?
The Jamba model is particularly useful for businesses involved in document analysis, legal reviews, customer service, and software development. It allows users to analyze entire documents or maintain extensive conversation histories efficiently, making it a valuable tool for sectors that require in-depth processing of lengthy texts.
How does the Jamba model compare to other models in terms of memory efficiency?
Jamba's hybrid architecture provides significant memory efficiency compared to pure Transformer models. While other large models like GPT-4o may have shorter context lengths, Jamba's integrated Mamba layers allow it to maintain a 256K token context effectively, making it suitable for extensive applications without the heavy computational costs associated with longer token counts.
Can businesses fine-tune the Jamba model to suit their specific needs?
Yes, some companies can fine-tune specific versions of the Jamba model with proprietary data for specialized tasks. However, the options for fine-tuning may be more constrained compared to fully open-source models. Developers can also leverage the API to customize their usage based on application needs.
What measures can developers take to manage costs when using Jamba?
To manage costs, developers should consider strategically chunking data and utilizing the full context window only when necessary. Optimizing the inputs and reducing the frequency of maximum-length requests can lead to significant savings, especially in high-volume applications.
What are the main limitations of using the Jamba model?
Some limitations include dependency on AI21 Labs' infrastructure, potential service outages, and latency with longer context requests. Additionally, the model may not perform as effectively in languages other than English and can struggle with maintaining detail in extremely lengthy contexts.
How can the Jamba model handle unstructured text inputs?
The Jamba model is optimized for handling structured inputs, such as well-organized markdown or formatted documents. However, unstructured texts may lead to inferior performance, so users are encouraged to format their prompts and provide context efficiently to enhance the model's output quality.
What are the future trends for models like Jamba in AI processing?
Future models will likely continue to focus on longer context windows and improved memory efficiency. Innovations in hybrid architectures, alongside augmented retrieval capabilities, may emerge to provide better support for specialized fields such as legal, financial, or healthcare applications that demand robust memory functions.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.