Falcon LLM by TII: Open Source AI Models Guide
Complete guide to Falcon LLM models by Technology Innovation Institute. Compare Falcon with Llama and Mistral, explore benchmarks and versions.
Falcon LLM: A Leading Open-Source AI Model by TII
Falcon LLM is a remarkable family of open-source large language models crafted by the Technology Innovation Institute (TII), a leading global applied research center under Abu Dhabi’s Advanced Technology Research Council (ATRC). Competing with models like Llama and Mistral, Falcon offers high-performance language understanding and generation capabilities, free for developers and researchers to use. Introduced to push AI research forward, TII released Falcon with the intention of offering powerful language models without restrictive licensing, exemplifying their dedication to advancing the frontiers of AI. The series spans multiple sizes, including the expansive Falcon 180B model, which contains 180 billion parameters and was trained on 3.5 trillion tokens, marking it as one of the largest open-access large language models released as of 2024. These models utilize transformer architecture and are trained on substantial datasets, adept at tasks like chatbots, code generation, and content creation, with Falcon 180B achieving a 68.74 score on the Hugging Face Open LLM Leaderboard at launch, outperforming LLaMA 2 70B.
What is Falcon LLM?
Falcon LLM encompasses a series of decoder-only language models developed by the Technology Innovation Institute, a UAE-based research institution focused on advancing technology. Released in 2023, Falcon quickly gained traction in the AI community. These models use transformer architecture, akin to GPT, and are accessible through platforms like Hugging Face. The name “Falcon” symbolizes speed and precision, inspired by the UAE’s national bird. Utilizing the custom RefinedWeb dataset, Falcon models offer commercial use under permissive licenses, distinguishing themselves from more restrictive counterparts.
Purpose and Impact of Falcon
Falcon Model Family Overview:
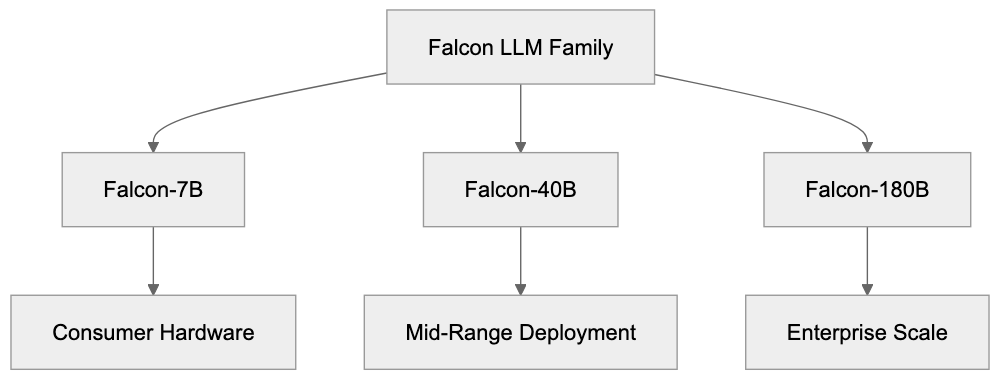
The Technology Innovation Institute created Falcon to support open AI research and reduce reliance on closed models. Prior to Falcon, access to powerful AI technology was often restricted by licensing. TII aimed to offer an alternative that anyone could use and modify. Supported by the UAE government’s AI strategy, Falcon aids in research, application development, and showcasing regional AI prowess. It’s employed in varied domains like chatbots, content tools, coding, and data analysis. Researchers benefit from Falcon for studying language understanding, testing training methods, and benchmarking.
Falcon Model Versions and Evolution
Falcon’s evolution includes several versions with varying capabilities. Initial releases featured Falcon-7B and Falcon-40B, noted for their effective deployment. Falcon-40B excelled on benchmarks, momentarily topping the Open LLM Leaderboard. In September 2023, TII unveiled Falcon-180B, boasting 180 billion parameters and competing with Meta’s Llama 2 70B. TII also developed Falcon-Instruct, designed for following user commands. The models enhance inference speed with multi-query attention, and leverage the high-quality RefinedWeb dataset.
Deploying Falcon Models
Falcon Architecture Components:
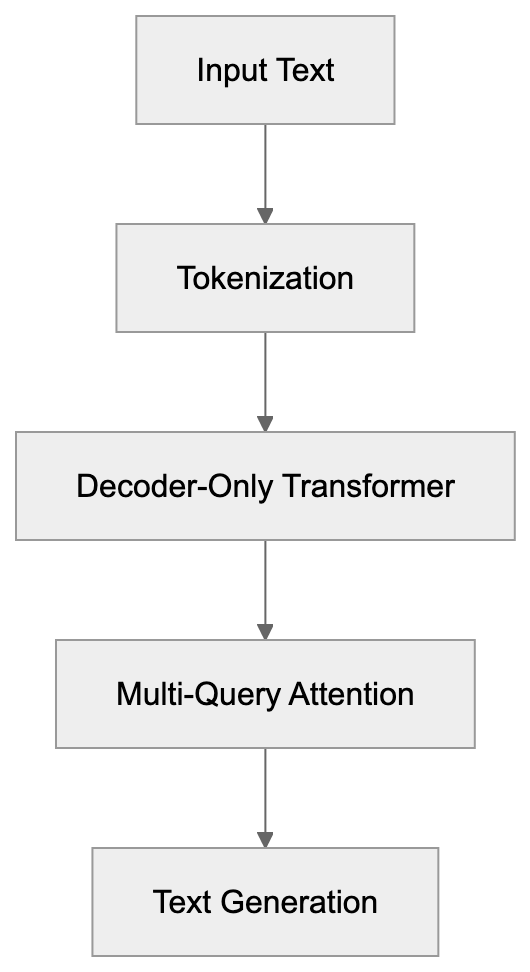
Falcon models are downloadable from platforms like Hugging Face, suitable for cloud or on-premises deployment. Falcon-7B runs on consumer GPUs, while Falcon-180B needs more robust hardware. Companies leverage Falcon in customer service chatbots and content creation platforms. Software tools use it for code completion, while researchers fine-tune it for domain-specific tasks. The open-source license allows commercial use, making it appealing for startups prioritizing data privacy.
Falcon Benchmarks and Comparisons
Falcon’s capabilities are measured against standard benchmarks like MMLU and HellaSwag, with Falcon-180B showcasing competitive performance. It aligns closely with Llama 2 70B, though task performance varies. Here’s a comparison of major models:
| Model | Parameters | MMLU Score | License Type | Training Tokens | Release Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Falcon-180B | 180B | ~68% | Apache 2.0 | 3.5T | Sept 2023 |
| Llama 2 70B | 70B | ~69% | Custom | 2T | July 2023 |
| Mistral 7B | 7B | ~62% | Apache 2.0 | Unknown | Sept 2023 |
| Falcon-40B | 40B | 60.6% | Apache 2.0 | 1T | May 2023 |
Falcon Deployment Options:
 | Llama 2 13B | 13B | ~55% | Custom | 2T | July 2023 |
| Llama 2 13B | 13B | ~55% | Custom | 2T | July 2023 |
Falcon-180B, while resource-intensive, delivers robust performance.
Technical Details and Architecture of Falcon
Falcon employs a decoder-only transformer architecture, featuring multi-query attention for reduced memory and faster generation. FlashAttention further boosts performance. Trained on RefinedWeb, Falcon models rely on extensive dataset filtering for quality. With up to 3.5 trillion tokens and trained over months, these models maintain standard tokenization and floating-point precision, with quantization options for deployment.
Licensing and Commercial Use of Falcon
Typically released under the Apache 2.0 license, Falcon models endorse commercial use, modification, and distribution. Users avoid licensing fees and retain patent protections. Some earlier versions had different licenses, but recent releases standardize on Apache 2.0. Unlike Meta’s Llama 2’s custom license, Falcon’s approach encourages adoption in commercial settings.
UAE’s AI Strategy and TII’s Role
The UAE prioritizes AI development for economic diversification, establishing TII in 2020 for advanced research. Part of the Advanced Technology Research Council, TII focuses on AI, robotics, and quantum computing. Falcon exemplifies their AI endeavors, aiming for global leadership in AI by 2031. Collaborating with international researchers, TII publishes research and releases open-source tools, highlighting regional contributions to AI.
Challenges and Limitations of Falcon
Falcon models face challenges typical of large language models, including high computational costs for training and deployment. Models like Falcon-180B demand extensive hardware, while limitations like context windows and biases remain. Compared to proprietary models, Falcon lacks built-in safety features. Training specifics are undisclosed, complicating reproduction. Despite being English-centric, Falcon holds value for open-source applications needing transparency and control.
Getting Started with Falcon LLM
Access Falcon models on Hugging Face, supported by thorough documentation and examples. Python, transformers, and torch are required, with smaller models operable on 16GB+ GPU systems. Larger models need cloud or multi-GPU setups. Hugging Face APIs facilitate model testing, with tools like TensorRT-LLM enhancing deployment. Developers can fine-tune Falcon with PEFT, guided by Hugging Face tutorials and community forums.
Falcon LLM stands as a pivotal open-source AI contribution from the UAE’s Technology Innovation Institute, spanning from Falcon-7B to Falcon-180B. Competing with models like Llama and Mistral, it excels on benchmarks without restrictive licensing. Despite challenges, Falcon offers a valuable alternative to proprietary systems. The UAE’s investment in AI through projects like Falcon underscores diverse regional contributions to global tech advancement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of applications can utilize Falcon LLM?
Falcon LLM can be used in various applications, including chatbots, content creation tools, data analysis, and software for code assistance. Its versatile architecture allows developers to tailor the model for specific tasks within these domains.
How do I deploy Falcon models in my projects?
Falcon models can be deployed through platforms like Hugging Face. Depending on the model size, you can run smaller models on consumer-grade GPUs, while larger models like Falcon-180B require more powerful hardware, such as cloud-based or multi-GPU setups.
What are the hardware requirements for running Falcon-180B?
Running Falcon-180B necessitates robust hardware, including high-memory GPUs, as it has 180 billion parameters. A cloud-based solution or a multi-GPU configuration is often recommended for optimal performance and efficiency.
Is there a cost associated with using Falcon models?
Falcon models are released under the Apache 2.0 license, which allows for free use, modification, and distribution, making them cost-effective for developers and researchers. This open-source model means you can use it for commercial purposes without incurring licensing fees.
What kind of support or resources are available for new users?
New users can access thorough documentation, tutorials, and a community forum on platforms like Hugging Face to get started with Falcon models. These resources provide guidance on installation, usage, and fine-tuning of the models.
How does Falcon LLM compare to proprietary models?
While Falcon LLM competes well against proprietary models like Llama and Mistral in benchmark performance, it offers the advantage of open-source accessibility. This allows users greater control and transparency but may require additional work to implement safety features that are often built into commercial models.
What is the significance of the UAE's investment in Falcon LLM?
The UAE's investment in Falcon LLM reflects its strategic initiative to advance AI technology, aiming for global leadership by 2031. This project showcases the region's commitment to fostering innovation and encourages collaboration with international researchers for broader contributions to AI development.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.