Google Gemma AI Models: Lightweight Design Guide
Learn about Google's Gemma AI models, their lightweight architecture, development from Gemini tech, and edge deployment capabilities.
Google Gemma: Lightweight AI Models for Edge AI Deployment
Google released Gemma as a family of lightweight open-source AI models in early 2024. These models, built with Gemini technology, are designed to be smaller and more effective than previous models, making them ideal for edge AI deployment. They can run on consumer hardware and edge devices, making them accessible to developers and researchers without massive computing resources.
The purpose of models like Gemma is straightforward. Not everyone needs the complexity of GPT-4. Many applications perform better with smaller, faster models that are cost-effective to run. Gemma AI fills this gap, offering quality AI performance without the infrastructure demands of larger models. These models come in different sizes (2B and 7B parameters initially, with newer versions expanding the lineup). They’re pre-trained and ready for fine-tuning on specific tasks.
What Are Gemma AI Models?
Gemma Model Family Overview:
Gemma represents Google’s entry into the lightweight open-source language model space. The name is derived from the Latin word for precious stone. Google DeepMind and the Gemini team developed these models using the same research and technology that powers Google Gemma, but Gemma models differ fundamentally in scale and application.
These are small language models or SLMs. The initial release included Gemma 2B and Gemma 7B variants. Later, Google introduced Gemma 1.1 with improved performance and Gemma 2 with sizes up to 27B parameters. Each model comes in base and instruction-tuned versions, with the latter optimized for following commands and chat applications.
Gemma models are open source AI models, meaning developers can download the model weights and use them under a permissive license that allows commercial use. The models are compatible with popular frameworks like PyTorch, JAX, and TensorFlow and can be run on various hardware, from laptops to cloud servers.
What makes Gemma special is its size-to-performance ratio. A 7B parameter model can fit into consumer GPU memory but still handles complex language tasks reasonably well. This opens up AI development to smaller teams and individual developers.
Why Gemma Exists and Its Purpose
The AI scene changed dramatically in 2023 and 2024. Large language models became powerful but also extremely costly to run. Companies like Meta released Llama 2, and Mistral AI introduced effective alternatives. Google needed a response in this space.
Gemma serves multiple purposes:
- Democratizes AI access: Researchers and small businesses can prototype AI features without enterprise budgets.
- Addresses privacy concerns: Models can be run on-device, ensuring sensitive data remains secure.
- Facilitates edge AI deployment: Smart devices and IoT systems benefit from local AI processing, reducing latency and functioning without internet connectivity.
Technically, Gemma is used for benchmarking and research. Open-source AI models enable researchers to study AI behavior, test safety measures, and develop new techniques. Google contributes to the research community while maintaining competitive positioning against Meta and Mistral AI.
Gemma Application Architecture:

How Gemma Models Are Used in Practice
Developers use Gemma for a variety of applications:
- Chatbots and virtual assistants: Instruction-tuned models handle conversational tasks effectively.
- Content generation: Marketing teams use Gemma to draft emails, social media posts, and product descriptions.
- Code assistance: Developers fine-tune models on programming languages for code completion and bug detection.
- Edge deployment: Mobile apps use quantized versions of Gemma for on-device text processing.
- Research: Academic teams fine-tune models for medical text analysis or legal document review.
Google itself leverages Gemma technology internally. The effective techniques developed for Gemma feed back into Google Gemma development, creating a two-way research process.
Development History and Technical Background
Google announced Gemma in February 2024, shortly after the Gemini launch in December 2023. This timing was intentional, offering both enterprise-scale AI (Google Gemma) and accessible AI (Gemma) simultaneously.
Trained on up to 6 trillion tokens of text data, these models were refined with insights from Gemini development, including safety filtering and alignment techniques. Gemma 1.1, released in April 2024, featured performance improvements, while Gemma 2 launched in June 2024 with expanded model sizes, offering capabilities closer to larger models.
Technically, Gemma uses a transformer architecture with specific optimizations like multi-query attention, grouped-query attention, and RoPE (Rotary Position Embeddings). The models support context windows of 8,192 tokens, allowing longer document processing. Google also released CodeGemma variants for code generation.
Comparison with Llama and Mistral Models
Edge AI Deployment Flow:
 The lightweight AI model market includes competitors like Meta’s Llama 2 and Mistral AI’s models. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right model for specific needs.
The lightweight AI model market includes competitors like Meta’s Llama 2 and Mistral AI’s models. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right model for specific needs.
| Feature | Gemma 7B | Llama 2 7B | Mistral 7B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Release Date | Feb 2024 | Jul 2023 | Sep 2023 |
| Context Length | 8,192 tokens | 4,096 tokens | 32,768 tokens |
| License | Gemma Terms of Use | Llama 2 License | Apache 2.0 |
| Commercial Use | Allowed | Allowed with restrictions | Fully allowed |
| Training Tokens | 6 trillion | 2 trillion | Unknown |
| Benchmark (MMLU) | ~64% | ~46% | ~62% |
Gemma generally outperforms Llama 2 in benchmarks due to additional training data and newer architecture. However, Mistral 7B excels in document processing with its long context window, using sliding window attention.
License types vary, affecting commercial deployment. Mistral’s Apache 2.0 license is most permissive, while Gemma’s terms allow commercial use with some restrictions.
For edge AI deployment, Gemma has advantages as it was improved specifically for mobile and embedded systems. Community support is strong, with Google documentation and integration with Kaggle and Colab platforms.
Edge Deployment and Practical Use Cases
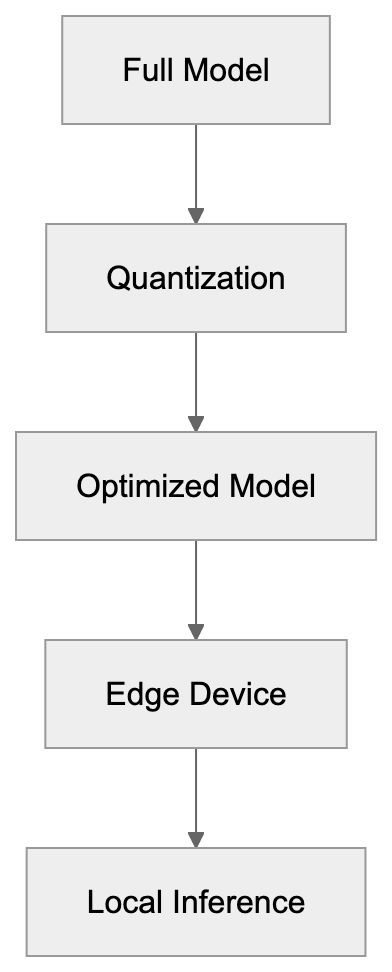
Edge deployment refers to running AI locally on devices rather than cloud servers, and Gemma is designed for this.
- Quantization: Reduces model size, allowing a 7B Gemma model to fit in consumer GPU memory.
- Mobile apps: Can embed quantized Gemma models via MediaPipe and TensorFlow Lite, enabling on-device AI capabilities.
- IoT devices: Use Gemma for local intelligence, reducing dependency on cloud connectivity.
- Healthcare: On-premise AI for regulatory compliance, with fine-tuned models assisting in medical analysis.
- Automotive: In-vehicle assistants run Gemma variants for rapid voice command processing.
Performance benchmarks demonstrate practical viability. A quantized Gemma 2B model generates around 20-30 tokens per second on a modern smartphone, suitable for interactive applications.
Alternatives and the Broader Ecosystem
Beyond Llama and Mistral, other models like Microsoft’s Phi-2, Falcon, and Stability AI’s StableLM offer different strengths:
| Model | Parameters | Key Strength | Primary Use Case | License Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gemma 2 | 2B-27B | Google ecosystem combination | Edge AI, research | Gemma ToU |
| Llama 2 | 7B-70B | Large community, extensive fine-tuning | General purpose | Llama 2 License |
| Mistral 7B | 7B | Long context, effectiveness | Document processing | Apache 2.0 |
| Phi-2 | 2.7B | Reasoning tasks | Education, research | MIT |
| Falcon | 7B-180B | Multilingual support | International applications | Apache 2.0 |
Each model release fosters improvement across the board, which benefits everyone building AI applications.
Conclusion
Google’s Gemma models fill an important gap in the AI ecosystem. Bringing Gemini technology to accessible hardware and edge devices, their lightweight design enables applications that weren’t feasible with larger models.
For edge deployment and resource-constrained environments, Gemma represents a strong option. The ongoing competition between Gemma, Llama, Mistral AI, and other lightweight models drives progress, benefiting the developer community. Understanding these tools ensures the right choice for specific applications and deployment scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions
What hardware do I need to run Gemma models?
Gemma models are designed to run on consumer hardware, making them accessible for laptops, desktops, and edge devices. A model like the 7B variant can fit into consumer GPU memory, allowing it to perform effectively without the need for high-end computing resources.
Can I use Gemma models for commercial purposes?
Yes, Gemma models are open-source and come with a permissive license that allows for commercial use. However, it’s essential to review the specific terms of use associated with the Gemma models to ensure compliance.
What applications are best suited for Gemma models?
Gemma models are suitable for a variety of applications, including chatbots, content generation, and code assistance. They excel in tasks that require on-device AI processing, particularly for mobile apps and IoT devices due to their lightweight design.
How does Gemma compare to other lightweight models like Llama and Mistral?
Gemma generally outperforms Llama 2 in various benchmarks due to its larger training datasets and more recent architecture. However, Mistral's models excel in processing longer contexts. Each model has unique strengths that may cater to specific needs, so choosing the right model depends on the application requirements.
What are quantized versions of Gemma models?
Quantized versions of Gemma models are optimized to reduce their size, allowing them to fit into smaller memory spaces on consumer devices while maintaining decent performance. This makes them particularly advantageous for edge AI deployment, where memory and processing power may be limited.
Are updates available for Gemma models?
Yes, Google has released updates to the Gemma models, such as the introduction of Gemma 1.1 and Gemma 2, which feature expanded sizes and improved performance. Being open-source, the community also contributes to the models, potentially leading to further enhancements.
How can I start using Gemma models in my projects?
You can begin using Gemma models by downloading them from the appropriate repositories and integrating them with popular AI frameworks like PyTorch, JAX, or TensorFlow. Documentation provided by Google will assist you in setting up and fine-tuning the models for your specific tasks.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.