OpenChat: Community Fine-Tuned LLM Guide
Explore OpenChat, the open-source chatbot with high-quality responses through efficient C-RLFT training. Compare benchmarks and licensing.
What OpenChat Is and Why It Matters
OpenChat is an open-source large language model developed by laion.ai. This language model serves as an open-source chatbot, utilizing a unique training method known as C-RLFT to produce responses that rival commercial models. The project’s main goal is to make high-quality AI accessible to everyone without the need for extensive computing power.
Language models like OpenChat are important as they provide chatbot alternatives to expensive proprietary systems. Many companies and researchers can’t afford the computational costs of training models from scratch. Fine-tuned models address this gap by enhancing existing base models with targeted training techniques. This enables small businesses, developers, and researchers to harness advanced AI capabilities without massive infrastructure investments.
OpenChat excels by delivering strong performance with significantly less training data than its competitors. Released under the Apache 2.0 license, it allows commercial use without restrictions, unlike some alternatives that impose limitations or require payment for commercial deployment.
Understanding the C-RLFT Training Method
The laion.ai team has developed a novel training approach called C-RLFT, which is the core differentiator of OpenChat from other open-source chatbots. C-RLFT trains the model with mixed-quality data, allowing it to generate high-quality outputs effectively.
Traditional fine-tuning demands large volumes of high-quality training examples, which are costly due to the need for human-rated responses. OpenChat reduces this requirement significantly through its conditioning technique, achieving similar results with fewer examples.
C-RLFT Training Process:
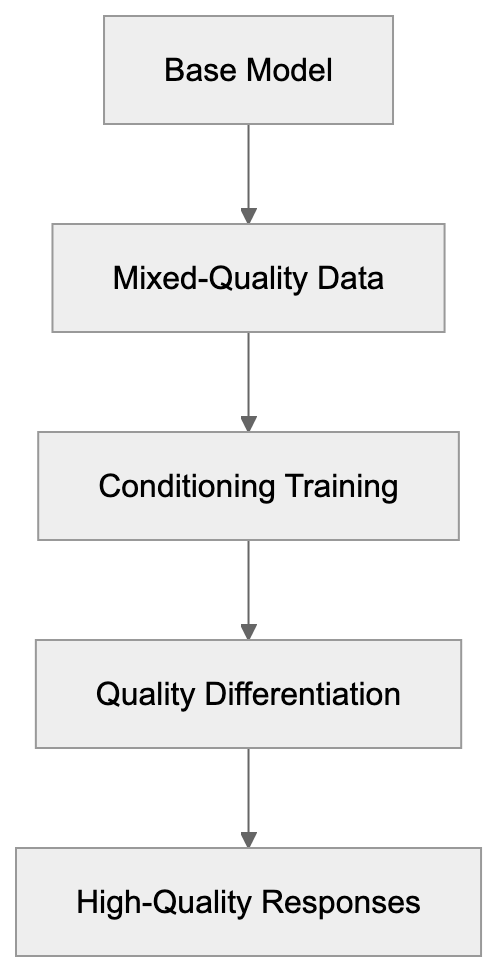
The C-RLFT process starts with a base model like Llama, which is fine-tuned with carefully selected conversational data. This conditioning helps the model learn to differentiate between high- and low-quality responses, resulting in a chatbot capable of producing more helpful and accurate answers than those trained with standard supervised fine-tuning.
Developers interested in C-RLFT should note it is grounded in reinforcement learning principles. During training, the model receives signals about response quality, guiding it towards better outputs. This method proves more effective than simply presenting the model with examples and expecting it to learn patterns autonomously.
How Organizations Use OpenChat
Organizations deploy OpenChat across various applications requiring conversational AI without vendor lock-in. Web developers integrate it into customer service systems to address frequent queries. Its open-source nature allows modifications for specific use cases or industries.
Marketing experts employ models like OpenChat to generate content ideas and draft text, all while keeping proprietary data secure by running on local infrastructure. This is vital for businesses that must avoid transmitting sensitive information to third-party APIs.
SEO professionals and content marketers use OpenChat for research and content enhancement. The model analyzes topics and suggests improvements without external data transfer. Small business owners benefit from manageable hosting costs compared to the per-token expenses of commercial providers.
Researchers adopt OpenChat as a basis for studying language model behavior. Under the Apache 2.0 license, they can modify and redistribute the model for academic pursuits, fostering a feedback loop where community-driven improvements benefit all users.
Performance Benchmarks and Comparisons
OpenChat demonstrates competitive performance on standard language model benchmarks. The UIUC AI team reports strong results for OpenChat in conversational tasks, setting it apart from other open-source chatbot alternatives. These benchmarks measure factors like response accuracy, helpfulness, and alignment with human preferences.
OpenChat Deployment Architecture:

In the MT-bench evaluation, which assesses multi-turn conversational ability, OpenChat scores comparably with much larger models. This benchmark is crucial as it reflects real-world scenarios where users engage in back-and-forth dialogues. OpenChat maintains context across multiple exchanges, which is essential for practical applications.
The AlpacaEval leaderboard showcases OpenChat’s performance against models trained with more extensive resources. This efficacy stems from the C-RLFT method, which maximizes the value of each training example. For developers selecting between models, this translates to better performance per parameter.
Here’s how OpenChat compares to similar open-source chatbots:
| Model | Base Model | Training Method | License | Benchmark Score (MT-bench) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenChat | Llama 2 | C-RLFT | Apache 2.0 | 7.81 |
| Vicuna | Llama 2 | Supervised FT | Non-commercial | 7.12 |
| Alpaca | Llama | Supervised FT | Non-commercial | 4.53 |
| Mistral-Instruct | Mistral | Supervised FT | Apache 2.0 | 7.60 |
| Llama-2-Chat | Llama 2 | RLHF | Custom | 6.27 |
These figures highlight OpenChat’s strong results while adhering to a commercially friendly Apache 2.0 license. Unlike models such as Vicuna, which restrict commercial use, OpenChat’s licensing is a significant advantage.
Technical Requirements and Deployment
Understanding the hardware requirements for inference is critical to running OpenChat. The model is available in various sizes, each with distinct memory needs. Smaller versions can run on consumer GPUs, while larger variants demand more robust hardware.
For software developers, deploying OpenChat entails loading the model weights and setting up an inference server. Frameworks like vLLM and FastChat support OpenChat seamlessly, handling batching and enhancements to optimize throughput.
OpenChat’s architecture is based on standard transformers, meaning existing improvement strategies can be applied. Quantization reduces memory usage from 16-bit to as low as 4-bit precision, allowing deployment on smaller GPUs without significant quality loss.
Web developers integrating OpenChat should account for response latency requirements. Running the model locally introduces complexity but removes per-request costs. For high-volume applications, this often makes self-hosting more favorable than using API services.
Licensing and Commercial Use
Model Selection Decision Flow:
OpenChat’s Apache 2.0 license is a major advantage for commercial deployment. This permissive license allows modification, use, and distribution of the model without royalties, enabling integration into proprietary products and services.
Many open-source language models have restrictive licenses prohibiting commercial use. For example, Llama 2 has specific terms for large-scale usage, and Vicuna explicitly disallows commercial applications. These constraints make them less suitable for businesses building products.
OpenChat’s approach aligns with renowned open-source projects across different domains. The Apache 2.0 license is well-established in software development, providing straightforward terms approved easily by corporate legal teams.
For small business owners, this means developing customer-facing tools without licensing fees. Marketing professionals can integrate the model into commercial content tools or services, as long as the license notice is maintained in derivative works.
Community and Development Activity
The OpenChat project is actively developed, with regular model releases and updates based on ongoing research. Community members contribute bug fixes, optimizations, and examples, enhancing the project’s value.
Developers can access OpenChat model weights via Hugging Face, the primary distribution platform. The repository contains model cards with comprehensive details about training data, intended uses, and limitations, ensuring users make informed deployment decisions.
On GitHub, the project repository includes the code to reproduce the training process. Researchers can experiment with C-RLFT using this resource as a starting point. The team promptly addresses issues and welcomes contributions according to standard open-source practices.
Community support is facilitated through GitHub discussions and various AI development forums, where users share deployment experiences, improvement tips, and use case examples. This collective knowledge helps newcomers avert common pitfalls during their initial setup.
Limitations and Considerations
Like all language models, OpenChat has limitations that users must consider. It can produce incorrect information presented confidently, a common challenge with current AI systems. Applications needing factual accuracy must implement additional verification layers.
The training data cutoff means the model lacks knowledge of recent events. Developers building applications should implement retrieval systems to provide current information, combining the model’s language capabilities with up-to-date data sources.
Despite efforts to mitigate bias during fine-tuning, training data biases affect model outputs. Organizations deploying OpenChat in customer-facing applications should rigorously test with diverse inputs. Monitoring production outputs helps catch problematic responses early.
Resource requirements mean not every organization can self-host effectively. Small businesses without technical staff might find managed API services more feasible, despite the higher per-use costs. The decision depends on usage volume, technical skills, and budget constraints.
Future Development and Roadmap
OpenChat’s developers are committed to improving the C-RLFT method further. Future iterations will likely integrate newer base models as they become available. Research findings are published, contributing to advancements in language model training.
Growing community interest in effective training methods supports ongoing development. As more organizations adopt OpenChat, the feedback loop of feature requests and bug reports drives development priorities.
The trend towards open-source AI models indicates projects like OpenChat will gain importance. Companies seek alternatives to proprietary systems for reasons of cost and control, encouraging continuous investment in open development.
As adoption increases, integration with popular frameworks will expand. Tool developers add native support when user bases reach critical mass, easing deployment for new users and reducing setup friction.
Conclusion
OpenChat represents a significant accomplishment in the realm of language model training. The C-RLFT method showcases that high-quality results don’t necessarily require vast datasets, making advanced conversational AI accessible to organizations without massive computing budgets.
The Apache 2.0 license eliminates commercial deployment barriers common with many open-source chatbot alternatives. Developers, small businesses, and researchers can create applications without license constraints or usage fees. This freedom accelerates the exploration of AI technologies.
Performance benchmarks reveal OpenChat competes effectively against models trained with considerably more resources. Its combination of high performance, quality, and permissive licensing makes it a strong choice for various applications. Organizations considering chatbot solutions should evaluate OpenChat alongside commercial options.
As the open-source AI ecosystem evolves, projects like OpenChat will play an increasingly vital role. They offer alternatives to vendor lock-in while maintaining high-quality standards. The community-driven development model ensures ongoing improvements and broad accessibility for all users.
Frequently Asked Questions
What hardware do I need to run OpenChat?
The hardware requirements for running OpenChat vary based on the model size you choose. Smaller versions can be run on consumer GPUs, while larger variants require more robust hardware for optimal performance. It's important to consider your specific application needs and expected load when selecting hardware.
Can OpenChat be used for commercial purposes?
Yes, OpenChat can be used for commercial purposes under its Apache 2.0 license. This license allows for modification, usage, and distribution without the need for payment or royalties, making it suitable for integration into proprietary products and services.
How does OpenChat compare to proprietary models?
OpenChat offers competitive performance with significantly lower training data requirements compared to many proprietary models. While commercial models often require expensive infrastructure, OpenChat allows smaller organizations to leverage advanced AI capabilities without high costs, making it an attractive alternative.
What is the C-RLFT method, and why is it important?
The C-RLFT method is a novel training approach developed by laion.ai that allows OpenChat to produce high-quality outputs using mixed-quality data. This method differentiates it from traditional fine-tuning techniques by achieving similar results with less specialized data, thus reducing costs and increasing accessibility for smaller organizations.
Are there any known limitations of using OpenChat?
Like all language models, OpenChat can present confidently incorrect information, which requires applications to implement additional verification layers. Additionally, its training data has a cutoff point, meaning it may not recognize recent events, posing a challenge for applications needing real-time information.
How is community involvement in the OpenChat project?
The OpenChat project is actively developed with significant community involvement. Users can contribute to bug fixes, optimizations, and enhancements via GitHub, and there is a supportive community sharing experiences and resources that help newcomers in their initial setup.
What industries can benefit from using OpenChat?
OpenChat can be utilized across various industries, including customer service, marketing, SEO, and research, where conversational AI is beneficial. Its open-source nature allows it to be tailored for specific use cases, making it a versatile tool for organizations looking to enhance their AI capabilities.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.