Microsoft Bingbot: Complete Guide for Website Owners
Everything you need to know about Bingbot, Microsoft's crawler that powers both Bing Search and Copilot AI. Learn user agents, blocking methods, and strategic tradeoffs.
What is Bingbot and Why It Matters
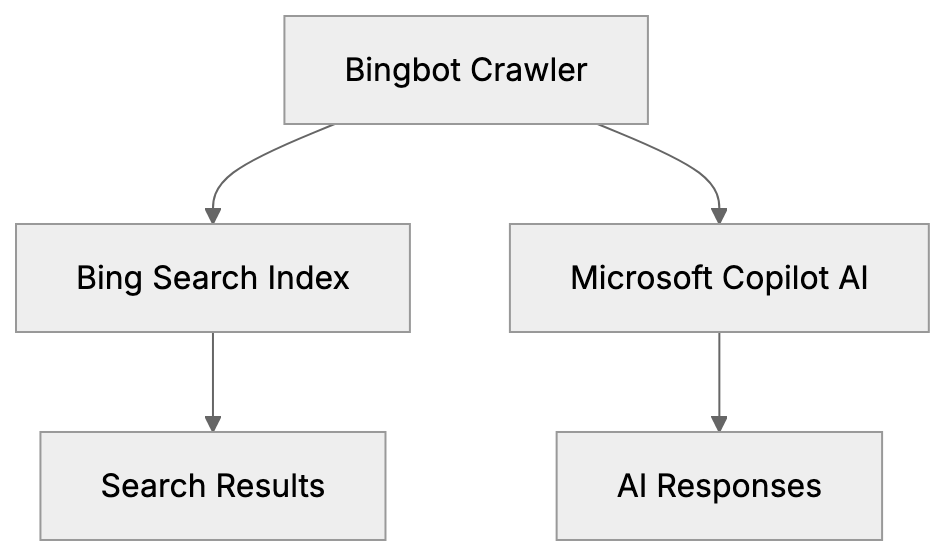
Bingbot, Microsoft’s web crawler, is crucial for website indexing on Bing Search and also feeds data to Microsoft Copilot, their AI assistant. Unlike Google, which uses separate crawlers for search and AI, Microsoft employs a single bot for both. This presents website owners with a unique challenge: you can’t block just the AI functionality without affecting your presence in Bing search results. It’s an all-or-nothing decision, especially important for small business owners and web developers to understand Bingbot’s role in their site’s visibility. The Microsoft crawler represents about 3 to 5 percent of search engine market share in many regions, so blocking it affects your site’s discoverability. This guide details what Bingbot does, how to identify it, and what happens if you block it.
Understanding Microsoft’s Web Crawler
Bingbot crawls websites to index web pages. It reads your content, follows links, and transmits the information back to Microsoft’s servers. This data becomes part of Bing’s search index and is used in Microsoft Copilot responses. Bingbot adheres to robots.txt files and standard crawling protocols. It identifies itself via specific user agent strings you can detect in server logs. Crawling is free and automatic once your site is discovered through links or manual submission. High-traffic sites with frequent updates get more frequent visits, while smaller sites might see Bingbot weekly or monthly.
Bingbot’s Dual Purpose:
The All or Nothing Approach
Microsoft differs from competitors by using a single Bingbot for search and AI purposes. Google, for instance, uses separate crawlers, allowing for selective blocking. Blocking Bingbot through robots.txt means removing your site from both Bing’s search results and Microsoft Copilot, making it a tough choice for website owners worried about AI training on their content. Blocking Bingbot reduces your search traffic by approximately 3 to 5 percent, which could add up over time.
Bingbot User Agent Strings
Microsoft vs Google Crawler Approaches:

Bingbot identifies itself via user agent strings in HTTP requests, revealing what’s visiting your site. The primary user agent for desktop crawling is:
Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; bingbot/2.0; +http://www.bing.com/bingbot.htm)
For mobile content, it uses:
Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS 7_0 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit/537.51.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/7.0 Mobile/11A465 Safari/9537.53 (compatible; bingbot/2.0; +http://www.bing.com/bingbot.htm)
Microsoft has kept these user agent strings consistent, making Bingbot easy to identify in logs. Legitimate Bingbot traffic comes from IP addresses resolving to search.msn.com domains, helping filter out fake bots.
How to Block Bingbot Using Robots.txt
To block Bingbot, you must update your robots.txt file in your website’s root directory with these lines:
User-agent: bingbot
Disallow: /This directive tells the Microsoft crawler it cannot access any pages, effectively removing your site from Bing Search and Copilot. To block specific sections, modify the file as follows:
User-agent: bingbot
Disallow: /private/
Disallow: /internal/This setup allows Bingbot to crawl most of your site while keeping particular areas off-limits. Changes take effect after Bingbot’s next visit, and the accuracy of your robots.txt can be validated online.
Strategic Considerations for Small Businesses
Blocking Decision Framework:
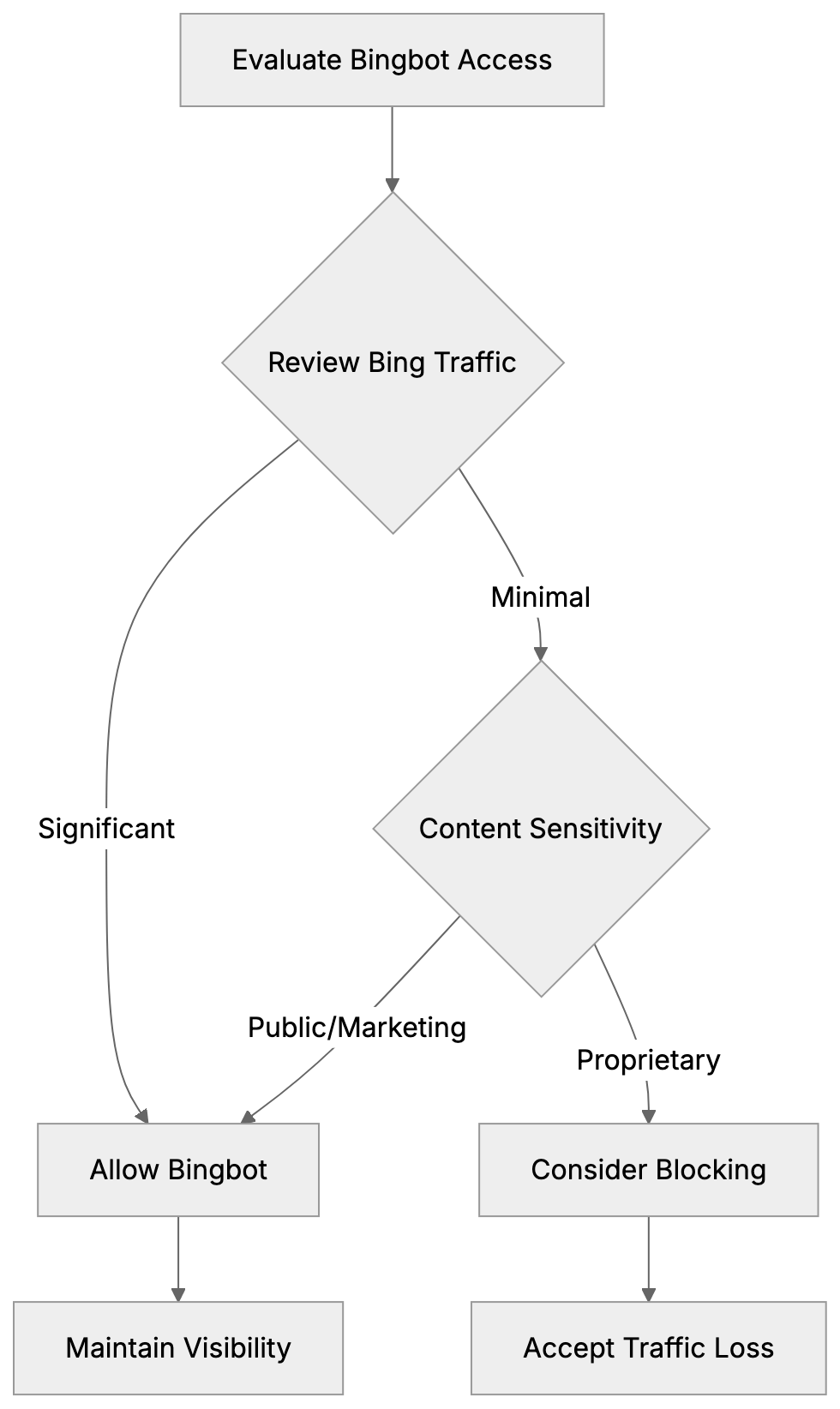 Most small businesses should permit Bingbot to crawl their sites. Bing’s search visibility is typically more valuable than concerns over AI training. Business information benefits from being discoverable; blocking Bingbot would mean losing potential exposure. Generally, business content like services, hours, and blog posts aid marketing purposes and enhance brand awareness. Blocking Bingbot may be a rare choice, suited for entities needing to protect proprietary content such as news organizations or research-heavy websites.
Most small businesses should permit Bingbot to crawl their sites. Bing’s search visibility is typically more valuable than concerns over AI training. Business information benefits from being discoverable; blocking Bingbot would mean losing potential exposure. Generally, business content like services, hours, and blog posts aid marketing purposes and enhance brand awareness. Blocking Bingbot may be a rare choice, suited for entities needing to protect proprietary content such as news organizations or research-heavy websites.
Comparing Microsoft Bingbot to Other Crawlers
Understanding the differences between Bingbot and other crawlers enables informed decision-making:
| Crawler | Company | Purpose | Can Separate AI/Search | User Agent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bingbot | Microsoft | Bing Search + Copilot AI | No | bingbot/2.0 |
| Googlebot | Google Search | Yes (via Google Extended) | Googlebot/2.1 | |
| Google-Extended | AI Training (Gemini) | Yes | Google-Extended | |
| GPTBot | OpenAI | ChatGPT Training | Yes | GPTBot/1.0 |
| CCBot | Common Crawl | Dataset for AI Training | Yes | CCBot/2.0 |
| Applebot | Apple | Apple Search, Siri, Spotlight | Partial | Applebot/0.1 |
Microsoft’s unified approach means you can’t separate search indexing from AI training. Unlike Google and others, Microsoft remains unable to provide this separation, aligning all content into one access.
What Happens When You Block Bingbot
Blocking Bingbot results in your pages gradually disappearing from Bing’s search index. Removal is not immediate and may take weeks or months for full effect. Newly published content won’t be indexed, reducing potential discovery avenues. Consequently, you won’t appear in Copilot responses, affecting brand visibility. While Bing typically represents 3 to 5 percent of site traffic, some regions see higher usage. You can reverse blocking by editing the robots.txt file; Bingbot will resume crawling at the subsequent visit.
Technical Details for Web Developers
Web developers managing multiple sites should monitor Bingbot through server logs, confirming crawl frequency and coverage. Most analytics tools filter out bot traffic, but a custom segment might help analyze Bingbot visits specifically. From Bing Webmaster Tools, developers can manage crawling behavior, control crawl rates, and verify indexing status. This free service is akin to Google Search Console, allowing for sitemap submissions, search queries checks, and error detections.
Microsoft Copilot and Content Usage
Microsoft Copilot employs crawled content for user responses. Unlike traditional search, which provides a list of links, Copilot delivers synthesized answers using various sources. The AI might quote, paraphrase, or inform responses from your web content without specific opt-ins, assuming access via Bingbot. Source attribution can be inconsistent, contrasting with search results linked to sites. As AI answers become more widespread, linkage visibility shifts, affecting potential traffic from these interactions.
Making the Right Choice for Your Website
Deciding whether to block Bingbot depends on several factors. Review how much traffic Bing contributes via analytics; it could incur significant costs if blocked. Evaluate your content’s uniqueness and its distribution benefits. Reflect on your business model; sites reliant on traffic may require different strategies than subscription-based sites. Comfort with AI learning from your content varies philosophically; some prioritize visibility while others opt for protection. The right choice should balance your strategic goals with the potential trade-offs between visibility and content protection.
Alternatives and Workarounds
With Microsoft’s unified approach, limited options exist for separating search visibility from AI training. Technical alternatives, like serving different content to Bingbot, risk violating search engine guidelines, leading to bans. Restricting content through paywalls can block Bingbot but impacts overall visibility. Selectively blocking Bingbot on certain sections or subdomains requires careful planning and may not suit every business model. Microsoft’s strategy essentially aims to prioritize search visibility over AI autonomy, confidently assuming most websites will choose access.
Monitoring and Managing Bingbot Access
After deciding on Bingbot’s presence, monitor activities to ensure policies are effective. Bing Webmaster Tools can provide insight into crawling habits, errors, and indexing status. Periodically review server logs to verify Bingbot compliance, catching any fake bots posing as Bingbot by inspecting IP ranges. Monitor server load during visits as high activity can degrade site performance, and adjust crawl rates if necessary. Staying proactive ensures seamless integration of roles Bingbot fulfills.
Future of Bingbot and Microsoft AI
Microsoft remains dedicated to a unified crawler framework. Despite the complexity, it simplifies their process and pressures website favoring visibility. As AI entwines more with search, expect increased leverage on Copilot combinations. The divide between search results and AI-generated responses will blur, accentuating AI’s prominence. Website owners must stay informed about possible updates to Microsoft’s policies affecting Bingbot. Monitoring their official channels helps keep up with changes. Currently, separating search and AI in Microsoft’s framework isn’t feasible, maintaining a single, encompassing approach.
End
Bingbot is Microsoft’s web crawler enabling both Bing Search and Microsoft Copilot usage. Unlike others, Microsoft doesn’t facilitate separate blocking of AI from search visibility, resulting in a comprehensive or nothing decision. Bingbot’s consistent user agents make identification straightforward. Blocking it involves using robots.txt, but that removes visibility in Bing search and Copilot answers. Most small businesses benefit from allowing Bingbot due to substantial search traffic. Exceptions exist for entities guarding exclusive content, but comprehension of Bingbot’s role is critical for informed decisions. Monitoring activities through tools and logs ensures your configurations align with your objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the consequences of blocking Bingbot on my site?
Blocking Bingbot means your site will not be indexed, leading to a gradual disappearance from Bing Search results. Consequently, you will also not appear in Microsoft Copilot responses, significantly impacting your brand's visibility and discoverability.
How can I determine if Bingbot is visiting my website?
You can identify Bingbot through user agent strings in server logs. Look for entries that include 'bingbot/2.0' for desktop and similar strings for mobile. Monitoring your server logs will provide insights into the frequency and coverage of Bingbot visits.
Can I restrict Bingbot from crawling specific parts of my website?
Yes, you can block Bingbot from accessing certain sections by adding specific directives in your robots.txt file. For example, you can allow it to crawl most of your site while disallowing access to certain directories by specifying those paths.
How often does Bingbot crawl my site?
Crawling frequency varies based on your site's traffic and how often you update content. High-traffic sites generally see Bingbot more frequently, while smaller sites might experience crawls on a weekly or monthly basis.
What should small businesses consider when deciding to block Bingbot?
Small businesses typically benefit from allowing Bingbot to index their sites due to the potential traffic from Bing Search. Consider the visibility and branding advantages against any concerns regarding content being used by Microsoft Copilot. Evaluating how much search traffic Bing contributes to your site can help inform this decision.
Is it possible to reverse the blocking of Bingbot after I've done it?
Yes, you can reverse the blocking of Bingbot by editing your robots.txt file. Once updated, Bingbot will resume crawling your site during its next visit, allowing your content to be reindexed.
What are the long-term implications of blocking Bingbot for my website?
Blocking Bingbot can have lasting effects on your site's search presence, as it may take weeks or months for pages to be fully removed from Bing's index. This can lead to a significant reduction in traffic, hindering potential customer acquisition and brand visibility over time.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.