ByteDance Bytespider: Complete Guide to Block This Crawler
ByteDance Bytespider ignores robots.txt and makes 1.4M daily requests. Learn how to block this aggressive crawler feeding Doubao LLM with server configs.
What is ByteDance Bytespider
Bytespider is a web crawler operated by ByteDance, the same company behind TikTok and the Doubao AI model. This crawler, known as the ByteDance crawler, scans websites across the internet to collect data for training ByteDance’s large language models and potentially other AI features. Unlike most legitimate crawlers, Bytespider has gained a reputation for being extremely aggressive. Research studies confirmed that the Bytespider bot often ignores standard robots.txt files. This means that the usual method of telling bots not to crawl your site doesn’t work.
Website owners report seeing up to 1.4 million requests per day from this single bot. That’s roughly 25 times faster than OpenAI’s GPTBot. The crawler feeds data into ByteDance’s Doubao LLM and possibly powers AI features within TikTok and other ByteDance products. No official documentation from ByteDance about Bytespider’s crawling policies or rate limits makes it difficult for webmasters to understand what data gets collected and how.
For developers and site owners concerned about their content being used for AI training without consent, blocking Bytespider requires server-level configurations since robots.txt proves ineffective.
Why ByteDance Created Bytespider
Bytespider Crawling Behavior:
ByteDance needs massive amounts of text data to train its AI models. Large language models like Doubao require billions of words from varied sources to function properly. Web crawling is the most effective way to gather this training data at scale. ByteDance competes directly with companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google in the AI space. To build competitive models, they need access to the same quality and quantity of data their competitors use.
The Doubao model serves primarily Chinese-speaking markets and requires substantial Chinese and English content for training. TikTok’s recommendation algorithms and potential AI features also benefit from understanding web content patterns. Bytespider operates similarly to other AI training crawlers like GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and Google-Extended. The difference is the aggressive crawling behavior and the lack of respect for standard web protocols.
ByteDance hasn’t published official guidelines about what Bytespider collects or how it respects site owner preferences. This creates friction between ByteDance and the web community. Many site owners view the crawler as taking content without permission and without offering clear opt-out methods that actually work. Bytespider exists because ByteDance needs data, and web scraping remains the fastest path to obtain it.
How Bytespider Operates and Its Impact
Bytespider crawls websites at extremely high rates compared to other bots. Research from multiple sources shows individual sites receiving between 500,000 to 1.4 million requests daily from Bytespider. Standard crawlers typically make thousands or tens of thousands of requests per day. This volume can strain server resources and increase hosting costs. Small business owners running sites on limited infrastructure see real performance impacts.
The crawler identifies itself through specific user agent strings, but the exact strings vary. Website logs show multiple variants of the Bytespider user agent, making detection slightly more complex than bots using consistent identifiers. The most concerning behavior is that Bytespider frequently ignores robots.txt directives. The robots.txt file is a standard protocol where site owners specify which bots can crawl which parts of their site. Most legitimate crawlers respect these rules.
ByteDance AI Data Pipeline:

Multiple confirmed reports and studies show Bytespider crawling pages explicitly disallowed in robots.txt. This forces site owners to implement server-level blocks instead. The data collected goes into training datasets for Doubao and potentially other ByteDance AI products. Once your content gets scraped and added to a training dataset, there’s no way to remove it. This creates permanent concerns about intellectual property and content ownership. Marketing professionals and content creators worry about their original work training competitor AI systems without compensation or attribution.
Bytespider User Agent Strings
Bytespider uses several user agent string variations. Knowing these exact strings is important for blocking the bot at the server level. The most common user agent format is:
Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 6.0; Nexus 5 Build/MRA58N) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/W.X.Y.Z Mobile Safari/537.36 (compatible; Bytespider; https://zhanzhang.toutiao.com/)
Another variant that appears in server logs is:
Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Bytespider; https://zhanzhang.toutiao.com/) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/70.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
Some logs also show simplified versions:
Bytespider
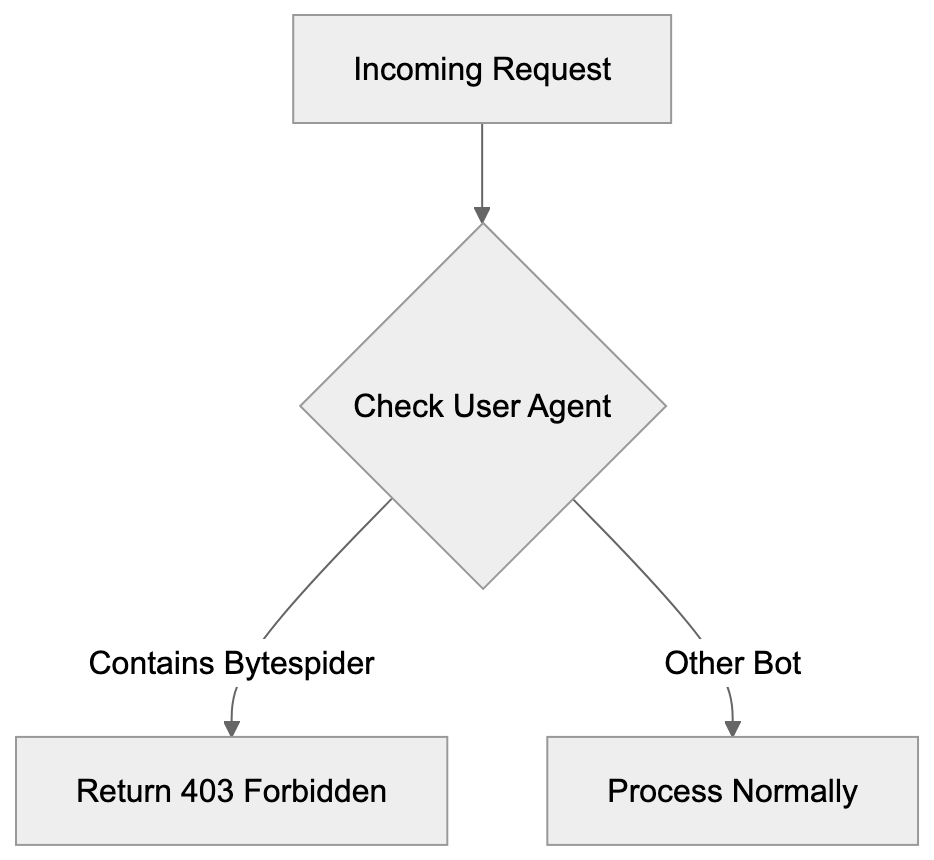
The user agent typically includes a reference to zhanzhang.toutiao.com, which is ByteDance’s webmaster tools domain, but ByteDance provides minimal information on that site about the crawler’s behavior or how to control it. When implementing blocks, you need to account for these variations. A partial match on “Bytespider” catches most cases, but some administrators prefer to block the full user agent string patterns. The lack of standardization suggests ByteDance either rotates user agents deliberately or operates multiple crawler versions simultaneously. Web developers should check their actual server logs to confirm which specific user agent strings appear in their traffic before implementing blocks.
How to Block Bytespider (Server-Level Configuration)
Since robots.txt doesn’t work, you must block Bytespider at the server level. The method depends on your web server software.
Apache Server (.htaccess)
For Apache servers, add these lines to your .htaccess file:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} Bytespider [NC]
RewriteRule ^ - [F,L]This configuration checks the user agent for “Bytespider” and returns a 403 Forbidden response. The [NC] flag makes it case-insensitive. The [F,L] flags mean Forbidden and Last rule.
Alternatively, you can use mod_setenvif:
SetEnvIfNoCase User-Agent "Bytespider" bad_bot
Deny from env=bad_botNginx Server
For Nginx servers, add this to your server block configuration:
if ($http_user_agent ~* (Bytespider)) {
return 403;
}This checks the user agent header and returns a 403 status code if it matches Bytespider.
A more complete approach for multiple bots:
map $http_user_agent $bad_bot {
default 0;
~*Bytespider 1;
}
server {
if ($bad_bot) {
return 403;
}
}Cloudflare WAF
If you use Cloudflare, create a WAF rule:
- Go to Security > WAF > Custom rules
- Create a new rule
- Set the field to “User Agent”
- Set the operator to “contains”
- Set the value to “Bytespider”
- Choose action “Block”
This method works regardless of your origin server configuration.
Testing Your Block
After implementing blocks, monitor your server logs to confirm Bytespider requests stop or receive 403 responses. You can also use online tools that simulate different user agents to test your configuration. Remember, blocking may take time to show effects since crawlers don’t check every site continuously.
Bytespider Compared to Other AI Crawlers
Several companies operate AI training crawlers. Understanding how Bytespider compares helps contextualize the blocking decision.
| Crawler | Company | Respects robots.txt | Approx Daily Requests | Primary Use | Official Docs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bytespider | ByteDance | No (confirmed) | 500k - 1.4M | Doubao LLM training | Minimal |
| GPTBot | OpenAI | Yes | 20k - 60k | GPT model training | Yes |
| ClaudeBot | Anthropic | Yes | 30k - 80k | Claude model training | Yes |
| Google-Extended | Yes | Varies | Gemini training | Yes | |
| CCBot | Common | Yes | 10k - 50k | Public dataset | Yes |
| FacebookBot | Meta | Yes | 5k - 30k | Search/AI features | Yes |
Server-Level Blocking Strategy:
Bytespider stands out for ignoring robots.txt and the extremely high request volume. Most other AI crawlers provide clear documentation and respect standard protocols. OpenAI’s GPTBot, for example, fully honors robots.txt disallow directives. Anthropic’s ClaudeBot also respects these rules and provides rate-limiting information. Google-Extended was specifically created as an opt-out mechanism separate from the regular Googlebot. These companies recognized that content owners deserve control over AI training use.
ByteDance took a different approach with Bytespider. The lack of official English documentation makes it harder for international site owners to understand the crawler’s purpose and controls. The request volume creates real infrastructure costs that other crawlers avoid through rate limiting. For SEO experts and content marketers, this matters because your content strategy might involve allowing some AI crawlers while blocking others. You might want your content in ChatGPT, but not in Doubao. The difference in crawler behavior means you need different blocking strategies for each.
The Robots.txt Problem with Bytespider
The robots.txt protocol has been the standard for crawler control since 1994. Site owners create a robots.txt file in their site root with rules like:
User-agent: Bytespider
Disallow: /This should tell Bytespider not to crawl any part of the site, but multiple independent reports confirm Bytespider ignores these directives. Research studies analyzing server logs show Bytespider crawling pages explicitly disallowed in robots.txt files. This isn’t occasional accidental crawling. It’s a systematic ignoring of the protocol. Other major crawlers might occasionally miss robots.txt rules due to caching or timing issues, but they generally comply. Bytespider shows a pattern of non-compliance.
ByteDance hasn’t publicly explained why their crawler ignores robots.txt. Possible reasons include technical issues, intentional design decisions, or lack of development priority. Whatever the reason, the result is the same for site owners. Your robots.txt rules don’t protect your content from Bytespider. This breaks an important trust mechanism in the web ecosystem. When crawlers ignore robots.txt, site owners lose a simple low-overhead method of controlling access. They must resort to server-level blocks which require more technical knowledge and server resources. For small business owners without technical staff, this creates a real barrier to protecting their content. The situation also raises questions about what other protocols or standards Bytespider might ignore.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The aggressive crawling behavior and robots.txt violations raise legal and ethical questions. In some jurisdictions, ignoring robots.txt might violate computer access laws. The legal scene around web scraping remains unclear in many countries. Courts have issued contradictory rulings about whether scraping public websites is legal. The question becomes more complex when the scraper explicitly ignores access control mechanisms like robots.txt.
From an ethical standpoint, many content creators argue they should control whether their work trains AI models. The content on websites represents significant investment in time, expertise, and money. Using that content without permission for commercial AI products seems unfair to many creators. ByteDance profits from AI products trained on scraped content while content creators receive nothing.
Different perspectives exist on this issue. Some argue that publicly accessible content is fair game for crawling and AI training. They compare it to humans reading and learning from public content. Others argue AI training represents a commercial use that requires permission or compensation. These debates continue in legal and policy circles. For now, site owners who object to their content training ByteDance models must take technical blocking measures. No legal framework currently prevents this crawling in most jurisdictions. Content marketers and publishers should understand that once Bytespider scrapes your content, removing it from training datasets is practically impossible. This makes the blocking decision time-sensitive.
Performance Impact on Websites
The high request volume from Bytespider creates measurable performance impacts. Server resources are finite, and excessive crawler traffic consumes CPU, memory, and bandwidth. Sites on shared hosting or limited infrastructure feel these effects most acutely. When a single bot makes over a million requests per day, it can overwhelm servers designed for normal human traffic patterns. This leads to slower page loads for real users. In extreme cases, it can cause server crashes or trigger hosting provider warnings about resource usage.
Bandwidth costs also increase. Each crawler request consumes bandwidth, which costs money on many hosting plans. High-volume crawling from Bytespider can push sites over their bandwidth limits, triggering overage charges. Small business owners running WordPress sites or similar platforms see their hosting bills increase due to crawler traffic they never authorized.
Web developers monitoring site performance notice unusual traffic spikes that trace back to Bytespider. CDN services like Cloudflare can help mitigate some impacts by caching content and filtering requests, but changing content that can’t be cached still hits the origin server. Database-driven sites face particular challenges when crawlers request many different URLs rapidly. Each request might trigger database queries that consume server resources. For e-commerce sites, this means crawler traffic competes with actual customer traffic for server capacity. Blocking Bytespider often results in immediate performance improvements and cost reductions.
Monitoring Bytespider in Server Logs
Before blocking, you should confirm Bytespider actually crawls your site. Check your server access logs for the user agent strings mentioned earlier. On Apache servers, access logs typically live at:
/var/log/apache2/access.log
On Nginx servers:
/var/log/nginx/access.log
Search for Bytespider:
grep -i "bytespider" /var/log/nginx/access.log
This shows all requests from Bytespider. Count requests per day:
grep -i "bytespider" /var/log/nginx/access.log | grep "$(date +%d/%b/%Y)" | wc -l
This gives you daily request volume. You can also use log analysis tools like GoAccess, AWStats, or Webalizer. These provide graphical representations of crawler traffic. Look for unusual traffic spikes that correlate with Bytespider activity. If you use Google Analytics or similar tools, crawler traffic usually doesn’t appear since those track JavaScript execution. Server logs give you raw request data including bot traffic. Many hosting control panels like cPanel or Plesk include log viewing tools that make this easier without command-line access. Understanding your actual Bytespider traffic volume helps you decide whether blocking is necessary. Sites with minimal Bytespider traffic might not need blocks. Sites seeing hundreds of thousands of daily requests definitely benefit from blocking.
Future of AI Crawlers and Content Protection
The Bytespider situation represents a larger trend in AI development. Companies need training data, and web scraping provides easy access. As more companies build AI models, expect more aggressive crawlers. The web community is pushing back with technical and legal measures. Some publishers block all AI crawlers by default. Others negotiate licensing deals with AI companies for training data access.
Reddit, Stack Overflow, and news organizations have signed content licensing agreements with AI companies. These deals provide revenue for content owners while giving AI companies legal access to training data. ByteDance hasn’t pursued many such deals publicly, instead relying on Bytespider’s aggressive crawling. New standards may appear for AI crawler control. The robots.txt protocol is being extended with AI-specific directives, but these only work if crawlers voluntarily respect them.
Technical solutions like server-level blocking remain the most reliable method. Legislation may eventually address AI training data rights. The EU’s AI Act and similar regulations touch on these issues, but complete frameworks don’t exist yet. Until legal clarity appears, site owners must rely on technical measures. For developers and site owners, the best practice is implementing granular crawler controls. Allow crawlers that respect your preferences and block those that don’t. Regularly review server logs to identify new crawlers and adjust blocks accordingly. The AI training data scene will continue evolving rapidly over the next few years.
Conclusion
Bytespider is ByteDance’s web crawler that feeds training data to their Doubao AI model and potentially TikTok features. Unlike most legitimate crawlers, Bytespider ignores robots.txt files and operates at extremely high request volumes. Sites report up to 1.4 million daily requests, roughly 25 times more aggressive than OpenAI’s GPTBot. This creates real performance and cost impacts for website owners.
The lack of official documentation and robots.txt violations make Bytespider particularly problematic for site owners who want to control how their content gets used. Blocking Bytespider requires server-level configuration using Apache .htaccess rules, Nginx configuration, or WAF services like Cloudflare. Simple robots.txt directives don’t work. Web developers, small business owners, and content creators should monitor their server logs for Bytespider activity and implement blocks if they object to their content training ByteDance’s AI models.
The crawler represents a broader challenge in the AI era where companies aggressively scrape content for training data without clear consent mechanisms. Understanding how to detect and block Bytespider gives you control over your content’s use in AI training.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I do if Bytespider is crawling my website?
If you notice Bytespider crawling your site excessively, you should implement server-level blocks since traditional robots.txt methods are ineffective. Adjust your .htaccess for Apache or configuration files for Nginx to deny requests from Bytespider based on its user agent strings.
How can I monitor Bytespider's activity on my website?
You can check your server access logs for user agent strings associated with Bytespider. On Apache servers, this is typically found at /var/log/apache2/access.log, and for Nginx, it's at /var/log/nginx/access.log. Use commands to filter logs for Bytespider requests to see how many times it's visiting your site.
Are there legal implications for Bytespider's crawling behavior?
The legality of Bytespider's actions is still debated, depending on the jurisdiction. While some argue that ignoring robots.txt might violate computer access laws, the legal landscape surrounding web scraping remains uncertain, with conflicting rulings in various regions.
What impacts does Bytespider have on website performance?
Bytespider's high request volume can strain server resources, leading to slower load times and even crashes, particularly for small businesses with limited infrastructure. Additionally, excessive crawling can increase bandwidth costs due to the high number of requests made.
Why doesn't ByteDance provide clear documentation on Bytespider?
ByteDance has not published comprehensive guidelines regarding Bytespider's crawling behavior or how it handles site owners' preferences. This lack of transparency contributes to frustration among webmasters, as they cannot effectively manage the bot's access to their content.
How does Bytespider compare to other AI crawlers?
Bytespider is more aggressive than most other AI crawlers, ignoring robots.txt regulations and making significantly higher daily requests. In contrast, many competitors like GPTBot and ClaudeBot respect these directives and provide clearer guidelines on their crawling behavior.
What future developments might impact AI crawlers like Bytespider?
The evolution of AI development has prompted discussions about standardized practices for crawler behavior and content protection. As legislation, such as the EU's AI Act, progresses, future frameworks may provide clearer guidelines regarding AI training data rights, impacting the operations of crawlers like Bytespider.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.