Understanding ChatGPT-User: OpenAI's Real-Time Browsing Bot
Learn about ChatGPT-User, OpenAI's bot for real-time browsing initiated by users, and how it differs from GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot.
What is ChatGPT-User
ChatGPT-User is a specialized real-time browsing bot created by OpenAI. It performs web crawling on demand when ChatGPT users request current information from the internet. Unlike traditional web crawlers, the ChatGPT-User retrieves data in real time as part of a conversation. When a user of ChatGPT requests up-to-date information, the ChatGPT-User bot visits specific web pages to fetch the required data. This service exists because ChatGPT’s training data has a cutoff date, and without real-time browsing capabilities, it cannot provide information on recent events or live data. OpenAI’s Deep Research feature addresses similar needs by autonomously browsing the web to generate cited reports on user-specified topics. The user-agent string for ChatGPT-User allows web developers to identify this bot in their server logs when triggered by browsing requests. OpenAI’s Crawlers Documentation provides detailed information on managing interactions with OpenAI’s bots. This transparency helps website owners decide whether to allow or block such access, a crucial consideration when dealing with OpenAI user-agent traffic.
Why ChatGPT-User Exists and Its Purpose
OpenAI designed ChatGPT-User to enhance ChatGPT’s capabilities beyond its training data limitations. AI language models are trained on datasets that have specific cutoff dates, which means ChatGPT cannot answer questions about events or information published after its training period without external data access. Real-time browsing fills this gap. When users ask ChatGPT for current stock prices, recent news, or weather updates, the ChatGPT-User bot performs the necessary web crawling. It accesses relevant websites, retrieves the requested information, and ChatGPT processes this data for its responses. Notably, ChatGPT-User is distinct from other bots like GPTBot because it doesn’t conduct bulk crawling or index entire websites; instead, it targets specific URLs to address user queries.
How ChatGPT-User Operates:
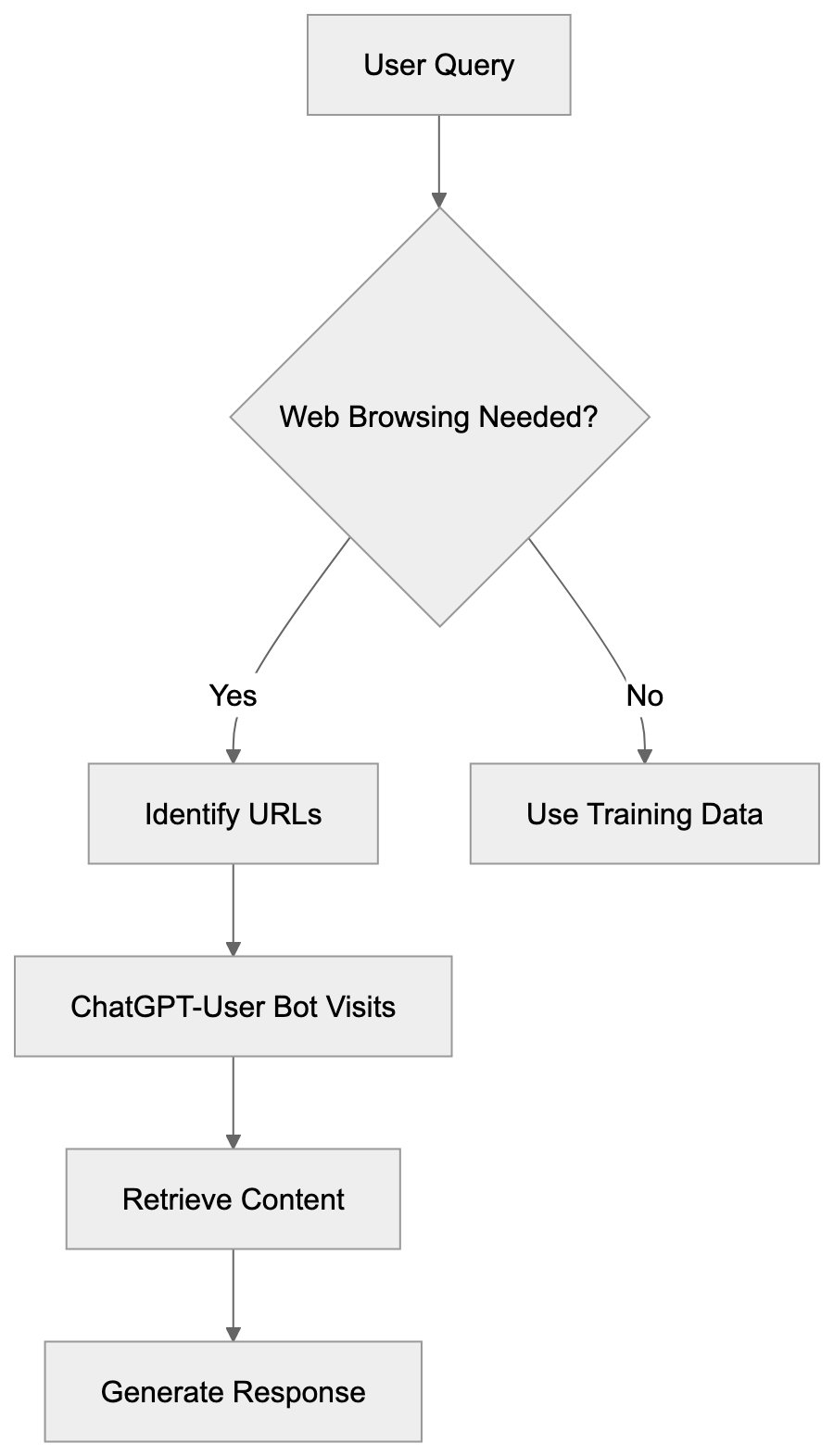
How ChatGPT-User Works in Practice
When a ChatGPT user inquires about current information, the system evaluates if web browsing is needed. If determined necessary, ChatGPT identifies specific URLs to visit. The ChatGPT-User bot executes HTTP requests to these web addresses, retrieves the page content, and processes it for an answer. All this happens within seconds, and users see an indication from ChatGPT that it’s browsing the web before presenting results. Website owners observe these visits in their access logs with the ChatGPT-User user-agent string: Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko; compatible; ChatGPT-User/1.0; +https://openai.com/bot). This transparency allows webmasters to identify traffic sources immediately. Additionally, the bot respects robots.txt files and won’t access sites that block it through such configurations.
ChatGPT-User vs GPTBot vs OAI-SearchBot
OpenAI operates multiple bots, each with distinct purposes. Understanding their differences is vital for website owners when considering bot blocking. Here is a comparison:
| Bot Name | Purpose | Activity Type | User-Agent String |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT-User | Real-time browsing for user queries | On-demand, per-request | Mozilla/5.0… ChatGPT-User/1.0 |
| GPTBot | Training data collection | Bulk crawling, systematic | Mozilla/5.0… GPTBot/1.0 |
| OAI-SearchBot | Search indexing for SearchGPT | Bulk crawling, indexing | OAI-SearchBot/1.0 |
OpenAI Bot Comparison:
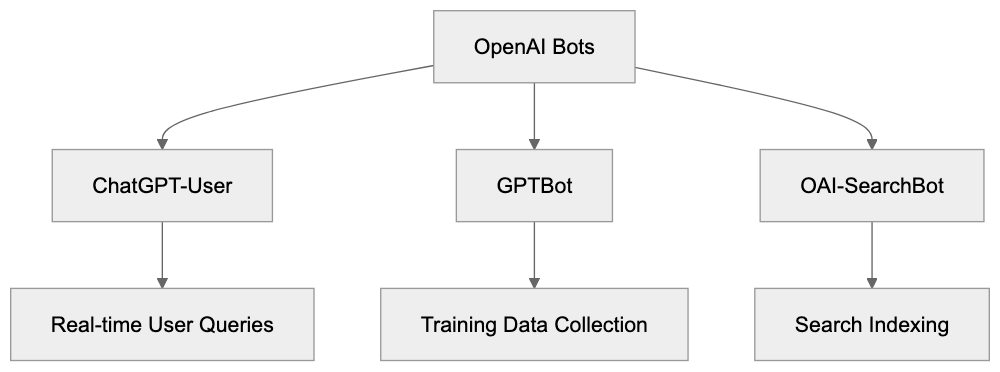
GPTBot systematically crawls websites to gather data for training future AI models, independent of user requests. OAI-SearchBot supports OpenAI’s search product, SearchGPT, by indexing web content. ChatGPT-User is unique as it is directly linked to individual user exchanges, focusing on real-time browsing.
How to Block or Allow ChatGPT-User
Website owners can control access to ChatGPT-User through the robots.txt file, which directs bots on which site sections they can access. To block ChatGPT-User completely, add the following lines to your robots.txt file:
User-agent: ChatGPT-User
Disallow: /This configuration prevents the bot from accessing any part of your website. For more granular control, you can allow ChatGPT-User but block other OpenAI bots:
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: OAI-SearchBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: ChatGPT-User
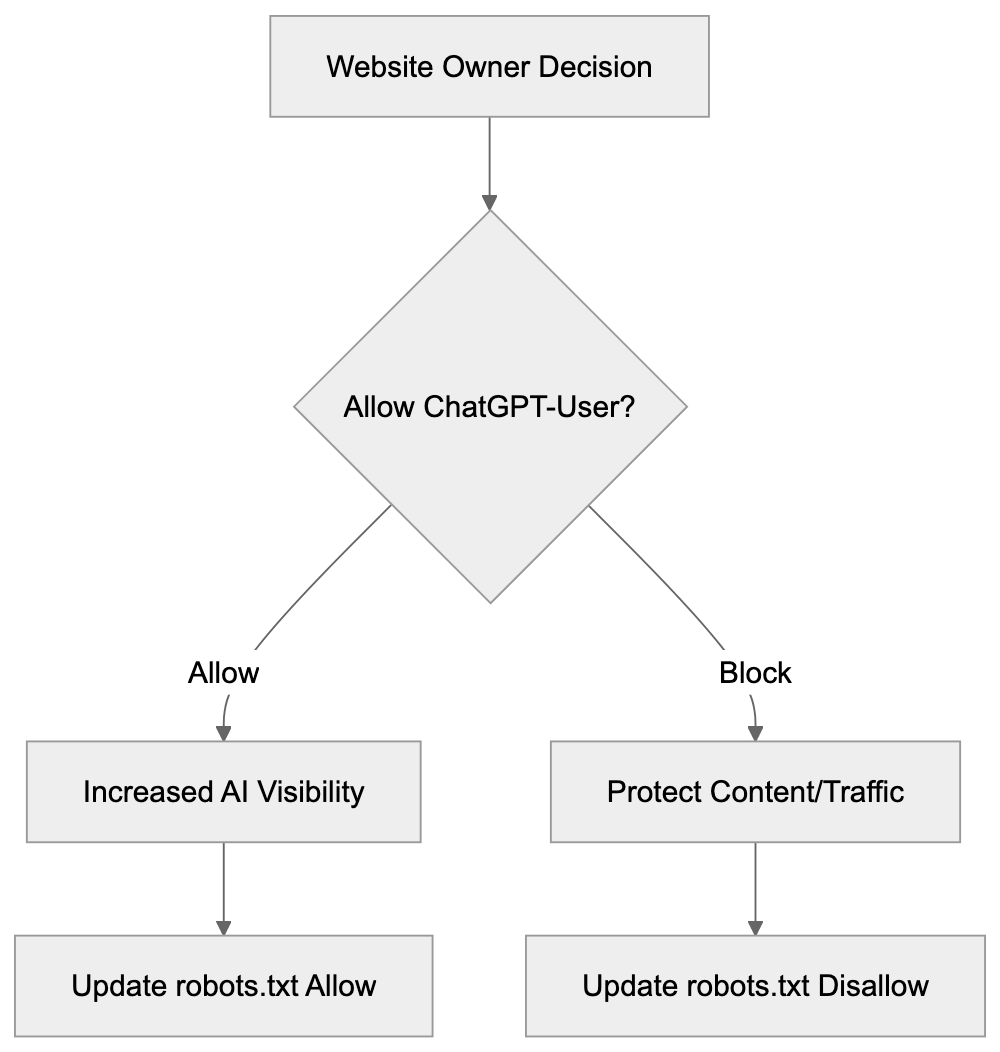
Allow: /Make your decision based on your business model, content strategy, and data policies. Some websites permit ChatGPT-User to increase visibility and reach users through AI assistants, while subscription-based sites might block it to protect paywalled content.
Access Control Decision Flow:
Comparing Similar Real-Time Browsing Bots
ChatGPT-User isn’t the only real-time browsing bot. Here’s a comparison of similar bots used by other AI companies:
| Bot Name | Company | Purpose | User-Agent Identifier |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT-User | OpenAI | Real-time browsing for ChatGPT | ChatGPT-User |
| Bingbot | Microsoft | Search indexing and Bing Chat | Bingbot |
| GoogleBot | Search indexing and Bard/Gemini | Googlebot | |
| ClaudeBot | Anthropic | Real-time browsing for Claude | ClaudeBot |
| PerplexityBot | Perplexity AI | Search and answer generation | PerplexityBot |
Understanding the role of each bot helps you establish a comprehensive bot policy for your website. Most companies adhere to robots.txt standards, but configurations may vary.
Privacy and Data Considerations
When ChatGPT-User accesses your website, it only retrieves publicly available content. It operates similarly to regular web browsers, adhering to publicly accessible data while not overstepping into content behind logins. OpenAI’s data policies specify that browsing data through ChatGPT-User is not utilized for training AI models, distinguishing it from GPTBot. Website owners should review OpenAI’s official documentation to stay updated with any policy changes and consider implementing technical measures such as rate limiting or monitoring tools if concerned about access.
Technical Implementation Details
ChatGPT-User makes standard HTTP requests akin to regular browsers and supports standard web technologies like HTML and JavaScript. It handles HTTP headers and status codes appropriately and respects robots.txt configurations. For server-level blocking, you can use the following for Apache servers in the .htaccess file:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} ChatGPT-User [NC]
RewriteRule .* - [F,L]For Nginx servers, add this:
if ($http_user_agent ~* ChatGPT-User) {
return 403;
}These methods provide more robust blocking but should be complemented by robots.txt directives for proper access management.
Business Implications for Website Owners
Allowing or blocking ChatGPT-User impacts your content’s reach and potential traffic. Allowing the bot might extend your content’s presence in AI-driven channels like ChatGPT, fostering visibility and discovery. However, this could reduce direct traffic if users find answers without visiting your site. The decision should align with your business model—content publishers may prioritize page views, while service providers benefit from increased visibility. Monitor your analytics to track the impact and adjust strategies based on real insights.
Conclusion
ChatGPT-User is OpenAI’s real-time browsing bot for responding to user queries with current information. Different from GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot, it performs real-time, on-demand web crawling tailored to specific queries. Website owners have the autonomy to allow or block this bot using robots.txt or server configurations. The decision hinges on your content strategy, business priorities, and data policies. An understanding of ChatGPT-User’s operation aids in managing your online presence effectively in an AI-driven environment. Stay informed about changes to bot behaviors and policies to make well-informed decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of information can ChatGPT-User retrieve?
ChatGPT-User can retrieve a variety of real-time information such as current stock prices, latest news updates, and weather forecasts. It targets specific URLs based on user queries to ensure that the information provided is both relevant and recent.
How can I identify if ChatGPT-User has accessed my website?
You can identify ChatGPT-User access in your server logs by looking for its user-agent string: `Mozilla/5.0... ChatGPT-User/1.0`. This can help you track bot activity and understand its impact on your website's traffic.
What should I do if I want to block ChatGPT-User from my website?
To block ChatGPT-User, you can add specific lines to your robots.txt file, such as `User-agent: ChatGPT-User` followed by `Disallow: /`. This will prevent the bot from accessing any part of your site.
How does allowing ChatGPT-User affect my website's traffic?
Allowing ChatGPT-User can increase your content's visibility in AI-driven channels, which may attract new users. However, it might also reduce direct traffic to your site if users find the answers they need without visiting.
Can ChatGPT-User access content behind paywalls?
No, ChatGPT-User only retrieves publicly available content and adheres to the same access restrictions as regular web browsers. It avoids content that requires login credentials or is behind paywalls.
Are there any privacy concerns with ChatGPT-User accessing my site?
ChatGPT-User operates according to OpenAI's data policies, ensuring it retrieves only publicly accessible content and does not use browsing data for training purposes. However, you should monitor your server logs and consider implementing rate limiting if you're concerned about bot traffic.
How does ChatGPT-User differ from other OpenAI bots like GPTBot?
ChatGPT-User is tailored for real-time browsing in response to specific user queries, while GPTBot performs systematic bulk crawling for training future models. Understanding these distinctions can help you manage how these bots interact with your online content.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.