Understanding facebookexternalhit: Facebook's Link Crawler
Learn what facebookexternalhit is, how it works for Facebook link previews, and best practices for handling this Meta crawler on your website.
What Is facebookexternalhit
You might have noticed something called facebookexternalhit in your server logs. This is Facebook’s web crawler, also known as the Facebook bot, which visits your site when someone shares a link on Facebook. The purpose of this Open Graph crawler is to scan your page and generate link previews you see in posts, complete with an image, title, and description. Open Graph protocol defines the metadata used for these previews.
The facebookexternalhit bot exists because Facebook needs to visually inform users about the content of a link before they click it. Without this crawler, every shared link would appear as plain text, lacking visual previews. The bot reads your page’s Open Graph tags and other metadata to create those previews.
For web developers and content marketers, it is crucial. It directly impacts how your content appears on Facebook and Instagram. If the crawler can’t access your site or read your metadata properly, your links will look broken or incomplete when shared, which can significantly hurt your social media engagement and traffic.
The main features of facebookexternalhit include reading Open Graph tags, following redirects, respecting robots.txt rules, and caching preview data. It supports various content types like images, videos, and article metadata. Understanding how it works helps you improve your content for better social sharing performance.
How facebookexternalhit Works
When someone pastes a URL into Facebook, the platform sends the facebookexternalhit bot to visit that page. It makes an HTTP request to your server similar to a regular browser, but instead of rendering the page, it reads the HTML source code. The social media crawler specifically looks for Open Graph meta tags in your page’s head section, such as og:title, og:description, og:image, and og:url. Facebook uses this data to build the preview card in the post. If your page lacks Open Graph tags, the crawler defaults to standard HTML meta tags or page content.
How facebookexternalhit Works:
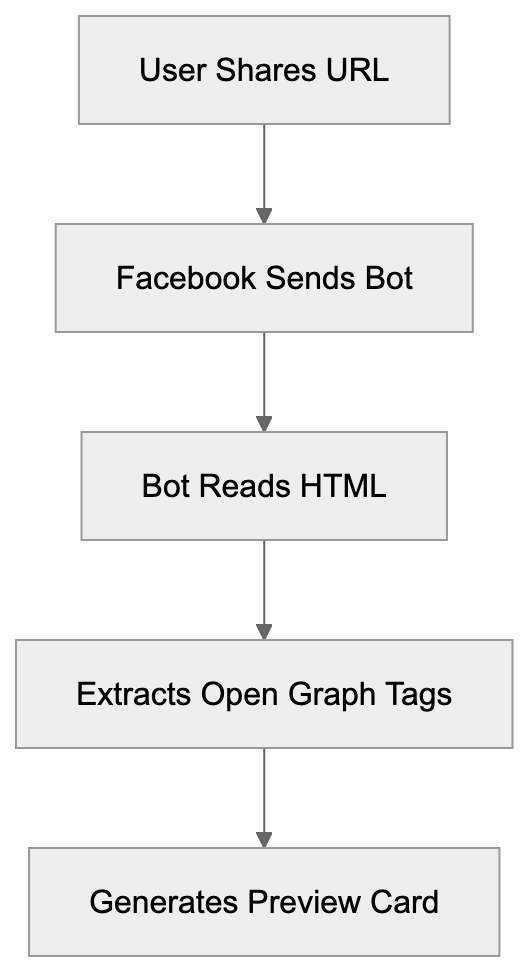
The user-agent string for this crawler typically appears as “facebookexternalhit/1.1 (+http://www.facebook.com/externalhit_uatext.php)”, where the version number might vary but the core identifier remains consistent.
After collecting metadata, Facebook caches the preview for a time to reduce server load. You can force a refresh using Facebook’s Sharing Debugger tool if you update your content.
Why Facebook Created This Crawler
Facebook launched facebookexternalhit to solve the issue of users sharing links without context, which harmed user experience and click-through rates. The Meta crawler automatically generates rich previews, making the platform more engaging and providing better visibility and higher engagement rates for businesses and publishers.
Link sharing is vital for social media platforms. Proper previews encourage sharing and clicks, thereby benefiting both Facebook and content creators.
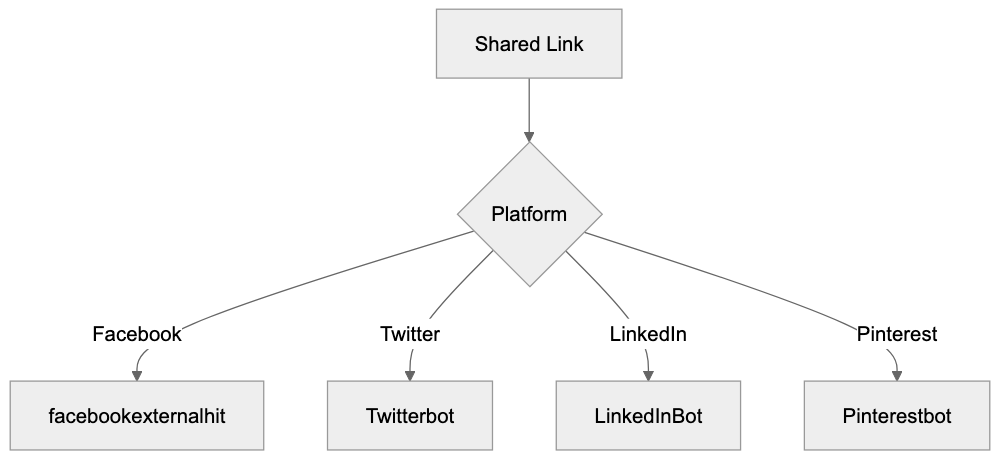
Facebook isn’t the only platform using this strategy. Twitter has Twitterbot, LinkedIn uses LinkedInBot, and Pinterest employs Pinterestbot, all serving the basic purpose of generating link previews for their respective platforms.
The User-Agent String Details
Link Preview Generation Process:

The facebookexternalhit user-agent string holds crucial information. The typical format is “facebookexternalhit/[version]” with a reference URL directing to Facebook’s documentation. Different versions of the crawler exist, with facebookexternalhit/1.1 handling most link previews. Meta also operates multiple crawlers beyond just facebookexternalhit, such as “facebookcatalog” for product catalogs and “Facebot” for other scraping tasks.
The newer Meta-ExternalAgent crawler is gradually replacing some functions of facebookexternalhit, handling certain types of content fetching across Meta’s apps.
Your server logs might show requests from multiple Meta crawlers, which is normal as they handle various tasks. The user-agent string helps you identify which Meta service is accessing your content.
How Businesses Use facebookexternalhit Data
Web developers monitor facebookexternalhit traffic to ensure their Open Graph setup works correctly, checking server logs for errors. Content marketers use Facebook’s Sharing Debugger to see how pages appear when shared. SEO experts refine Open Graph tags to boost social media engagement, testing different images, titles, and descriptions.
Small business owners should understand this crawler as it affects their social media presence. Proper link previews prevent a decrease in potential customers and engagement.
Developers also use the crawler’s behavior to debug caching issues, using the Sharing Debugger tool to force refreshes when needed.
Blocking facebookexternalhit: What Happens
You can block facebookexternalhit with robots.txt or server rules, but doing so affects social sharing. Links will appear as plain text without previews. Some sites block the crawler for privacy or security reasons, such as paywalled content sites. Blocking affects engagement rates and traffic. Partial blocking is possible with careful configuration, but generally, allowing the crawler is beneficial.
Comparison With Similar Social Media Crawlers
Various platforms employ different crawlers for link preview generation:
| Crawler Name | Platform | User-Agent Identifier | Primary Purpose | Cache Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| facebookexternalhit | facebookexternalhit/1.1 | Link previews | Days to weeks | |
| Twitterbot | Twitter/X | Twitterbot/1.0 | Card generation | Hours to days |
| LinkedInBot | LinkedInBot/1.0 | Link previews | Days | |
| Pinterestbot | Pinterest/0.2 | Pin previews | Varies | |
| Slackbot | Slack | Slackbot-LinkExpanding | Message unfurling | Hours |
These crawlers use Open Graph tags as the main metadata source, though platforms may have tag preferences. Caching frequency varies, respecting robots.txt is standard, and Facebook’s crawler is efficient regarding server load.
Best Practices For Handling facebookexternalhit
- Implement appropriate Open Graph tags: At minimum, include og:title, og:description, og:image, and og:url.
- Use high-quality images: At least 1200x630 pixels for best display.
- Test pages with Facebook’s Sharing Debugger before sharing crucial content.
- Avoid blocking facebookexternalhit unless necessary. It uses minimal bandwidth, offering significant social sharing value.
- Monitor server logs for errors like 403, 404, or 500.
- Keep Open Graph tags updated whenever you change content and use the Sharing Debugger for cache refreshes.
- Consider fallback meta tags for platforms that don’t support Open Graph.
Social Media Crawler Comparison:
Technical Implementation Details
facebookexternalhit follows standard web protocols, respects redirects, and times out if pages are too slow. It doesn’t execute JavaScript and reads raw HTML source code. Use server-side rendering for important Open Graph tags.
The crawler supports both IPv4 and IPv6 and respects canonical URLs. It also has built-in rate limiting, meaning most shared links trigger just one or two visits.
Security Considerations
Verify requests claiming to be facebookexternalhit against Facebook’s IP ranges. Avoid sensitive information in Open Graph tags and ensure images required for previews are accessible. Be cautious with preview generation for private content to prevent leaking information through metadata.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- No preview: Ensure facebookexternalhit can access your site.
- Wrong images: Check og:image tags and URLs.
- Outdated previews: Use the Sharing Debugger for cache updates.
- Missing/truncated descriptions: Ensure og:description tags are correct.
- Image access issues: Verify CORS settings.
Future Of Meta’s Crawling Infrastructure
Meta is evolving its crawler ecosystem, with the Meta-ExternalAgent crawler supplementing facebookexternalhit for certain tasks. facebookexternalhit remains focused on Facebook link previews. Developers should stay informed about Meta’s updates to maintain compatibility. Link preview crawlers will only grow in importance as social media remains central to web traffic management.
Conclusion
Facebookexternalhit is Facebook’s key tool for generating link previews during URL sharing on the platform. It reads Open Graph tags and metadata to create preview cards. Understanding its functionality is necessary for web developers and content marketers. Supporting facebookexternalhit involves best practices like proper Open Graph tagging and regular testing. This benefits your social media performance and traffic from shared links.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I block facebookexternalhit?
Blocking facebookexternalhit will prevent the Facebook bot from accessing your Open Graph tags, meaning your shared links will appear as plain text without rich previews. This can significantly reduce user engagement and click-through rates, as users may be less inclined to click links that don't provide visual context.
How can I ensure my Open Graph tags are set up correctly?
You can ensure your Open Graph tags are correctly implemented by using Facebook's Sharing Debugger tool. This tool allows you to test how your pages will appear when shared and helps identify any issues with your Open Graph metadata.
What should I do if I see errors in my server logs related to facebookexternalhit?
If you notice errors such as 403, 404, or 500 in your server logs related to facebookexternalhit, you should investigate the root cause of these issues. Ensure that the Open Graph tags are accessible and correctly configured, and that the server is not misconfigured to block the bot.
How can I prevent stale link previews after updating content?
To prevent stale link previews once you've updated content on your site, use Facebook's Sharing Debugger to refresh the cache for that URL. This forces Facebook to recrawl the page and generate a new preview using the updated Open Graph tags.
What are the minimum Open Graph tags I should implement?
At minimum, you should implement the following Open Graph tags: og:title, og:description, og:image, and og:url. These tags provide essential information that Facebook uses to create link previews, enhancing your content's visibility on the platform.
What is the significance of using high-quality images for Facebook link previews?
Using high-quality images, ideally at least 1200x630 pixels, is essential for Facebook link previews as they enhance visual appeal and engagement. Higher quality images are more likely to attract users' attention, increasing the chances of clicks and shares.
How often should I check and update my Open Graph tags?
It is advisable to check and update your Open Graph tags whenever there are changes in your content. Regular auditing, especially before major promotions or campaigns, ensures that your shared links always provide accurate and engaging information to users.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.