Googlebot: Google's Primary Web Crawler and SEO Impact
Learn how Googlebot works, its user-agent types, crawl budget management, and relationship to Google-Extended for AI training data collection.
What is Googlebot and Why It Matters
Googlebot, Google’s primary web crawler, is a critical tool for search indexing on Google. Googlebot FAQ It scans websites across the internet to collect information, ensuring your website appears in Google search results. This SEO crawler continuously visits billions of web pages, reading content, following links, and reporting back to Google’s indexing systems.
Web crawlers like Googlebot are essential for search engines to gather fresh data. Google Search Central Blog on Crawling They help understand what content exists online and determine page rankings for relevant search queries. For website owners and SEO experts, understanding Googlebot and Google spider is crucial as it directly impacts site visibility. This crawler decides which pages get indexed, how often they are updated, and how much information is collected from your site.
How Googlebot Actually Works
Googlebot starts with a list of URLs from previous crawls and sitemaps submitted by website owners. Google Search Central Documentation It visits these URLs, reads the HTML content, and follows links to discover new URLs, adding them to the crawling queue.
Googlebot Crawling Process:
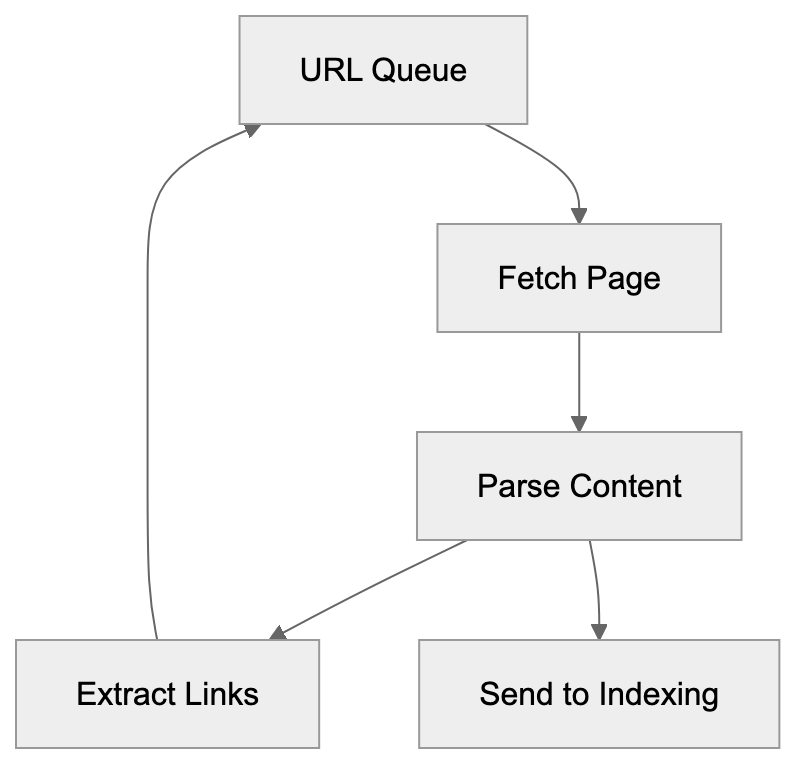
The process consists of two main stages. The first stage involves crawling the page and downloading content. In the second stage, Google’s search indexing systems process the content by analyzing text, images, and other elements to understand the page’s purpose and decide its inclusion in search results.
Googlebot doesn’t visit every page on your site every day. It has a crawl budget, which is the number of pages it will crawl on your site within a given timeframe. High-authority sites generally receive a more substantial crawl budget, whereas smaller or newer sites may receive less. The crawler also respects rules set in your robots.txt file, which tells Googlebot which pages or sections to crawl.
Googlebot User-Agent Types
Googlebot isn’t monolithic; it employs multiple user-agent variants for different purposes. Understanding these helps control how Google interacts with your site.
- Googlebot Desktop: Crawls as if it’s a desktop browser.
- Googlebot Smartphone: Focuses on mobile devices to understand mobile site functionality.
- Googlebot Image: Crawls images to populate Google Images search.
- Googlebot Video: Similar to the image crawler, but for video content.
- Googlebot News: Specializes in news content for Google News.
Googlebot User-Agent Variants:
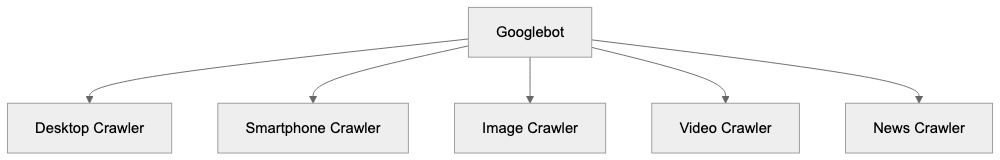
Each variant serves a unique purpose, and most websites will see visits from multiple types. You can check which ones visit your site by examining server logs that identify the user-agent string.
For SEO, the desktop and smartphone variants are crucial, as mobile-first indexing has made the smartphone crawler particularly important. Google primarily uses your content’s mobile version for indexing and ranking.
Understanding Crawl Budget Management
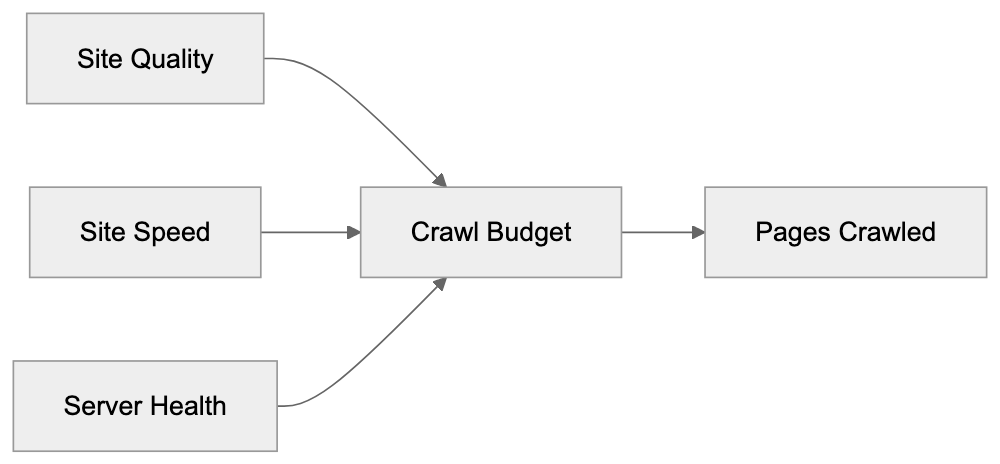
Crawl budget is the number of pages Googlebot crawls on your site, influenced by several factors. Site speed significantly impacts crawl frequency, and server errors can reduce your crawl budget if Googlebot encounters many errors.
To manage crawl budget:
- Fix technical issues: Resolve server errors and improve page load speed.
- Use robots.txt strategically: Block low-value pages like admin sections from being crawled.
- Submit an XML sitemap: This helps Googlebot efficiently find your important pages.
- Manage URL parameters: Utilize Google Search Console to inform Google which parameters to ignore to reduce crawling duplicate pages.
Internal linking is also pivotal. Pages well-connected within your site structure are crawled more frequently, while orphan pages may not be crawled at all.
Googlebot vs Google-Extended: AI Training Data
Crawl Budget Optimization Strategy:
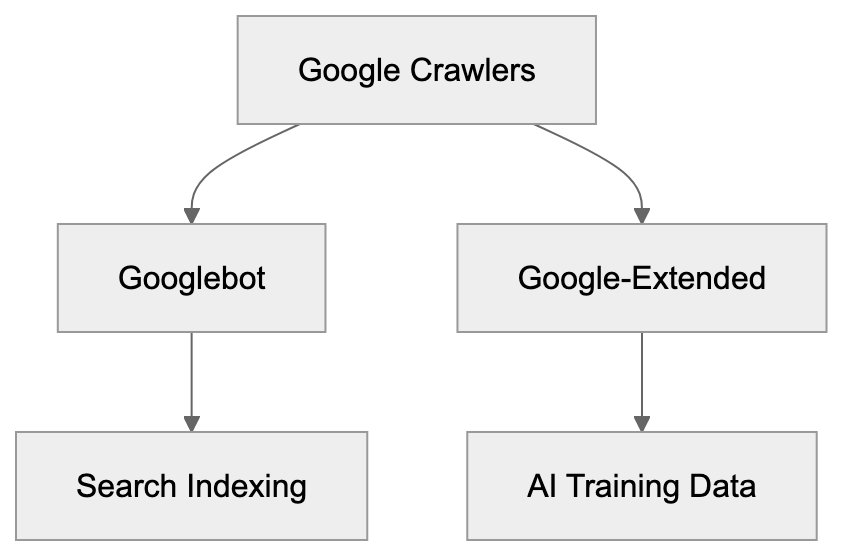
In 2024, Google introduced Google-Extended, a crawler distinct from Googlebot. Google-Extended collects data for AI training to support products like Gemini and Vertex AI, while Googlebot focuses on search indexing.
To block Google-Extended, add rules to your robots.txt file using the user-agent “Google-Extended.” Many opt to block this crawler to keep their content in search results without it being used for AI training. This separation provides more control over data use without affecting search rankings.
Understanding this distinction allows SEO experts and web developers to decide on AI training data involvement without impacting search performance.
Googlebot Compared to Other Search Crawlers
Googlebot vs Google-Extended:
Googlebot is not the only web crawler, though it is the most sophisticated and operates with a mobile-first indexing approach. Here’s how it compares with other crawlers:
- Bingbot: Offers good JavaScript handling, respects crawl-delay settings.
- Yandex Bot: Strong in Russian content, features detailed user-agents.
- Baiduspider: Focuses on Chinese web content with less aggressive crawling.
- DuckDuckBot: Privacy-focused with a smaller crawl budget.
While Googlebot has the most significant crawl budget and advanced rendering capabilities, including JavaScript execution, site managers should also consider other search crawlers if they target international markets. Ensure robots.txt isn’t blocking crucial crawlers.
Technical Details for Developers
Handling Googlebot properly is essential for developers. Several technical considerations include:
- Verify Googlebot Visits: Some bots spoof the user-agent string. Verify using reverse DNS lookup.
- Understand Rendering: Googlebot’s JavaScript rendering involves a delayed, two-wave process. Use server-side rendering for effective SEO.
- Server Resource Management: Handle Googlebot requests effectively, use caching, and consider using a CDN.
- Proper Status Codes: Ensure accurate status codes like 200, 404, and 301 for redirects.
- Optimize robots.txt: Locate it at your domain root, avoid blocking CSS/JavaScript files, and test using Google Search Console.
- Implement Structured Data: Schema markup aids Googlebot in understanding content, potentially leading to rich search results.
Monitoring Googlebot Activity
Monitoring Googlebot interactions is critical. Use Google Search Console for:
- Coverage Report: Shows indexed pages and errors affecting indexing.
- URL Inspection Tool: Checks when Googlebot last crawled a page and requests indexing for updates.
- Crawl Stats Report: Displays crawling activity, requests per day, and downloaded kilobytes.
Leverage server logs for raw crawler visit data, and consider third-party tools like Screaming Frog for simulating Googlebot crawls. Set up monitoring alerts for crawl errors and drops in crawled pages to quickly address issues.
Common Googlebot Issues and Solutions
Addressing common Googlebot issues is essential:
- Blocked Resources: Ensure robots.txt allows access to necessary files.
- Server Errors: Resolve server issues and improve hosting.
- Slow Page Speed: Optimize images, minify code, and use CDNs.
- Redirect Chains: Simplify links to direct destinations.
- Duplicate Content: Use canonical tags and redirects.
- Soft 404 Errors: Return correct 404 status codes for non-existent pages.
- Crawl Budget Waste: Streamline your site’s internal linking structure and fix duplicate content.
Conduct regular audits, using automated tools, to quickly identify and resolve issues.
Impact on SEO and Search Rankings
Googlebot’s crawling affects SEO performance. If it can’t efficiently crawl your pages, they won’t rank well. Effective crawling is crucial for large sites, helping prioritize vital content through clear site architecture and robust internal linking.
Mobile crawling is now pivotal, with mobile-first indexing meaning the mobile version of your content matters most. Ensure equivalency between desktop and mobile content.
Page speed influences crawl rate and rankings, with faster sites achieved through Core Web Vitals improvements.
Structured data aids Googlebot in understanding content but doesn’t directly impact rankings. It can, however, improve ranking potential and achieve rich results through better content understanding.
Future of Googlebot and Web Crawling
Googlebot continues to evolve, improving JavaScript rendering and other capabilities. AI components are expanding, with Google using AI to better interpret content context.
The separation between Googlebot and Google-Extended may grow, with specialized crawlers for different purposes giving more granular control to content creators.
Crawl budget optimization will be increasingly critical as the web expands. Effective crawling will advantage sites facilitating Googlebot’s work.
Privacy considerations, like GDPR, may impact crawler operations. Expect more transparency about data collection and usage.
Core Web Vitals and user experience signals are likely to influence crawling, rewarding better site performance with more crawl budget.
Summary
Googlebot builds Google’s search index. The desktop and smartphone variants matter most for SEO, with mobile-first indexing making the smartphone crawler particularly important.
Crawl budget affects how much of your site gets crawled. Improve it with faster page speeds, fewer server errors, and strategic robots.txt rules. Google-Extended is a separate crawler for AI training data, which you can block independently from Googlebot.
Monitor crawling through Google Search Console’s Coverage, URL Inspection, and Crawl Stats reports. Fix technical issues promptly since they affect whether your pages get indexed and ranked.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors influence Googlebot's crawl budget for my site?
A website's crawl budget is affected by factors like site speed, server errors, and the overall authority of the site. High-authority sites typically receive more frequent crawls, while sites with many technical issues may be crawled less often.
How can I check if Googlebot is accessing my site correctly?
You can check Googlebot's access by reviewing your server logs for user-agent strings. Additionally, Google Search Console provides tools like the URL Inspection Tool to see when Googlebot last crawled specific pages.
What should I do if Googlebot is encountering errors on my site?
If Googlebot is facing errors such as blocked resources or server issues, you should resolve these by ensuring proper settings in your robots.txt file and addressing server errors. Regular audits can help identify and fix these issues promptly.
Why is mobile crawling important for my website's SEO?
Mobile crawling is crucial because Google primarily uses the mobile version of your site for indexing and ranking. With mobile-first indexing, it's essential that your mobile content is optimized to ensure high search visibility.
How can I optimize my site's crawl budget?
To optimize your crawl budget, fix technical issues, use robots.txt to block low-value pages, and submit an XML sitemap to guide Googlebot. Additionally, maintain a strong internal linking structure to help ensure all critical pages are crawled.
What is the difference between Googlebot and Google-Extended?
Googlebot focuses on crawling for search indexing, while Google-Extended collects data for AI training, impacting how content may be utilized beyond traditional search results. Content creators can block Google-Extended via the robots.txt file for better control over data usage.
How can structured data impact my site's visibility?
Structured data helps Googlebot understand the content on your site better, which can lead to richer search results. While it doesn't directly affect rankings, it can enhance your site's visibility and click-through rates, potentially improving overall performance in search results.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.