Understanding GoogleOther: Google's R&D Crawler
Learn about GoogleOther, Google's internal R&D bot for product development and how it differs from Googlebot for web indexing.
What is GoogleOther
GoogleOther is a specialized web crawler operated by Google. It serves a completely different purpose than Googlebot, which is more familiar to most people. While Googlebot crawls websites to index content for Google Search, GoogleOther is utilized for internal research and development projects at Google. The GoogleOther crawler appears in server logs with a distinct user agent string that identifies it as GoogleOther. Web developers and site owners often spot this bot in their analytics and wonder what it does. Unlike Googlebot, GoogleOther traffic doesn’t directly impact your search rankings. The bot collects data for various Google projects that aren’t related to the main search engine. This includes AI training data, product development, and experimental features. Understanding the Googlebot distinction from GoogleOther helps website owners make informed decisions about which Google crawlers to allow or block. GoogleOther represents Google’s effort to separate its core search indexing from other data collection activities. Many site owners were unaware of this distinction until Google made it more transparent in recent years.
Why GoogleOther Exists
Google operates multiple products beyond its search engine. YouTube, Google Maps, Google Assistant, and various AI services all need data. GoogleOther is the Google R&D crawler for these non-search initiatives. The company created this separate crawler to give website owners more control. If you want Google to index your site for search but don’t want your content used for AI training or other R&D purposes, you can block GoogleOther specifically while still allowing Googlebot. This separation happened because of growing concerns about how tech companies use web data. Website owners demanded transparency about what their content gets used for. Google responded by splitting crawling activities into different bots with different user agents. The Google R&D crawler helps Google develop new products and improve existing ones. This might include training large language models, testing new algorithms, or building datasets for machine learning projects. The bot doesn’t follow the same rules as Googlebot. It might crawl pages at different frequencies or target different types of content. Google hasn’t disclosed every specific project that uses GoogleOther data, but the general purpose is clear: internal development work that’s separate from web search.
How GoogleOther Works
Google Crawler Types Overview:
GoogleOther identifies itself through its user agent string. When it requests a page from your server, the user agent typically looks like this: “GoogleOther” or variations that include version numbers and additional identifiers. The crawler respects robots.txt files just like other legitimate bots. You can block it by adding specific rules to your robots.txt file. Website owners who check their server logs regularly will see GoogleOther requests mixed in with other bot traffic. The frequency of GoogleOther visits varies widely. Some sites report seeing it daily while others see it sporadically. The crawling pattern depends on what Google projects need your type of content. Unlike Googlebot, which focuses heavily on text content and page structure, GoogleOther might target different elements. It could be collecting images, videos, code snippets, or other specific data types. The crawler doesn’t provide detailed feedback about crawl errors like Google Search Console does for Googlebot. This makes it harder to troubleshoot issues if GoogleOther is causing problems on your server. Most sites can handle the additional traffic without issues, but high-traffic sites or those with limited server resources might want to monitor and potentially limit GoogleOther access. The bot generally follows standard web protocols and doesn’t try to circumvent security measures or rate limits.
GoogleOther vs Googlebot Comparison
The key differences between these two crawlers matter for website management. Googlebot focuses exclusively on indexing content for Google Search results. GoogleOther serves Google’s other products and research needs. Here’s a detailed comparison:
| Feature | Googlebot | GoogleOther |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Index content for Google Search | R&D projects and AI training |
| Impact on Rankings | Direct impact on search visibility | No impact on search rankings |
| Crawl Frequency | High for important pages | Varies by project needs |
| Transparency | Detailed in Search Console | Limited visibility |
| Blocking Impact | Site won’t appear in search | Only affects non-search uses |
| User Agent | Contains “Googlebot” | Contains “GoogleOther” |
Blocking Googlebot means your site won’t show up in Google search results. This is rarely what website owners want. Blocking GoogleOther only prevents Google from using your content for internal projects. Your search visibility stays intact. Many sites choose to allow both crawlers. Others specifically block GoogleOther to prevent their content from being used in AI training datasets. The decision depends on your content strategy and how you feel about data usage. Some content creators worry about AI models being trained on their work without compensation. Blocking GoogleOther is one way to opt out of this, but there’s no guarantee about what happens to data that was already collected before you blocked the crawler.
Alternative Web Crawlers and Comparison
GoogleOther isn’t the only specialized crawler from major tech companies. Understanding the scene helps you make informed decisions about bot access. Here are the main alternatives:
| Crawler | Company | Primary Purpose | AI Training | Block Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GoogleOther | R&D and product development | Yes | No search impact | |
| GPTBot | OpenAI | Training ChatGPT models | Yes | Blocks AI training |
| CCBot | Common Crawl | Building web archives | Sometimes | Blocks archiving |
| Bingbot | Microsoft | Bing search indexing | Some variants | Loses Bing visibility |
| Applebot-Extended | Apple | AI and ML features | Yes | No search impact |
GoogleOther vs Googlebot Purpose:
GPTBot from OpenAI explicitly crawls for training GPT models. Blocking it prevents OpenAI from using your content in future training runs. Common Crawl’s CCBot builds public web archives that many AI companies use for training. Blocking CCBot is less effective since many models were already trained on existing Common Crawl datasets. Microsoft split Bingbot into regular Bingbot for search and additional variants for AI purposes. Apple introduced Applebot-Extended specifically for AI features separate from regular Applebot, which powers Siri and Spotlight. The trend across the industry is clear. Major tech companies are separating search crawlers from AI training crawlers. This gives website owners granular control over how their content gets used. Each crawler respects robots.txt directives. You can allow or block them individually based on your preferences.
Managing GoogleOther Access
Controlling GoogleOther requires editing your robots.txt file. This file sits in your website’s root directory and tells crawlers what they can access. To block GoogleOther completely, add these lines:
User-agent: GoogleOther
Disallow: /This tells GoogleOther it cannot crawl any part of your site. If you want to block only specific sections, specify those paths instead of the forward slash. For example, to block only your blog section:
User-agent: GoogleOther
Disallow: /blog/Robots.txt Control Flow:
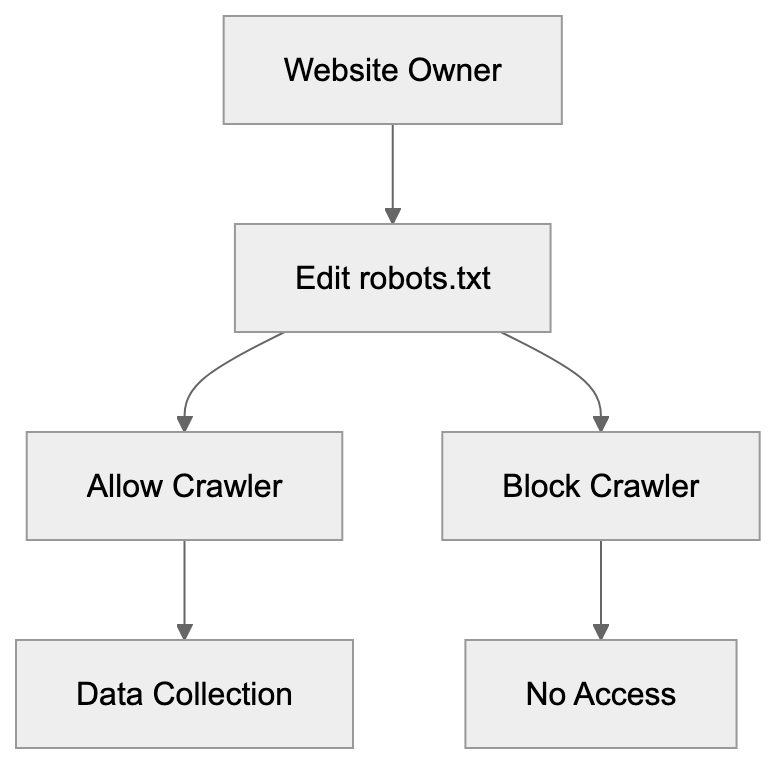
Remember, robots.txt is a request, not enforcement. Well-behaved bots like GoogleOther respect it, but malicious crawlers ignore it. Most website owners don’t need to block GoogleOther unless they have specific concerns about data usage. The crawler doesn’t harm your site or affect search rankings. Some reasons you might block it include concerns about AI training on your content, server resource limitations, or company policies about data sharing. After making robots.txt changes, the effects aren’t immediate. Crawlers check robots.txt periodically, so it might take days or weeks for GoogleOther to stop visiting. You can verify the block is working by monitoring your server logs. Look for requests from the GoogleOther user agent. They should stop appearing after the bot respects your new rules. Keep in mind that blocking GoogleOther won’t remove data Google already collected. It only prevents future crawling.
GoogleOther and AI Development
The rise of GoogleOther coincides with the AI boom. Google needs massive amounts of data to train models like Gemini and improve products like Google Assistant. Web content provides valuable training material for language models. GoogleOther likely plays a role in collecting this data, but Google hasn’t published detailed information about exactly which projects use GoogleOther data. The company maintains that the crawler supports various R&D initiatives. AI training is presumably one major use case. Website owners who create original content face a dilemma. Allowing GoogleOther might mean contributing to AI systems that could eventually compete with human creators. Blocking it means potentially missing out on visibility in future Google products. There’s no perfect answer. The decision depends on your values and business model. Some creators view AI training as fair use of public web content. Others see it as unauthorized exploitation. The legal scene around this issue is still evolving. Courts haven’t definitively ruled on whether using web content for AI training requires permission. GoogleOther at least provides transparency. You know when Google is accessing your content for non-search purposes. This is better than undisclosed data collection. Making an informed choice requires understanding what GoogleOther does and deciding whether you’re comfortable with it.
Impact on Website Performance
Most websites won’t notice performance issues from GoogleOther. The crawler is generally well-behaved and doesn’t overwhelm servers. However, high-traffic sites or those with complex pages might see some impact. Excessive crawling from any bot can slow down server response times. This affects real user experience. If GoogleOther visits too frequently, you might need to implement rate limiting. Check your server logs to see how often GoogleOther accesses your site. Normal crawling might be a few times per day or week. If you see hundreds of requests per hour, something might be wrong. You can use robots.txt to slow down the crawler without blocking it completely. The Crawl-delay directive tells bots to wait between requests. Not all crawlers respect this directive, but it’s worth trying. Server-side solutions like rate limiting based on user agent provide more control. You can configure your web server to limit how many requests per minute GoogleOther can make. This protects your server resources while still allowing the bot access. Most content management systems and hosting providers offer tools for managing bot traffic. WordPress plugins, CDN settings, and firewall rules can all help control crawler access. The key is monitoring and adjusting based on your specific situation.
Conclusion
GoogleOther represents Google’s separation of search indexing from other data collection activities. The crawler serves internal R&D projects, including likely AI training and product development. Unlike Googlebot, it doesn’t affect your search rankings. Website owners can block GoogleOther through robots.txt without impacting their Google Search visibility. This gives you control over whether Google uses your content for purposes beyond search indexing. The crawler is part of a broader industry trend. Major tech companies now use separate bots for AI training versus search indexing. Understanding these different crawlers helps you make informed decisions about data sharing. Whether you allow or block GoogleOther depends on your comfort level with AI training and data usage. There’s no objectively correct choice. Consider your content strategy, values, and technical requirements. Monitor your server logs to see how GoogleOther interacts with your site. Most sites can safely allow the crawler without issues, but those with specific concerns about AI training or data usage have clear options for blocking it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What distinguishes GoogleOther from Googlebot?
GoogleOther is specifically designed for research and development projects at Google, while Googlebot primarily focuses on indexing content for Google Search. Traffic from GoogleOther does not affect your search rankings, allowing website owners to maintain search visibility while selectively controlling data usage.
How can I block GoogleOther from crawling my site?
You can block GoogleOther by adding specific lines to your robots.txt file, such as: User-agent: GoogleOther followed by Disallow: /. This will prevent GoogleOther from accessing any part of your website.
What should I do if GoogleOther is affecting my website's performance?
If you notice that GoogleOther is generating excessive requests, you can implement rate limiting based on the user agent, or use the Crawl-delay directive in your robots.txt file to slow down its crawling frequency. Monitoring server logs will help you assess the traffic from this bot and adjust accordingly.
Does blocking GoogleOther impact my search rankings?
No, blocking GoogleOther will not affect your search rankings since it serves different purposes unrelated to Google Search indexing. Your site's visibility in search results will remain intact while preventing Google from using your content for R&D purposes.
What type of data does GoogleOther collect?
GoogleOther collects a variety of data types for internal projects, including images, videos, and code snippets. While it primarily supports R&D and AI training initiatives, Google has not disclosed specifics about the projects utilizing this data.
How often does GoogleOther crawl websites?
The crawling frequency of GoogleOther varies depending on the research needs of Google. Some websites may see daily visits, while others might experience sporadic crawling based on specific project requirements.
Will blocking GoogleOther remove previously collected data by Google?
No, blocking GoogleOther will prevent future crawling, but it will not remove data that has already been collected prior to blocking the bot. The measures taken through robots.txt apply only to future requests.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.