OpenAI GPTBot, OAI-SearchBot & ChatGPT-User Guide
Complete guide to OpenAI's web crawlers: GPTBot for AI training, OAI-SearchBot for ChatGPT Search, and ChatGPT-User. Learn how to block them via robots.txt.
Introduction
OpenAI operates three different web crawlers Each OpenAI bot serves a specific purpose. GPTBot collects data to train future GPT models. OAI-SearchBot powers the ChatGPT Search feature with real-time web results. ChatGPT-User fetches pages when users ask ChatGPT to look up specific URLs. Understanding these OpenAI crawlers is crucial for website owners who want control over how their content gets used. Many sites already block GPTBot to prevent their content from training AI models. As of mid-2024, approximately 22% of top websites block the GPTBot user agent, but some sites allow OAI-SearchBot because it brings traffic through ChatGPT Search while not using content for training. This guide explains what each OpenAI bot does and how to manage them through your robots.txt file.
OpenAI Crawler Overview:
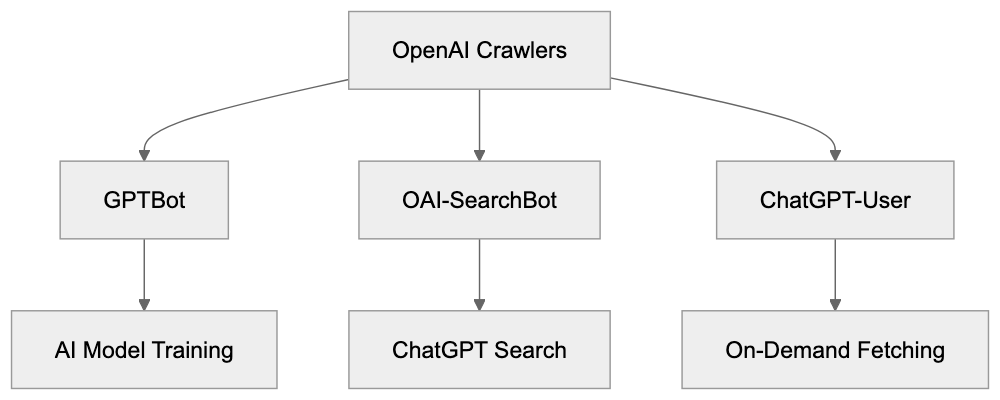
What is GPTBot and What Does It Do
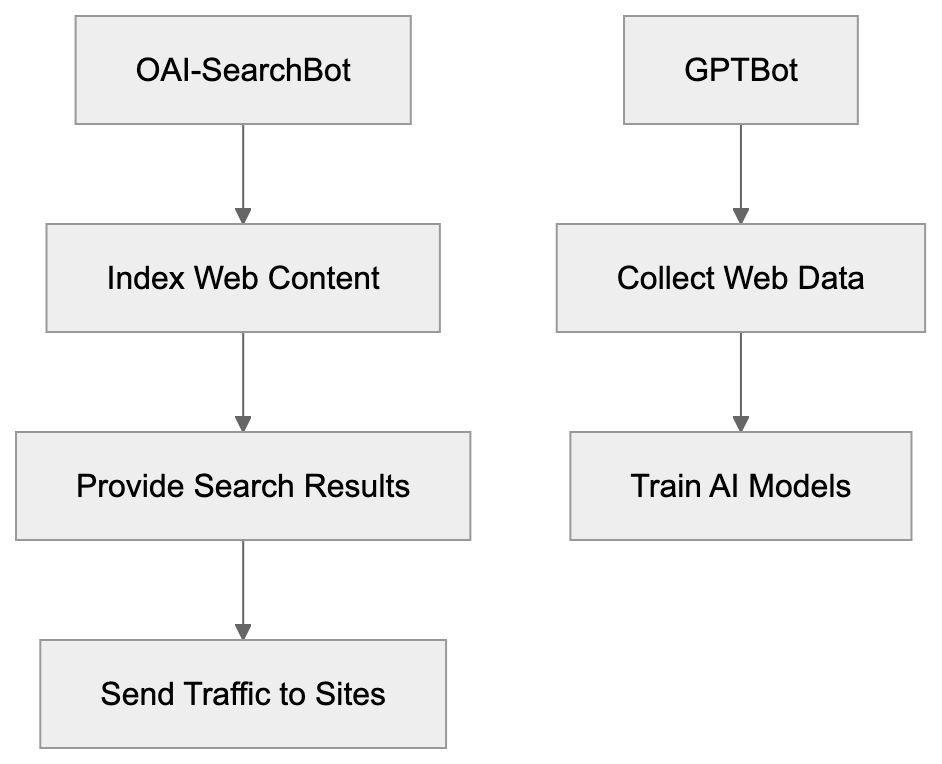
GPTBot is the OpenAI crawler designed to collect web content for training future versions of GPT language models. The full GPTBot user agent string looks like this: GPTBot/1.3. When GPTBot visits your website, it reads and downloads publicly available content. OpenAI then uses this collected data to improve and train new AI models. The bot follows standard web crawling practices and respects robots.txt directives. GPTBot does not collect content behind paywalls or login walls. It also skips pages that require user interaction to access. The crawler identifies itself clearly in server logs so website administrators can track its activity. OpenAI provides an IP verification method through openai.com/gptbot.json where you can confirm if requests actually come from legitimate GPTBot instances. This helps prevent spoofing where other bots pretend to be GPTBot. The purpose of GPTBot is straightforward: gather varied web content to make GPT models smarter and more knowledgeable about various topics.
Understanding OAI-SearchBot for ChatGPT Search
OAI-SearchBot is the OpenAI crawler that powers ChatGPT Search functionality. This bot works differently from GPTBot because it does NOT collect data for AI model training. Instead, OAI-SearchBot crawls and indexes web content to provide real-time search results inside ChatGPT. When users ask ChatGPT questions that need current information, the system uses OAI-SearchBot’s index to find relevant pages. The search results include attribution links that direct users to the original sources. This creates a traffic opportunity for websites since ChatGPT can send users to your pages. The OAI-SearchBot user agent identifies itself clearly in web server logs. Website owners who block GPTBot might still want to allow OAI-SearchBot because it functions like a traditional search engine crawler. It helps your content get discovered through ChatGPT Search without contributing to AI training datasets. Many businesses prefer this arrangement because they gain visibility in ChatGPT while maintaining control over whether their content trains AI models. OAI-SearchBot respects standard robots.txt rules and crawl-delay directives.
GPTBot Data Collection Process:

How ChatGPT-User Works On-Demand
ChatGPT-User is different from both GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot. This bot fetches web pages only when a ChatGPT user specifically requests information from a particular URL. It does not proactively crawl the web. Instead, it operates on-demand based on user actions. When someone asks ChatGPT to summarize a specific webpage or fetch content from a URL, the ChatGPT-User bot makes that request. The user agent string for ChatGPT-User clearly identifies these requests in your server logs. This bot also respects robots.txt directives. If you block ChatGPT-User, then ChatGPT cannot fetch pages even when users explicitly request them. The data retrieved by ChatGPT-User helps answer individual user queries, but OpenAI has stated this method does not contribute to large-scale training datasets. The bot operates more like a browser fetching a page on behalf of a user. Traffic from ChatGPT-User might include a referral parameter utm_source=chatgpt.com which helps you track visits originating from ChatGPT conversations. This allows you to measure how much traffic comes from people using ChatGPT to access your content.
Why OpenAI Created These Bots
OpenAI developed these three bots to serve distinct business and technical needs. GPTBot exists because AI language models need massive amounts of text data for training. Web content provides varied information across countless topics and writing styles. Collecting this data helps create more capable and knowledgeable AI models. The OpenAI crawler GPTBot automates this collection process at scale. OAI-SearchBot was created to make ChatGPT more useful by adding real-time web search capabilities. Users want current information about news, weather, stock prices, and other time-sensitive topics. Large language models alone cannot provide this because they have knowledge cutoff dates. OAI-SearchBot solves this by indexing fresh web content. ChatGPT-User enables interactive use cases where people want ChatGPT to analyze specific webpages they’re reading. All three bots help OpenAI build better products while giving website owners control through standard robots.txt mechanisms. The separation into three distinct bots lets website owners make granular decisions about what they allow.
OAI-SearchBot vs GPTBot Purpose:
How to Verify OpenAI Bot Requests
OpenAI provides a verification method to confirm that requests actually come from legitimate OpenAI bots. You can verify GPTBot requests by checking the IP address against the official list at openai.com/gptbot.json. This JSON file contains the current IP ranges used by OpenAI crawlers. To verify a request, first extract the IP address from your server logs. Then fetch the gptbot.json file and check if the IP falls within the listed ranges. This prevents spoofing where malicious bots fake the GPTBot user agent string. The same verification process works for OAI-SearchBot and ChatGPT-User requests. Always verify bot requests before making decisions based on the user agent string alone. Some bad actors impersonate legitimate crawlers to bypass blocking rules. Proper verification makes sure you’re actually dealing with OpenAI bots and not imposters. You can automate this verification in your server configuration or analytics tools. Regular monitoring helps you understand how often these bots access your site and what content they request.
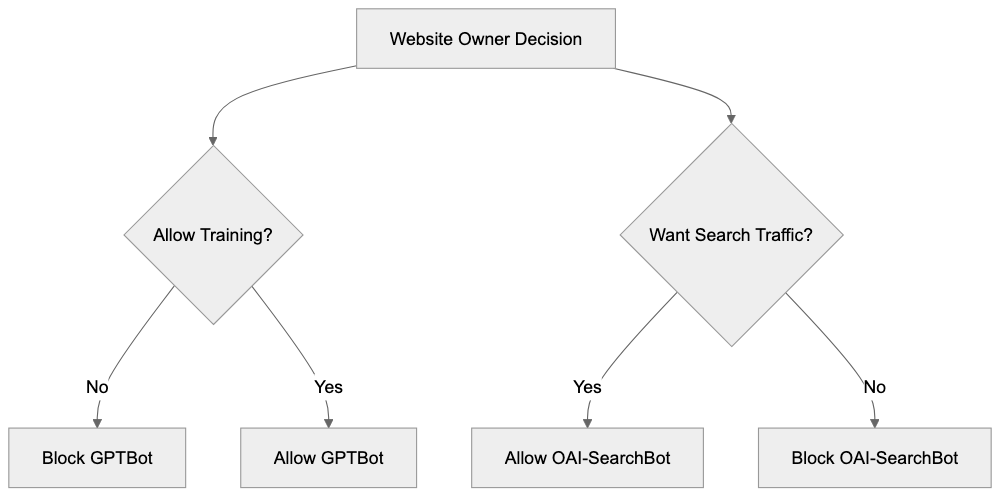
Blocking OpenAI Bots with robots.txt
The robots.txt file is the standard method to control which bots can access your website. To block GPTBot completely, add these lines to your robots.txt file:
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /This tells GPTBot it cannot crawl any part of your site. To block OAI-SearchBot use:
User-agent: OAI-SearchBot
Disallow: /For ChatGPT-User the syntax is:
User-agent: ChatGPT-User
Disallow: /You can mix and match these rules based on your preferences. Many sites block GPTBot but allow OAI-SearchBot to maintain search visibility. A common configuration looks like:
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: OAI-SearchBot
Allow: /
User-agent: ChatGPT-User
Allow: /This blocks AI training while allowing search indexing and on-demand fetches. You can also block specific directories instead of your entire site. For example, to protect only your blog from training:
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /blog/Robots.txt Control Strategy:
The robots.txt file must be placed at your domain root (example.com/robots.txt). Changes take effect after the bots next check your robots.txt file.
Tracking ChatGPT Traffic with UTM Parameters
When ChatGPT sends users to your website through search results or direct links, those visits often include the parameter utm_source=chatgpt.com in the URL. This referral parameter helps you track traffic coming from ChatGPT in your analytics tool. For example, a user clicking a link in ChatGPT might land on:
example.com/article?utm_source=chatgpt.comYou can filter for this parameter in Google Analytics or other analytics platforms to see how much traffic ChatGPT generates. This data helps you understand whether allowing OAI-SearchBot brings meaningful visitors to your site. The utm_source parameter is added automatically by ChatGPT when it generates links to external websites. You do not need to configure anything to receive these tagged visits. Monitor this traffic over time to evaluate whether ChatGPT Search provides value for your business. Some websites see significant referral traffic from ChatGPT while others see minimal impact. Your analytics will show the actual numbers for your specific site. You can also create custom reports or dashboards focused on chatgpt.com as a traffic source.
Comparing OpenAI Bots to Other AI Crawlers
OpenAI is not the only company operating AI training crawlers. Multiple tech companies run similar bots to collect web data. Here is how GPTBot and related OpenAI crawlers compare to alternatives:
| Bot Name | Company | Primary Purpose | User Agent | Blocks Training |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPTBot | OpenAI | AI model training | GPTBot/1.3 | User-agent: GPTBot |
| Google-Extended | AI model training | Google-Extended | User-agent: Google-Extended | |
| CCBot | Common Crawl | Dataset collection | CCBot | User-agent: CCBot |
| Anthropic-AI | Anthropic | AI model training | anthropic-ai | User-agent: anthropic-ai |
| ClaudeBot | Anthropic | AI model training | ClaudeBot | User-agent: ClaudeBot |
| Bingbot | Microsoft | Search indexing | Bingbot | User-agent: Bingbot |
Each crawler serves different purposes. Some companies use one bot for both search and training while OpenAI separates these functions. Google-Extended specifically handles AI training separately from regular Googlebot search crawling. CCBot collects data for Common Crawl which many AI companies use as a training source. Anthropic operates both Anthropic-AI and ClaudeBot for training Claude models. Most of these bots respect robots.txt directives. Website owners often block multiple AI training bots simultaneously while allowing search engine crawlers. The choice depends on your content strategy and views on AI training.
OpenAI Crawler Statistics and Adoption
As of mid-2024, data shows that approximately 22% of top-ranked websites block GPTBot through robots.txt rules. This percentage has grown since GPTBot launched as more website owners became aware of AI training practices. The blocking rate varies by industry, with news publishers and content creators showing higher blocking rates. Technical and educational sites show lower blocking rates. OAI-SearchBot sees fewer blocks because it provides search functionality without training AI models. Exact statistics for OAI-SearchBot blocking are not widely published, but the rate appears significantly lower than GPTBot. ChatGPT-User blocking is also less common since it only fetches pages on user request. The trend shows increasing awareness among website administrators about different OpenAI bots and their purposes. More sites are implementing selective blocking strategies that allow search visibility while preventing training data collection. Analytics from various web hosting companies indicate GPTBot generates substantial crawl traffic on sites that allow it. The OpenAI crawler operates continuously to keep training data current.
Making the Right Choice for Your Website
Deciding whether to allow or block OpenAI crawlers depends on your goals and concerns. Consider blocking GPTBot if you create original content that represents significant investment and you want to prevent AI models from training on it without compensation. Many publishers, writers, and content creators choose this approach. Consider allowing OAI-SearchBot if you want visibility in ChatGPT Search results and the potential referral traffic. This bot does not contribute to training datasets so you get search benefits without enabling AI training. ChatGPT-User is less important to block since it only operates on-demand when users request specific pages. Blocking it prevents ChatGPT from summarizing your pages for users who ask. Some websites allow all three bots because they see AI as a traffic source and discovery channel. Others block all three over concerns about AI’s impact on their business model. There is no universal right answer. Review your content strategy, business model, and views on AI to make an informed decision. You can always change your robots.txt rules later if your position changes.
Summary
OpenAI operates three web crawlers: GPTBot collects training data for future GPT models, OAI-SearchBot powers ChatGPT Search without using content for training, and ChatGPT-User fetches pages on-demand when users request specific URLs.
Each bot respects robots.txt directives and can be blocked independently. As of mid-2024, about 22% of top websites block GPTBot while fewer block the search and on-demand bots. Verify legitimate requests using the IP ranges at openai.com/gptbot.json. Track traffic from ChatGPT using the utm_source=chatgpt.com parameter in analytics.
A common approach is blocking GPTBot to prevent AI training while allowing OAI-SearchBot to maintain visibility in ChatGPT Search. The choice depends on your content strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I block GPTBot from accessing my website?
You can block GPTBot by adding specific directives to your robots.txt file. For example, use: User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /. This tells GPTBot it cannot crawl any part of your site. Make sure to place the robots.txt file at the root of your domain.
What is the difference between GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot?
GPTBot is designed to collect data for training future GPT models, while OAI-SearchBot indexes web content for real-time search results in ChatGPT. OAI-SearchBot does not use the content for AI training, making it a preferred option for many website owners who still want traffic without contributing to AI training datasets.
Can I track traffic from ChatGPT users to my website?
Yes, when users visit your site through ChatGPT, the URLs usually include the parameter utm_source=chatgpt.com. This allows you to track these visits in analytics tools, helping you evaluate how much traffic ChatGPT generates for your content.
What if I want to block only GPTBot but allow other crawlers?
You can create a selective blocking strategy in your robots.txt file by specifying directives for each bot. For example, you might block GPTBot while allowing OAI-SearchBot and ChatGPT-User by using the following configuration:
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: OAI-SearchBot
Allow: /
User-agent: ChatGPT-User
Allow: /
How can I verify if a request came from an OpenAI bot?
You can verify requests by checking the IP address against the official list provided at openai.com/gptbot.json. You should extract the IP from your server logs and confirm that it falls within the listed ranges to ensure it's a legitimate OpenAI bot.
Is it possible to allow OAI-SearchBot but block GPTBot?
Yes, many website owners choose this option because OAI-SearchBot can drive traffic and improve visibility without contributing to AI training. Use the appropriate directives in your robots.txt to block GPTBot while allowing OAI-SearchBot to crawl your site.
What are some reasons to block all OpenAI bots?
Some website owners may choose to block all OpenAI bots due to concerns about content ownership, potential misuse of original material, or simply a desire to maintain strict control over their web content. Artists, writers, and publishers often adopt this strategy to protect their intellectual property.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.