GrokBot: xAI's Web Crawler for Training Grok AI Model
Learn about xAI's GrokBot web crawler, its purpose, user-agent spoofing issues, and how to block it from accessing your website.
Introduction
GrokBot is a web crawler operated by xAI, the artificial intelligence company founded by Elon Musk in 2023. xAI is known for developing advanced AI technologies. This bot, known as the xAI crawler, collects data from websites across the internet to train Grok, xAI’s conversational AI chatbot. Web crawlers like GrokBot automate the process of visiting websites and extracting text, images, and other content. Robots.txt files are commonly used to manage crawler access. Companies build large datasets for training AI language models using this data. GrokBot appeared in website server logs in late 2023 and early 2024 as xAI expanded data collection. TechCrunch reported on xAI’s data collection practices. The crawler has sparked discussions among webmasters and developers due to allegations of user-agent spoofing and limited official documentation from xAI. Understanding how GrokBot operates helps website owners make informed decisions about allowing or blocking access to their content. CrawlerCheck provides tools to manage bot access effectively.
What is GrokBot
GrokBot is xAI’s automated web crawling tool designed to gather training data from publicly accessible websites. The bot systematically visits web pages, downloads their content, and processes information for use in training the Grok AI model. Like other AI training crawlers such as GPTBot from OpenAI or Google-Extended, GrokBot scans through HTML content, extracts text and metadata, and adds this information to xAI’s training datasets.
The official user-agent string for GrokBot typically identifies itself in server logs, allowing website administrators to recognize when the bot accesses their pages. However, the crawler has been observed using different user-agent strings in some cases. GrokBot respects robots.txt files when properly configured, enabling website owners to control whether the bot crawls their content. The crawler operates continuously as xAI requires fresh data to improve and update the Grok AI model.
Why GrokBot Exists and Its Purpose
GrokBot Operation Overview:
xAI created GrokBot to solve a fundamental challenge in AI development: acquiring enough high-quality training data. Large language models like Grok require massive text datasets to learn language patterns, factual information, and reasoning capabilities. Web crawling remains one of the most effective methods to collect data on this scale.
- Gathering Diverse Content: GrokBot collects varied content from across the internet, including news articles, forum discussions, and technical documentation.
- Reducing Dependency: It helps xAI reduce reliance on third-party datasets, which may have licensing restrictions or quality issues.
- Keeping Knowledge Current: Continuous crawling allows xAI to maintain Grok’s knowledge currency by regularly ingesting new content.
Beyond simple data collection, GrokBot helps xAI understand the structure of web content, organize information, and comprehend relationships between different topics, enhancing Grok’s ability to process user queries.
User-Agent Spoofing Allegations
Several website administrators and security researchers have reported instances where GrokBot used misleading user-agent strings. User-agent spoofing occurs when a crawler identifies itself as a different bot or even as a regular web browser to avoid detection or blocking. Some reports indicate that traffic attributed to GrokBot used generic browser user-agents like Chrome or Firefox rather than accurately identifying itself.
Data Collection Purpose:

This practice creates problems for website owners, preventing informed decisions about which crawlers can access their content. If a bot does not accurately identify itself, it bypasses rules set in robots.txt files and complicates traffic analysis. The extent of these spoofing allegations remains unclear, as xAI has provided limited public statements about GrokBot’s behavior. Misidentifications or unrelated traffic incorrectly attributed to xAI may explain some instances, but the reports raise valid transparency concerns in AI training data collection.
Limited Documentation from xAI
One persistent challenge with GrokBot is the sparseness of official documentation from xAI. Unlike major tech companies offering detailed crawler documentation, xAI has released minimal information about GrokBot’s operations. There is no dedicated page explaining the crawler’s behavior, crawl rates, IP address ranges, or contact information for webmasters.
This absence of documentation hinders website administrators from verifying legitimate GrokBot traffic versus potential impersonators. Most information about the crawler comes from community observations, server log analysis, and informal reports. The limited documentation also means website owners lack clear guidance on:
- How xAI uses collected data
- Data retention duration
- Content removal requests
Other AI companies typically provide transparency reports or data collection policies addressing these questions. This documentation gap frustrates developers and webmasters who prefer working with well-documented crawlers following clear, published guidelines.
How to Block GrokBot from Your Website
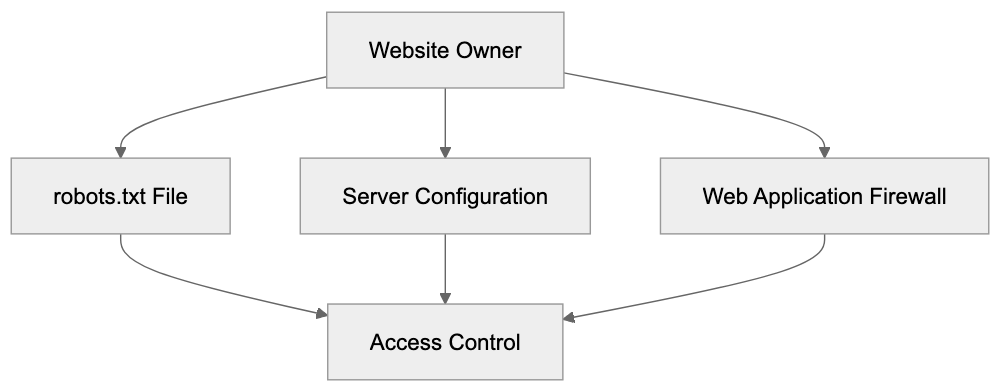
Website owners wanting to prevent GrokBot from crawling their content have several options. Using the robots.txt file is the most straightforward method. It tells crawlers which parts of a site they can access. To block GrokBot specifically, add these lines to your robots.txt file located at your domain root:
User-agent: GrokBot
Disallow: /This tells any crawler identifying as GrokBot to avoid crawling any pages on your site. If you suspect user-agent spoofing, additional blocking methods are necessary. Server-level blocking through .htaccess files (for Apache servers) or nginx configuration files provides stronger control. You can block based on IP address ranges if xAI publishes them or specific request patterns. Web Application Firewalls can identify and block suspicious crawler behavior regardless of the stated user-agent. For complete protection, consider combining multiple methods, as no single technique is foolproof against sophisticated crawlers.
Comparison with Other AI Training Crawlers
GrokBot operates in a crowded field of AI training crawlers, each with unique characteristics and policies. Understanding the comparisons helps website owners make informed decisions.
| Crawler | Company | Documentation Quality | Respects robots.txt | Spoofing Reports |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GrokBot | xAI | Limited | Yes (claimed) | Some reports |
| GPTBot | OpenAI | Extensive | Yes | Rare |
| Google-Extended | Good | Yes | None known | |
| CCBot | Common Crawl | Extensive | Yes | Rare |
| Anthropic-AI | Anthropic | Moderate | Yes | None known |
| FacebookBot | Meta | Good | Yes | Rare |
GPTBot from OpenAI is well-documented with clear opt-out instructions and transparent policies. Google-Extended benefits from Google’s established web crawling infrastructure and detailed webmaster resources. CCBot is known for consistent behavior and extensive documentation through the Common Crawl project. Anthropic-AI from Anthropic (creators of Claude) offers moderate documentation with clear identification. FacebookBot’s documentation is complete as part of Meta’s broader web crawling operations. GrokBot’s main weaknesses compared to these alternatives are limited documentation and user-agent spoofing allegations. Its primary advantage is newer and potentially less intrusive crawling activity.
Impact on Website Performance and Bandwidth
Methods to Block GrokBot:
Aggressive web crawling can adversely affect website performance and consume significant bandwidth. When GrokBot or any crawler visits your site, it generates HTTP requests that your server must process. Each request uses server resources, including CPU time, memory, and network bandwidth.
High-frequency crawling can slow down your site for legitimate users, especially if you’re on shared hosting or have limited server capacity. AI web scraping crawlers can be more aggressive than traditional search engine crawlers since they require rapid data collection. Website owners should monitor server logs to understand crawling patterns and frequency. Look for repeated requests from the same user-agent or IP addresses over short periods.
If GrokBot consumes excessive resources, options beyond complete blocking exist. Use the Crawl-delay directive in robots.txt to slow the crawler, giving your server breathing room between requests. Rate limiting at the server level also works well for controlling crawler impact. For high-traffic websites, crawler activity may be negligible compared to normal user traffic. For smaller sites, even moderate crawling can cause noticeable performance issues.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The legal landscape around AI training data collection remains unsettled with ongoing debates about copyright, fair use, and website terms of service. When GrokBot crawls publicly accessible web content, questions arise about whether this constitutes fair use of copyrighted material. Different jurisdictions have varying laws regarding automated data collection and use.
Website owners often include terms of service prohibiting automated scraping, although enforceability varies. Ethical considerations extend beyond legal questions. Some argue publicly posted content should be available for AI training to advance technology benefiting everyone. Others contend content creators should control whether their work trains commercial AI systems. The user-agent spoofing allegations add an ethical dimension since transparent identification is a best practice in web crawling.
Website owners concerned about these issues should clearly state preferences through robots.txt, terms of service, and copyright notices. If you create original content, consider whether you want it used for AI web scraping training and implement appropriate technical controls. The debate will likely continue as AI capabilities expand and more companies launch training crawlers.
Future of GrokBot and xAI’s Data Collection
As xAI continues developing Grok and potentially other AI models, GrokBot’s role will likely evolve. The company may improve documentation in response to community feedback and industry pressure for transparency. We might see xAI publish official guidelines, IP ranges, and more detailed data usage policies.
The crawler’s behavior could become more sophisticated with better rate limiting and more respectful crawling patterns. Alternatively, xAI might shift towards licensing data from publishers rather than relying on web crawling. This approach has gained traction among AI companies facing legal challenges over training data.
The volume of content GrokBot needs depends on xAI’s model development roadmap and whether they expand beyond the current Grok chatbot. Website owners should expect continued crawling activity as long as xAI operates AI models needing data. Monitoring your server logs and staying informed about xAI’s policies will help adapt your blocking or allowing decisions as necessary. The broader industry trend is toward more regulation and standardization of AI training data collection, likely affecting GrokBot’s operations in the future.
Conclusion
GrokBot represents xAI’s entry into the competitive field of AI training data collection through web crawling. The crawler serves the necessary purpose of gathering varied internet content to train the Grok AI model. However, limited documentation and user-agent spoofing allegations have created uncertainty. Understanding what GrokBot is, why it exists, and how to control its access helps you make informed decisions about your content. Website owners can block GrokBot through robots.txt files, server configurations, or web application firewalls based on their preferences. Compared to more established AI training crawlers like GPTBot or Google-Extended, GrokBot has room for improvement in transparency and documentation. The legal and ethical questions surrounding AI training data collection continue to evolve. As xAI matures and potentially faces regulatory pressure, improvements in GrokBot’s operation and webmaster communication are expected.
Frequently Asked Questions
What can I do if I notice GrokBot crawling my website?
If you see GrokBot accessing your site and want to restrict its activity, you can use the robots.txt file to disallow it from crawling your content. Additionally, consider implementing server-level blocking or a web application firewall to manage and mitigate its impact.
How does GrokBot compare to other AI crawlers?
GrokBot has limited documentation and is associated with user-agent spoofing, unlike other crawlers like OpenAI's GPTBot or Google's crawler, which are better documented and more transparent. Understanding these differences helps website owners make informed decisions about managing their online content.
What are user-agent spoofing allegations regarding GrokBot?
User-agent spoofing involves GrokBot using misleading user-agent strings to mask its identity, which can make it difficult for website owners to manage its access effectively. This practice leads to transparency issues and complicates traffic analysis, as legitimate requests may go unrecognized.
What legal considerations should I be aware of with GrokBot?
The legal landscape for data collection by crawlers like GrokBot is complex, involving copyright and fair use debates. Website owners should be aware of their own terms of service regarding scraping and consider clearly stating their preferences in robots.txt files to protect their content.
Can I improve the way GrokBot interacts with my website?
You can manage GrokBot's activity by adjusting the robots.txt file to specify which sections it can or cannot crawl. Implementing crawl-delay settings may also help prevent performance degradation on your website while allowing controlled access.
What can I do about the limited documentation from xAI?
The limited documentation from xAI can be frustrating for webmasters. Engaging with community knowledge and using server log analysis may help mitigate uncertainty. Additionally, reaching out to xAI for clarification on best practices can be beneficial.
What steps might xAI take to address concerns about GrokBot?
As xAI grows, it may improve GrokBot's documentation and transparency policies in response to feedback from the web community. This could lead to better guidelines on data usage and clearer identification practices to alleviate concerns about user-agent spoofing.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.