AI Crawler Bots: Understanding Their Role in AI Systems
Learn how AI crawler bots gather data for AI systems, their operations, and impact on modern AI data collection and training processes.
What Are AI Crawler Bots and Why They Matter
AI crawler bots are automated programs that navigate the internet to collect data for AI systems, playing a crucial role in training large language models and other AI applications. These bots visit websites, read content, and extract information that becomes AI training data. Think of them as digital scouts gathering raw materials for AI development. Without AI crawler bots, companies would struggle to create the massive datasets necessary for training language models, image recognition systems, and other AI tools.
The data gathering process is crucial because modern AI models require billions of data points to function correctly. Companies like OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic heavily rely on web crawlers to build their AI products, utilizing vast amounts of data scraped from the web to enhance their models’ performance. These data collection bots work continuously, scanning public web pages and storing valuable information. Recently, this process has become controversial as website owners question whether AI companies should use their content without permission or compensation, leading to increased blocking of AI crawlers and discussions about fair use and data ownership.
How AI Crawler Bots Actually Work
AI Crawler Bot Data Collection Process:
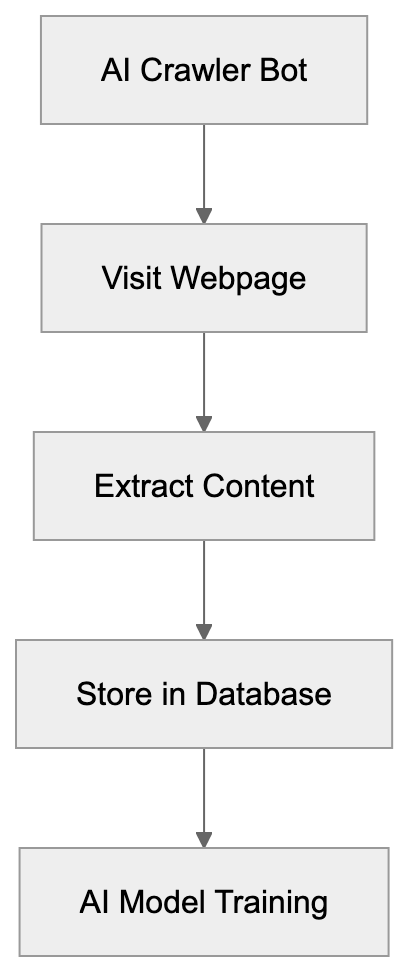
AI crawler bots start with a list of URLs to visit. The bot loads each webpage like a browser. It parses the HTML code to extract text, images, and other data types. Most web crawlers follow a specific pattern. They begin at seed URLs and follow links to discover new pages. The bot checks a file called robots.txt before crawling. This file tells crawlers which parts of a site they can access, but not all bots respect these rules. Some AI companies have been caught ignoring robots.txt directives.
The bot stores collected data in databases for later processing, enabling AI models to learn from diverse and extensive datasets. Advanced crawlers can handle JavaScript-heavy sites and changing content by waiting for pages to load fully before extracting data. The crawling speed varies based on the bot’s configuration. Polite crawlers add delays between requests to avoid overloading servers, while aggressive crawlers might send hundreds of requests per second.
Collected data gets cleaned and formatted before use in AI training. Duplicate content is removed, and text is normalized. Large-scale operations can take weeks or months.
Why AI Companies Need Crawler Technology
AI models learn patterns from vast amounts of data. Building a good language model requires more than a few thousand examples. Companies need billions of text samples to train models like GPT-4 or Claude. Crawler technology provides the most efficient way to gather this data at scale. Manual data collection would take years and cost millions in labor.
Web crawling automates the data gathering process and operates 24/7 without breaks. Data diversity is also crucial. AI data scraping allows crawlers to visit millions of websites across various topics and languages. This variety helps AI systems understand different writing styles and subject matters. Without web crawlers, AI systems would have limited knowledge and poor performance.
Web Crawling Workflow:
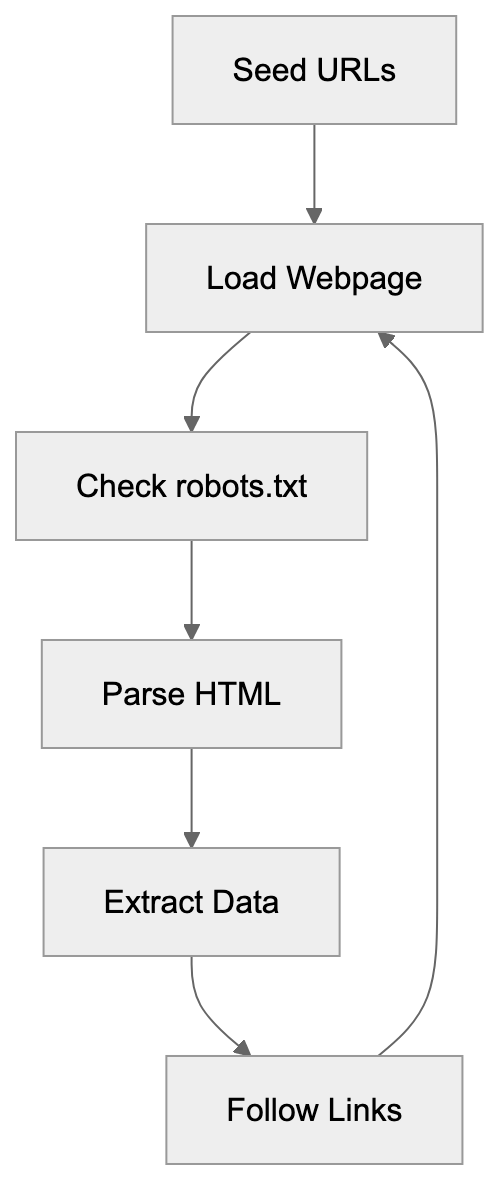
The bots also keep AI models updated with current information. New crawls record recent content and trends. Companies use this fresh data to improve existing models. Some crawlers target specific content types, like code repositories or scientific papers, aiding the creation of domain-specific AI tools.
The economic impact of crawler technology is substantial. AI crawler bots dramatically reduce data acquisition costs compared to licensing content or manual collection.
Common AI Crawler Bots and Their Characteristics
Several major AI companies operate their own crawler bots, each with different behaviors and purposes. GPTBot belongs to OpenAI and gathers AI training data for ChatGPT. Google uses GoogleBot for search and Google-Extended for AI training. Anthropic runs ClaudeBot for Claude models. Meta operates Meta-ExternalAgent for AI projects.
These bots have distinct user-agent strings that identify them in server logs. Website administrators can block specific bots using robots.txt or server configurations. Crawling frequency varies. Some bots visit sites daily, others weekly or monthly. Respect for website rules also varies. Most major company bots honor robots.txt, but some smaller operations ignore it completely.
Performance impact on servers depends on crawl rate. Aggressive bots can slow down websites or increase hosting costs, while polite bots limit their request rate to minimize server load.
| Bot Name | Company | Primary Purpose | Respects robots.txt | Blocking Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPTBot | OpenAI | Training data for ChatGPT | Yes | robots.txt, User-Agent |
| Google-Extended | AI model training | Yes | robots.txt | |
| ClaudeBot | Anthropic | Training data for Claude | Yes | robots.txt, User-Agent |
| CCBot | Common Crawl | Open dataset creation | Yes | robots.txt |
| Meta-ExternalAgent | Meta | AI research and training | Yes | robots.txt |
Impact on Website Owners and Content Creators
Website owners face new challenges with AI crawler bots. Server costs can increase from additional traffic. A popular site might receive thousands of crawler requests daily, quickly adding up bandwidth usage and costs. Some small sites have reported significant cost increases.
Content creators worry about their work being used without compensation. A blogger spends hours writing an article, only for AI bots to scrape it for free. The AI company profits from models trained on that content, while the original creator gets nothing. This has sparked debates about fair use and copyright.
Many publishers have started blocking AI crawlers entirely. The New York Times blocked OpenAI’s crawler in 2023, and other major publications followed. Some websites use technical measures beyond robots.txt, implementing rate limiting or IP blocking for known crawler addresses. The cat-and-mouse game continues as crawlers adapt. Website analytics get skewed by bot traffic too, making it harder to separate real users from crawlers. Some crawlers don’t properly identify themselves, complicating detection.
Search Crawler vs AI Crawler Comparison:
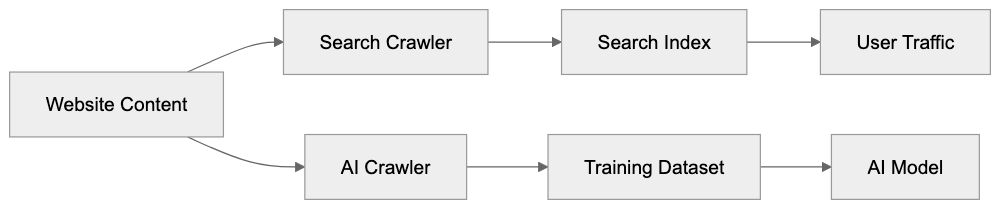
AI Crawler Bots vs. Traditional Search Engine Crawlers
Traditional search crawlers and AI crawlers have different goals. Google’s main crawler indexes content for search results, helping users find information and driving traffic back to websites. This creates value for content creators through visitor clicks. AI training crawlers extract data but don’t send traffic back. The website only experiences server load.
Search crawlers have been around for decades, and established norms exist. Website owners accept them because they benefit from search visibility. AI crawlers are newer, and the value exchange is unclear. Search bots update their index regularly to show current results, while AI training crawlers might visit once and never return. The data gets locked into a model that doesn’t credit sources.
Technical setups differ too. Search crawlers focus on indexing structure and keywords, while AI crawlers want full-text content and semantic meaning. Search bots respect canonical tags and structured data; AI crawlers might ignore these signals entirely. Frequency patterns vary as well. Search bots maintain freshness by regular revisits, and AI training bots might perform periodic large crawls instead.
The Future of AI Crawler Bots and Data Gathering
The AI crawler scene is rapidly evolving. As more companies launch AI products, the need for training data increases, leading to more bots constantly crawling the web. Website owners are pushing back harder against unrestricted crawling.
New technical standards are emerging for AI bot management. The robots.txt protocol might get extended with AI-specific directives. Some proposals suggest paid crawling models where AI companies compensate websites. Blockchain-based solutions for tracking content usage are being explored. Legal frameworks are also developing. The EU AI Act and similar regulations will affect crawler behavior. Courts are hearing cases about whether AI training constitutes fair use, shaping future crawler operations.
Technical arms races continue between crawlers and blocking measures. AI companies develop smarter bots that mimic human behavior better, while website owners create more sophisticated detection systems. Data quality focus is increasing. Companies want high-quality, curated data rather than everything, potentially leading to more selective crawling patterns.
Partnerships between AI companies and publishers are forming. Some content creators license their data directly instead of being crawled. The next few years will determine the sustainable model for AI data gathering.
End
AI crawler bots are foundational for modern AI systems by gathering the massive datasets needed for training. These automated programs scan websites continuously to extract text, images, and other content. Companies like OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic depend on crawler bots to build their AI products. The bots work differently than traditional search crawlers because they extract data without sending value back to websites, creating tension between AI companies and content creators. Website owners can block crawlers using robots.txt files and other technical measures. The future will likely bring new regulations and business models for AI data gathering. Understanding how these bots work helps developers and business owners make informed decisions about their content. As AI technology advances, the role of crawler bots in data collection will remain essential, but the rules around their use will continue evolving.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main functions of AI crawler bots?
AI crawler bots are primarily designed to automate the data collection process for training AI models. They navigate the web, extracting text, images, and other content types to create large datasets that are critical for machine learning applications.
How do AI crawler bots differ from traditional search engine crawlers?
While traditional search engine crawlers index web content to improve search results and drive traffic to websites, AI crawler bots extract data for training AI models without returning traffic or benefits to the site. This creates a different value exchange and raises questions about fair use and compensation.
Can website owners prevent AI crawlers from accessing their content?
Yes, website owners can use a robots.txt file to specify which parts of their sites are off-limits to crawlers. Additionally, they can implement more technical measures like rate limiting and IP blocking to control or prevent access by AI crawlers.
What types of data do AI crawler bots collect?
AI crawler bots collect a wide range of data, including textual content, images, and metadata from web pages. They are particularly interested in full-text content and semantic meaning to help train AI models effectively.
What challenges do content creators face due to AI crawler bots?
Content creators often worry about their original work being scraped and used without compensation. As AI companies profit from models trained on this content, creators seek to assert their rights and find ways to protect their intellectual property.
What future developments can we expect in AI crawler technology?
The future of AI crawler bots may include new regulations, improved technical standards for bot management, and potential partnerships between AI companies and content publishers for licensing data. Emerging legal frameworks will also shape how crawlers operate in relation to content ownership.
Are there ethical considerations surrounding the use of AI crawler bots?
Yes, ethical concerns center around data ownership, fair use, and the potential exploitation of content creators' work without proper compensation. As AI technology evolves, ongoing discussions about the rights of website owners and the responsibilities of AI companies will become increasingly important.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.