Kangaroo Bot: Understanding AI Data Collection Crawlers
Explore Kangaroo Bot's role in AI data collection, its user-agent string, crawling behavior, and how to manage its access to your website.
What is Kangaroo Bot
Kangaroo Bot is an AI crawler bot designed for web data collection to train machine learning models, similar to other AI web crawlers like GPTBot and Google-Extended. Serving as an AI web scraper, it visits websites automatically to gather text content, images, and other publicly available information. Unlike search engine crawlers that index content for search results, Kangaroo Bot focuses on building datasets for AI training.
Web crawlers like Kangaroo Bot exist because AI companies require massive amounts of data to train their language models and other AI systems, a practice that has raised concerns about data rights and ethics. These crawler bots scan millions of websites daily, extracting content that forms the core of training datasets. This collected information aids AI models in learning language patterns, understanding context, and generating human-like responses. For website owners and developers, understanding these bots is crucial because they impact server resources and raise questions about data usage rights.
Why AI Crawlers Like Kangaroo Bot Exist
AI companies need enormous datasets to train their models effectively. Training a modern language model requires billions of words and examples from varied sources. Manual data collection at this scale is impossible and extremely expensive. Automated AI crawler bots solve this problem by continuously scanning the web and gathering publicly accessible content.
AI Crawler Bot Operation Model:
Kangaroo Bot automates the process of building training datasets. These AI bots collect text from blogs, forums, news sites, documentation, and other web pages. The collected data is then processed, cleaned, and formatted for AI model training. Without these automated systems, developing AI would move much slower and cost significantly more.
Web scraping for AI training has become standard practice in the industry. Most major AI companies operate their own crawler bots or rely on third-party services. While these bots typically follow robots.txt directives, compliance is not guaranteed. This inconsistency fuels debates about data rights, copyright, and the ethics of automated content collection.
How Kangaroo Bot Operates
Kangaroo Bot identifies itself through its user-agent string when making requests to web servers. The user-agent contains the name ‘Kangaroo’ and additional identification details. Website administrators can examine their server logs to see if Kangaroo Bot has visited their sites by searching for this user-agent string.
The bot crawls websites by following links and downloading page content, starting with seed URLs and discovering new pages through hyperlinks. Its crawling pattern resembles that of standard web crawlers, sending HTTP requests, receiving HTML responses, and extracting text content from pages. Crawling frequency varies with the bot’s configuration and target website size.
Public documentation on Kangaroo Bot is limited compared to well-known crawlers like Googlebot or Bingbot. This lack of transparency makes it challenging for website owners to understand the bot’s behavior patterns, crawling frequency, and data usage policies. The scarcity of information also complicates efforts to verify the bot’s legitimacy or contact its operators.
Managing Kangaroo Bot Access
Kangaroo Bot Crawling Process:
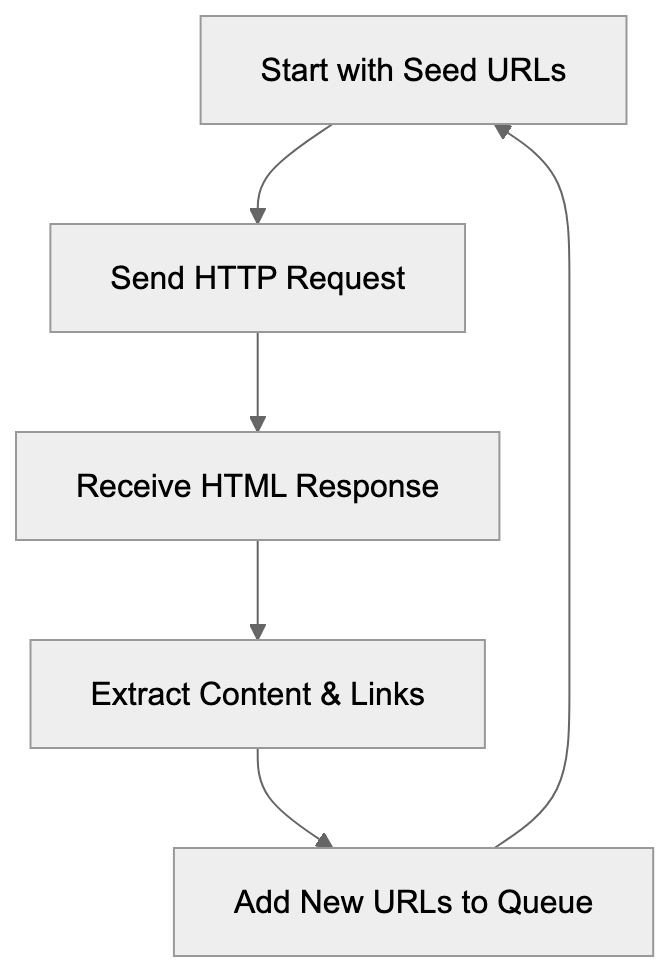
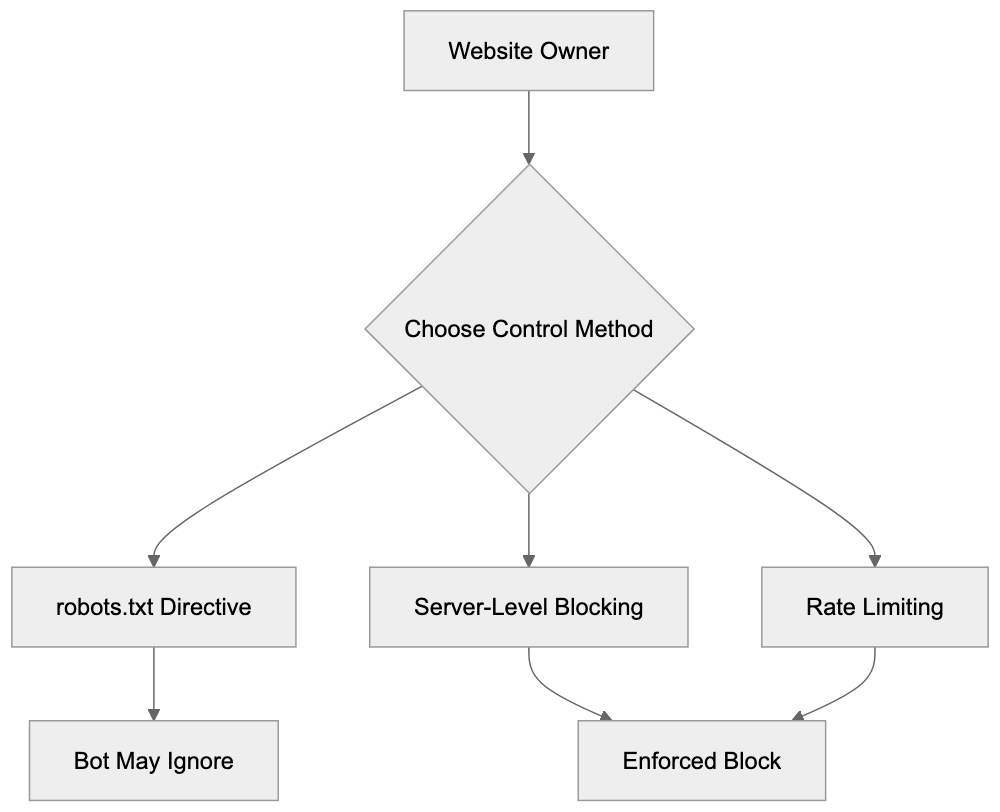
Website owners have several options for managing Kangaroo Bot’s access to their content. The most common method involves using the robots.txt file. This file instructs crawlers which parts of a website they can access.
To block Kangaroo Bot using robots.txt, add these lines to the file located in your website’s root directory:
User-agent: Kangaroo
Disallow: /This directive tells the bot not to crawl any pages on your site. However, not all crawlers respect these directives. If Kangaroo Bot continues crawling despite the robots.txt block, you may need to implement server-level blocking based on the user-agent string or IP addresses.
Server-level blocking requires configuring your web server to reject requests from specific user agents. For Apache servers, you can add rules to the .htaccess file. For Nginx, modify the server configuration. This method is more effective than robots.txt because it prevents the bot from accessing any content, regardless of whether it respects standard crawler protocols.
Monitoring server logs helps in tracking crawler activity. Regularly check your access logs for Kangaroo Bot requests. Look for patterns in crawling frequency, requested URLs, and response codes. High crawling rates can impact server performance and bandwidth usage. If you notice excessive crawling, consider implementing rate limiting or blocking measures.
Comparing AI Crawler Bots
Kangaroo Bot is one among many AI crawler bots operating on the web. Different companies deploy various bots for data collection purposes. These bots vary in their characteristics, respect for website preferences, and transparency about their operations.
| Bot Name | Operator | Robots.txt Compliance | Public Documentation | Blocking Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kangaroo Bot | Unknown/Limited Info | Unknown | Minimal | robots.txt, user-agent |
| GPTBot | OpenAI | Yes | Detailed | robots.txt, user-agent |
| Google-Extended | Yes | Detailed | robots.txt, user-agent | |
| CCBot | Common Crawl | Yes | Extensive | robots.txt, user-agent |
| ClaudeBot | Anthropic | Yes | Detailed | robots.txt, user-agent |
| Bytespider | ByteDance | Partial | Limited | robots.txt, user-agent, IP blocking |
GPTBot is OpenAI’s crawler used for training ChatGPT and other models, providing clear documentation about the bot’s purpose and blocking instructions. Google-Extended is Google’s AI training data crawler, distinct from Googlebot for search indexing. Google provides extensive transparency and instructions for opting out without affecting search visibility. CCBot from Common Crawl is highly transparent, offering extensive documentation on its crawling practices. ClaudeBot, used by Anthropic, maintains transparency and respects website preferences through robots.txt. Bytespider from ByteDance offers less complete documentation, with reports of partial compliance with robots.txt directives.
Technical Identification Methods
Identifying Kangaroo Bot in server logs involves examining user-agent strings and request patterns. The user-agent field in HTTP requests usually contains the bot’s name and version information. Search your access logs for entries with “Kangaroo” in the user-agent field to determine if and when the bot visited your site.
Request patterns can also reveal bot activity. Crawlers typically make rapid sequential requests, accessing multiple pages in short timeframes, following systematic patterns. In contrast, human visitors exhibit more random browsing behavior with longer delays between requests. Analyzing these patterns helps distinguish bot traffic from human visitors.
IP address tracking provides another identification method. Bots often operate from specific IP ranges or data centers. Recording IP addresses associated with Kangaroo Bot requests helps in building blocking rules. However, sophisticated crawlers might rotate IP addresses or use distributed networks, making IP-based identification less reliable.
Behavior analysis tools can automatically detect bot activity. Many web analytics and security tools include bot detection features, analyzing request patterns, user-agent strings, IP addresses, and other signals to identify automated crawlers. Some tools specifically flag AI training bots and provide options for blocking them.
Data Collection Ethics and Website Rights
The practice of automated web scraping for AI training raises significant questions about data rights and ethics. Website owners create content for specific purposes, and using that content for AI training without explicit permission raises concerns for many creators and publishers. Publicly accessible content is often considered fair game for collection. However, some believe scraping violates creator rights regardless of public accessibility.
Legal frameworks surrounding web scraping remain unclear in many jurisdictions. Copyright law, terms of service, and computer access laws are potential areas of concern. Courts in different countries have issued conflicting rulings on scraping legality, creating uncertainty for both AI companies and website owners.
Respecting robots.txt is basic etiquette for web crawlers, a standard governing crawler behavior for decades. Bots that ignore these directives face criticism for disrespecting website owner preferences. Major AI companies generally claim to adhere to these standards, though enforcement and verification remain challenging.
Website owners should clearly state their data usage preferences. Beyond robots.txt, consider adding terms of service that explicitly address AI training and automated scraping. Some sites now include specific language prohibiting the use of their content for AI training purposes. While legal enforceability varies, clear statements establish intent and expectations.
Impact on Website Performance
AI crawler bots can significantly impact website performance and infrastructure costs. Aggressive crawling generates high request volumes, consuming server resources, bandwidth, and processing power. Websites with limited hosting resources may experience slowdowns or service disruptions due to excessive bot traffic.
Bot Access Control Methods:
 Bandwidth costs escalate when bots download large amounts of content. For sites paying for data transfer, crawler activity directly impacts operating expenses. A single aggressive crawler can download gigabytes of content in short periods. Multiplied across multiple AI bots, costs quickly add up.
Bandwidth costs escalate when bots download large amounts of content. For sites paying for data transfer, crawler activity directly impacts operating expenses. A single aggressive crawler can download gigabytes of content in short periods. Multiplied across multiple AI bots, costs quickly add up.
Server load from bot requests affects legitimate user experience. When crawlers consume significant CPU and memory resources, response times for human visitors may increase. In extreme cases, heavy crawler activity can cause server crashes or trigger rate limiting affecting all visitors.
Monitoring tools help track crawler impact on site performance. Web analytics platforms display bot traffic separately from human visits. Server monitoring tools reveal resource usage spikes correlated with crawler activity. Content delivery networks and caching systems can help mitigate crawler impact by serving cached content instead of hitting origin servers for every request.
Future of AI Web Crawlers
The AI crawler scene continues to evolve as more companies develop language models and AI systems. Expect more crawlers to emerge as AI development accelerates, complicating bot traffic management for website administrators.
Industry standards for AI crawling may develop as awareness grows. Organizations and standards bodies are discussing best practices for AI data collection, including clearer identification requirements, standardized opt-out mechanisms, and transparency about data usage. However, adoption remains voluntary without regulatory enforcement.
Regulatory attention on AI training data is increasing. Governments are considering or implementing laws addressing AI data collection and usage. European regulations around data protection and copyright may impact crawler operations. Future regulations could impose stricter requirements on how AI companies collect and use web data.
Technical solutions for data protection are advancing. New methods for preventing content scraping while maintaining accessibility for legitimate users are under development. Techniques like selective content rendering, authentication requirements, and anti-bot systems are becoming more sophisticated. The arms race between scrapers and protections is likely to continue.
Conclusion
Kangaroo Bot is one of many AI crawlers collecting web data for machine learning purposes. Understanding these bots helps website owners make informed decisions about data access and usage. While public information about Kangaroo Bot specifically remains limited, general principles for managing AI crawlers apply.
Website administrators can control crawler access through robots.txt directives, server-level blocking, and monitoring tools. Comparing different AI crawlers reveals varying levels of transparency and respect for website preferences. Major company crawlers like GPTBot and Google-Extended offer clear documentation and opt-out methods, while less documented crawlers like Kangaroo Bot require more effort to identify and manage.
The broader context of AI data collection involves ongoing debates about ethics, legality, and website rights. As AI development continues, managing crawler access becomes increasingly important for website owners who want control over how their content is used. Staying informed about crawler activity and implementing appropriate access controls helps protect your content and server resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
What kind of data does Kangaroo Bot collect?
Kangaroo Bot primarily collects publicly available text content, images, and other information from websites. This includes data from blogs, forums, news sites, and documentation that are essential for building datasets used in training AI models.
How can website owners manage Kangaroo Bot's access to their sites?
Website owners can manage Kangaroo Bot's access using a robots.txt file to instruct the bot which pages to avoid. For more effective control, server-level blocking can also be implemented by configuring the web server to reject requests from specific user agents or IP addresses associated with the bot.
What should I do if Kangaroo Bot continues to crawl my site despite blocking it?
If Kangaroo Bot ignores the robots.txt directives, it may be necessary to implement server-level blocking based on its user-agent string or known IP addresses. Monitoring server logs can help track its activity, and adjusting server settings can prevent unauthorized access more effectively.
What are the ethical implications of using Kangaroo Bot for data collection?
The use of Kangaroo Bot and similar crawlers raises concerns about data rights and ethical practices. Although publicly available content can be collected, many believe it is unethical to use such content for AI training without explicit permission from the creators and publishers.
Is there a way to identify if Kangaroo Bot has visited my website?
Yes, you can identify Kangaroo Bot's activity by examining your server logs for entries containing the user-agent string with 'Kangaroo'. Additionally, patterns of rapid sequential requests can be indicative of bot activity as opposed to typical human browsing behavior.
How does Kangaroo Bot differ from other well-known crawlers?
Kangaroo Bot operates with less transparency than established crawlers like Googlebot or GPTBot, which provide extensive documentation and compliance standards. This lack of clarity can make it difficult for website owners to understand its crawling behavior and data usage policies.
What future changes can we expect in AI crawling practices?
The AI crawling landscape is expected to evolve with emerging standards and regulations governing data collection. As discussions around ethical AI practices gain momentum, new technical solutions and legal frameworks may influence how crawlers like Kangaroo Bot operate and how website owners can manage their access.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.