Understanding Naverbot: The Korean Search Engine Crawler
Learn about Naverbot, the Yeti crawler powering South Korea's top search engine Naver, its role in indexing and AI training with HyperCLOVA.
Introduction
Naverbot is the web crawler operated by Naver, South Korea’s dominant search engine. Known by the name Yeti, this Naver crawler scans websites across the internet to index content for Naver’s search results. Web crawlers like Naverbot are critical tools that search engines, including the Korean search engine Naver, use to find and catalog web pages. Without these bots, search engines couldn’t provide up-to-date results to users. Naverbot serves two main purposes: indexing web content for search results and collecting data for AI training data, such as feeding into Naver’s HyperCLOVA, a large language model. For website owners and developers, understanding how Naverbot works is important for ensuring your content appears in Naver search results. This is particularly vital if you target Korean-speaking audiences, as Naver holds about 70% market share in search indexing in South Korea, a unique situation compared to many countries where Google leads.
What is Naverbot
Naverbot is a web crawler software that automatically visits websites and reads their content. Technically known as Yeti, when it visits your website, it analyzes the HTML, text, images, and other elements on your pages. The bot follows links from one page to another, building a map of your site’s structure and content. This information is sent to Naver’s servers, where it’s processed and added to their search index.
Naverbot Crawling Process:
The Naver bot identifies itself in server logs with a user agent string that includes “Yeti” or “Naverbot.” Website administrators can see these visits in their analytics and server logs. The bot respects the robots.txt file, a standard way for websites to instruct crawlers on which pages they should or shouldn’t access.
Naverbot operates continuously, revisiting websites to check for new content or updates, similar to other major web crawlers like Googlebot and Bingbot. Popular sites with frequently updated content get crawled more often, while smaller or less active sites might see the bot less frequently. The crawling frequency depends on factors like site authority, update frequency, and server response times.
Why Naverbot Exists and Its Purpose
Search engines need crawlers because there’s no central directory of all web pages. Naverbot exists to solve this discovery problem for Naver. Its primary job is finding and indexing Korean language content relevant to Korean users, enabling Naver to provide comprehensive search results.
Naver dominates the search market in South Korea, capturing more than half of all search traffic, a unique situation compared to many countries where Google leads. Naver’s success is partly due to its deep understanding of Korean language details and local content, an advantage maintained by continuously updating its index with fresh content via Naverbot.
Naverbot Dual Purpose:
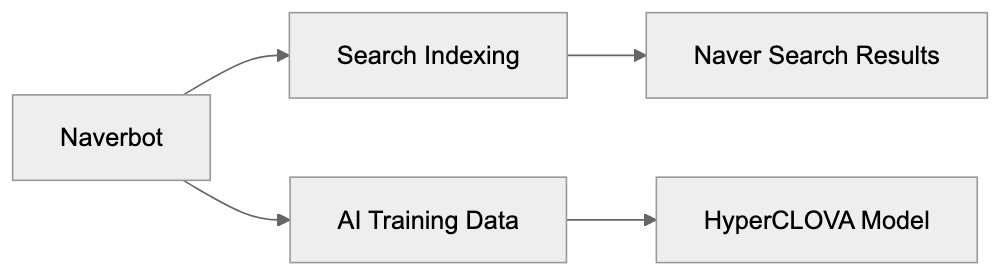
Beyond search indexing, Naverbot serves another essential function by collecting data for AI model training. Naver has heavily invested in artificial intelligence, especially with HyperCLOVA, a large language model specially crafted for understanding the Korean language. The text data gathered by Naverbot across the web provides crucial training material for these AI systems.
Naverbot helps Naver stay competitive in both search and AI development. As AI increasingly influences search rankings and features, having access to extensive Korean text data becomes invaluable. Naverbot is essential for providing this resource, as it helps Naver stay competitive in both search and AI development.
How Naver and Users Utilize Naverbot
Naver uses the data collected by Naverbot in several ways, the most obvious being populating their search index. When someone searches on Naver, the results come from pages previously crawled and indexed by Naverbot, directly impacting what users find through Naver search.
The company also uses crawler data to train and improve HyperCLOVA. This AI model launched in 2022, containing 204 billion parameters, is trained primarily on Korean text to better understand Korean language context, culture, and nuance than models trained mainly on English. Naverbot’s web crawling provides a significant portion of the training data for this system.
Website owners interact with Naverbot by optimizing their sites for crawling. This includes creating clear site structures, using proper HTML markup, and submitting sitemaps through Naver Webmaster Tools. The platform lets site owners see how Naverbot views their site, check for crawling errors, and request re-indexing of updated pages.
Developers working on Korean-focused websites must ensure Naverbot can access and understand their content. This involves avoiding crawling barriers like aggressive bot blocking, excessive JavaScript rendering requirements, or broken robots.txt configurations. Sites seeking visibility in Korea’s largest search engine must make themselves accessible to this crawler.
Content creators targeting Korean audiences benefit from understanding what Naverbot prioritizes. Fresh content, proper Korean language encoding, and mobile-friendly designs all aid in crawler accessibility and indexing.
Key Facts About Naverbot
Naverbot typically uses the user agent string “Yeti” in most cases. Website logs will show visits from “Yeti/1.0” or similar identifiers, with some versions potentially including “Naverbot” directly in the user agent string.
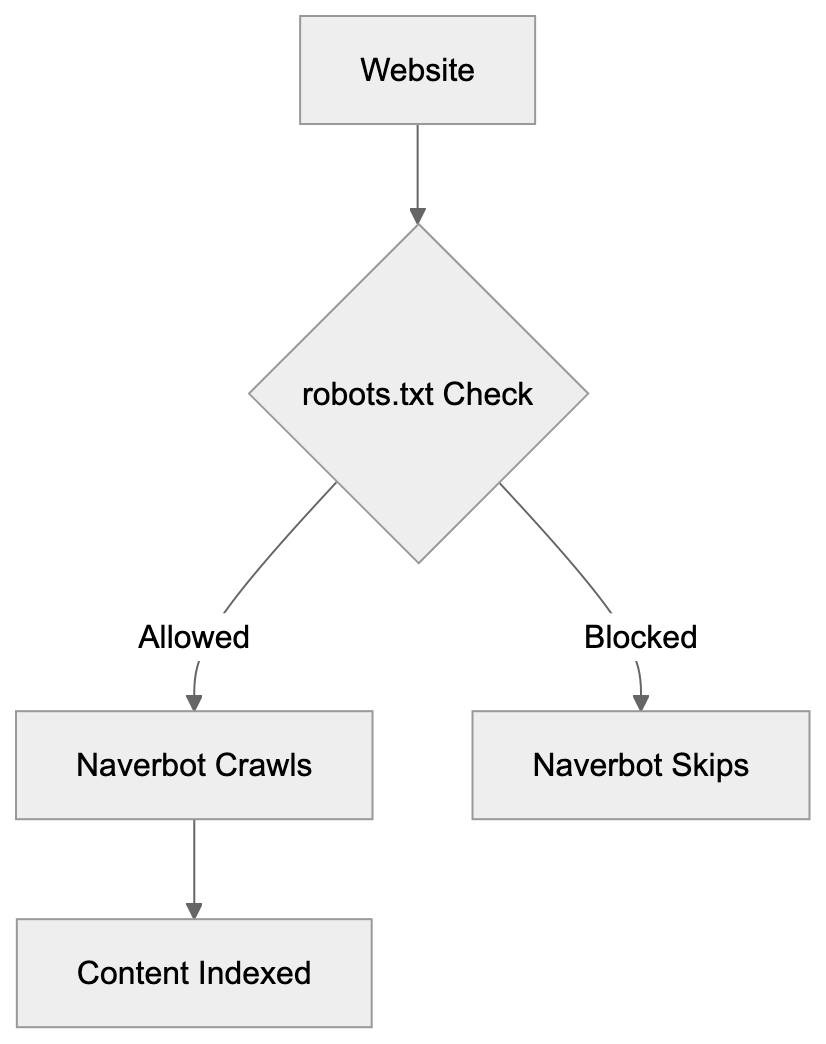
The crawler respects standard web protocols, following robots.txt directives and observing crawl delay settings. Website owners can control Naverbot’s access through these standard mechanisms without needing special Naver-specific configurations.
Naver operates primarily in South Korea, but the crawler visits websites globally. Any publicly accessible website might receive visits from Naverbot, especially if it contains Korean language content or links from Korean websites.
The crawling rate varies based on site characteristics. High authority sites with frequent updates see more regular crawling. New or smaller sites might wait longer between crawler visits. Server response time also affects crawling frequency since slow sites get crawled less aggressively.
Naverbot collects data that may be used for AI training purposes. Like many search engines, Naver uses crawled web content as training data for their machine learning systems, including HyperCLOVA. Website owners should be aware of the potential use of publicly accessible content for this purpose.
Comparing Naverbot to Alternative Crawlers
Different search engines and services operate their own web crawlers. Here’s how Naverbot compares to other major crawlers:
| Crawler | Company | Primary Market | AI Training Use | Market Share |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naverbot (Yeti) | Naver | South Korea | HyperCLOVA | 50%+ in South Korea |
| Googlebot | Global | Gemini, other models | 90%+ globally | |
| Bingbot | Microsoft | Global | Models via OpenAI partnership | 3% globally |
| Yandex Bot | Yandex | Russia, CIS | YandexGPT | 60%+ in Russia |
| Baiduspider | Baidu | China | ERNIE | 70%+ in China |
Managing Naverbot with robots.txt:
Naverbot differs from Googlebot primarily in its focus on Korean content and the South Korean market. While Googlebot crawls globally, Naverbot prioritizes Korean-language sites and content relevant to Korean users. This specialization helps Naver maintain its dominant position in South Korea despite Google’s global reach.
Compared to Bingbot, Naverbot serves a more geographically concentrated user base. Bing operates globally but with a smaller market share. Naver focuses on South Korea, where it dominates. Both companies use crawler data for AI training, yet Naver’s HyperCLOVA specifically targets Korean language understanding.
Yandex Bot serves a similar role for Russian language content as Naverbot does for Korean. Both crawlers support regionally dominant search engines that successfully compete against Google in their home markets. Their technical approaches are similar, but the language focus differs.
Baiduspider operates in the Chinese market with similar functions. It crawls primarily for search indexing and AI training with Chinese language content. Like Naverbot, it serves a non-English speaking market where a local search engine maintains a strong position against international competitors.
The key difference across all these crawlers is their training data usage. Most modern search engine crawlers now collect data that feeds AI development. Naverbot’s contribution to HyperCLOVA epitomizes this trend. Website owners should understand that crawler visits may mean their content becomes part of AI training datasets.
Managing Naverbot Access
Website administrators can control how Naverbot interacts with their sites. The robots.txt file provides the primary control mechanism. Adding specific directives for Yeti or Naverbot allows blocking or limiting crawler access to certain directories or pages.
To block Naverbot completely, add these lines to your robots.txt file:
User-agent: Yeti
Disallow: /This tells the crawler not to access any pages on your site. Most site owners don’t want complete blocking since it removes their content from Naver search results. Selective blocking of specific directories is more practical for most situations.
Crawl rate limiting can be set through robots.txt using the Crawl-delay directive. This tells the bot to wait a specified number of seconds between requests, helping if the bot’s visits create excessive server load.
Naver Webmaster Tools provides additional control options. Site owners can request crawling of specific pages, check indexing status, and see how Naverbot views their site. The platform shows crawl errors and provides tools for submitting sitemaps.
For sites that don’t want their content used in AI training, options are limited. Web crawling for AI training purposes is common practice among major tech companies. Blocking the crawler entirely removes your site from search results. Some site owners accept crawler visits for search indexing while expressing concerns about AI training use.
The meta robots tag offers page-level control. Adding noindex or nofollow directives to specific pages guides crawler behavior without needing robots.txt changes. This provides more granular control for sites with mixed content policies.
Technical Specifications and Behavior
Naverbot typically identifies itself with user agent strings containing “Yeti” followed by version information. The exact string varies but commonly appears as “Yeti/1.0” or includes additional details about the crawling system.
The crawler makes HTTP or HTTPS requests to websites just like a regular browser. It processes HTML content, follows links, and downloads resources needed to understand page content. The bot can handle JavaScript to some extent but performs best with server-side rendered HTML.
Crawling happens from IP addresses owned by Naver’s infrastructure. Website administrators can verify legitimate Naverbot visits by checking if the IP address reverse DNS resolves to Naver’s domain. This helps distinguish real Naverbot from spoofed user agents.
The bot respects standard HTTP status codes. A 404 error tells it the page doesn’t exist, while a 301 redirect indicates permanent URL changes. Proper use of status codes helps the crawler maintain an accurate index.
Naverbot handles cookies and can process some dynamic content, but static HTML with clear structure provides the most reliable crawling results. Sites heavily dependent on client-side rendering may face indexing challenges.
The crawler follows link depth through sites but prioritizes important pages. Homepage and high-level navigation pages typically get crawled more frequently than deep-linked content. Proper internal linking helps ensure that all important pages get discovered and indexed.
Naverbot and SEO Considerations
Optimizing for Naverbot is crucial if your target audience includes Korean users. Naver’s dominant market position in South Korea means Naverbot visibility directly impacts Korean language traffic potential.
Page speed affects crawling effectiveness. Faster loading pages allow the bot to crawl more content in the same period, leading to more complete indexing and fresher search results. Improving server response times and page load speeds helps.
Mobile improvement is increasingly important. Like other search engines, Naver prioritizes mobile-friendly content. Sites that work well on mobile devices tend to perform better in search results, with Naverbot evaluating mobile compatibility as part of its crawling process.
Structured data markup helps the crawler understand content context. Using schema.org markup or Naver-specific structured data formats provides additional signals about page content and purpose, improving how your content appears in search results.
Korean language encoding must be correct. Content should use UTF-8 encoding to ensure Korean characters display properly. Encoding errors can prevent the crawler from correctly reading and indexing Korean text.
Regular content updates encourage more frequent crawling. Sites that consistently publish new content tend to get crawled more often than static sites. This means fresher indexing and quicker appearance in search results for new pages.
Quality signals matter for Naver, just like other search engines. Original content, proper grammar, and useful information help pages rank better. While Naverbot’s job is crawling and indexing, content quality affects how Naver’s algorithm treats those indexed pages.
End
Naverbot serves as the web crawler for South Korea’s leading search engine. It indexes content for Naver search results and collects training data for AI systems like HyperCLOVA. Understanding how this Naver bot works is important for anyone targeting Korean audiences or concerned about how their web content is used. The bot operates similarly to other major search engine crawlers but focuses specifically on Korean language content and the South Korean market. Website owners can manage Naverbot access through standard tools like robots.txt and Naver Webmaster Tools. As AI development continues, crawlers like Naverbot play dual roles in both search indexing and machine learning training. For developers and content creators working with Korean language sites, ensuring Naverbot can properly access and understand your content remains critical for visibility in South Korea’s dominant search engine.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I check if Naverbot has visited my site?
You can verify Naverbot visits by examining your server logs for entries that include the user agent string "Yeti". Additionally, using web analytics tools can help track the frequency and behavior of Naverbot on your site.
What should I include in my robots.txt file to manage Naverbot?
To manage Naverbot access, you can add specific lines to your robots.txt file. For instance, using "User-agent: Yeti" followed by "Disallow: /" entirely blocks Naverbot, while selective disallow commands can restrict access to specific pages or directories.
Does Naverbot respect my site's robots.txt file?
Yes, Naverbot adheres to the instructions provided in your robots.txt file. It uses this file to determine which pages it is allowed or disallowed to crawl, so correctly configuring it is important for managing Naverbot's behavior.
How often does Naverbot crawl my website?
The frequency with which Naverbot crawls your site depends on several factors, including your site's authority, the frequency of content updates, and overall server performance. Popular sites with frequent updates are crawled more regularly than smaller or less active ones.
What can I do to improve my site's visibility in Naver's search results?
To enhance visibility in Naver's search results, ensure your site is mobile-friendly, optimized for speed, and has clear structured data markup. Regularly updating your content and using correct Korean language encoding also play significant roles in boosting your indexing.
Can I prevent my content from being used for AI training purposes?
While blocking Naverbot from accessing your site entirely can prevent your content from being used for AI training, this action also removes your site from Naver's search results. Unfortunately, there are limited options for preventing content use specifically for AI training without impacting search indexing.
How does Naverbot differ from other web crawlers?
Naverbot primarily focuses on indexing Korean language content for South Korean users, while crawlers like Googlebot operate on a global scale. This specialization allows Naver to maintain its dominant position in the Korean search market, distinctly tailoring its algorithms and services to local content needs.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.