Understanding OAI-SearchBot: OpenAI's Search Indexing Crawler
Explore OAI-SearchBot's role in indexing for ChatGPT Search, its differences from GPTBot, and how to manage its impact on your site.
What is OAI-SearchBot and Why Does It Matter
OAI-SearchBot is OpenAI’s web crawler designed specifically for ChatGPT Search. This OpenAI search bot crawls and indexes web content to enhance the search functionality in ChatGPT. Understanding the role and function of this bot is crucial for website owners and developers, as it impacts how content appears in ChatGPT Search results. Similar to traditional search engine crawlers like Googlebot but serving a different purpose, it collects web pages, analyzes content, and builds an index for ChatGPT’s search feature. Read more about OpenAI’s crawlers. This allows ChatGPT to deliver real-time search results and answer queries with current information from the web. For web developers and SEO professionals, managing this crawler has become as important as managing Google’s crawlers. The OAI-SearchBot respects standard web protocols and can be managed through robots.txt files. Understanding this bot helps you decide whether you want your content included in ChatGPT Search results.
How OAI-SearchBot Works and Its Technical Details
OAI-SearchBot identifies itself through a specific user agent string when visiting websites. The user agent is “OAI-SearchBot,” and it sends requests to web servers like any other crawler. The bot follows links, downloads HTML content, and processes the information for indexing. It respects the standard robots.txt protocol, meaning website owners can manage access. The web crawler operates at a reasonable rate to avoid overloading servers. While it primarily focuses on static HTML content, it doesn’t typically execute JavaScript by default. Targeting publicly accessible web pages, it doesn’t attempt to access password-protected areas. When it crawls a page, it collects text content, metadata, and the structure of links. This data is processed and added to the search index that ChatGPT Search uses. Running continuously ensures the index stays fresh with updated content. Website logs will show visits from this user agent, allowing site administrators to monitor its activity effectively. The bot follows standard HTTP protocols and respects cache control headers when given.
OAI-SearchBot vs GPTBot: Key Differences Explained
OAI-SearchBot Crawling Process:
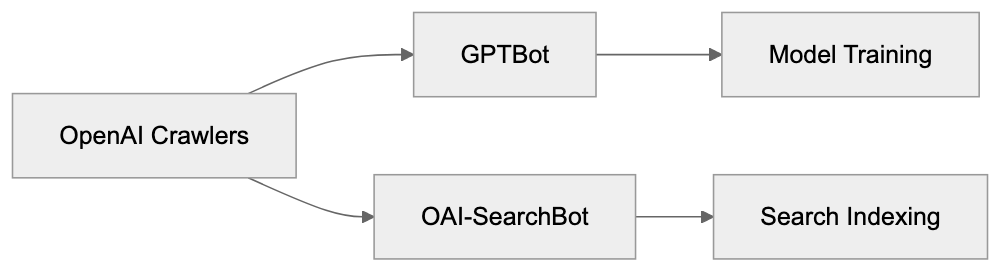
OpenAI manages two different crawlers serving completely different purposes. GPTBot is designed for collecting training data to enhance OpenAI’s language models, while OAI-SearchBot is built specifically for indexing content for ChatGPT Search functionality. The user agent strings differ: GPTBot uses “GPTBot,” while the search crawler uses “OAI-SearchBot.” Blocking one doesn’t automatically block the other, requiring separate robots.txt rules for each if independent control is desired. GPTBot crawls content that might be used to train future AI models, whereas OAI-SearchBot indexes content for real-time search results within ChatGPT. Many websites choose to block GPTBot to prevent content use in AI training, but blocking OAI-SearchBot means exclusion from ChatGPT Search results. The crawling frequency and patterns also differ; GPTBot does broader crawls for data collection, while OAI-SearchBot focuses on indexing for search retrieval. Understanding this distinction is crucial for making informed decisions about your robots.txt configuration.
Managing OAI-SearchBot Access to Your Website
Controlling OAI-SearchBot access happens through your robots.txt file. To block the crawler completely, add these lines to your robots.txt:
User-agent: OAI-SearchBot
Disallow: /OpenAI Crawler Comparison:
This command instructs the bot not to crawl any part of your site. To allow most content but block specific sections, you can specify particular paths. For example, to block just your admin area:
User-agent: OAI-SearchBot
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /private/Robots.txt Access Control:
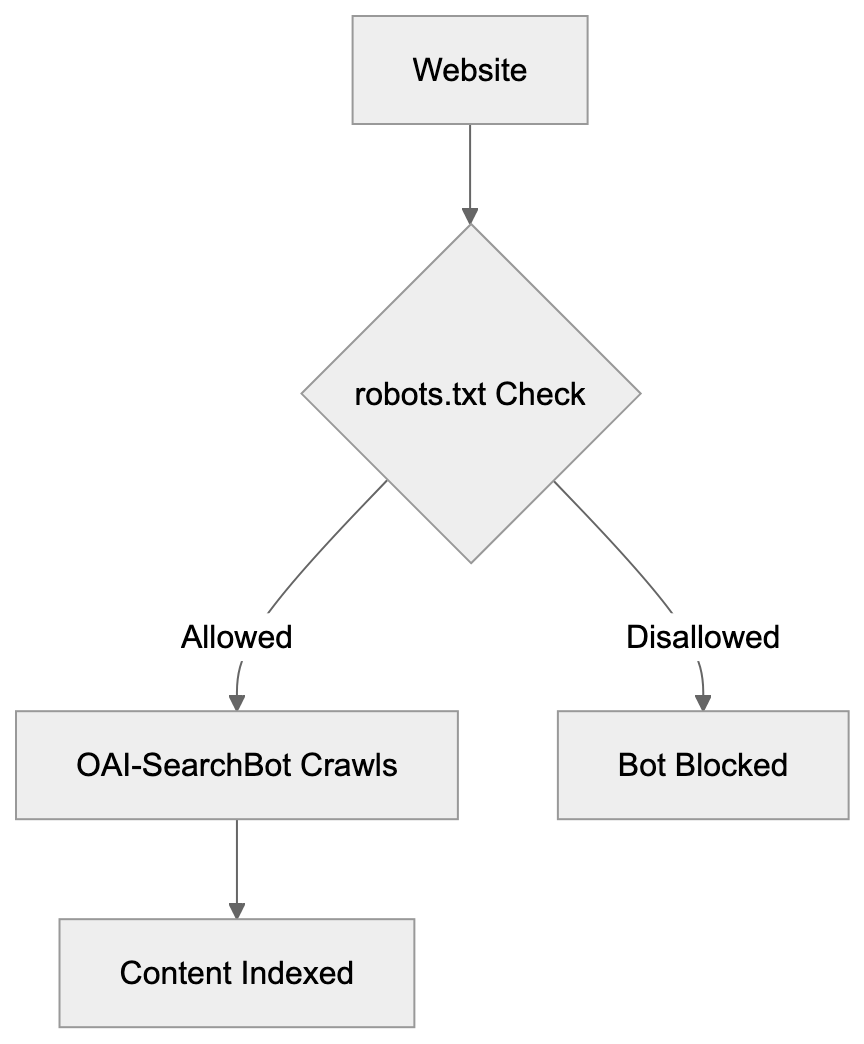
To allow the crawler everywhere, no additional configuration is necessary; the bot will default to crawling unless explicitly blocked. Some websites choose to block GPTBot but allow OAI-SearchBot to maintain visibility in ChatGPT Search. Others block both to maintain strict control over their content usage, a decision influenced by content strategy and business goals. After updating robots.txt, changes take effect during the bot’s next crawl—there’s no immediate removal process akin to Google Search Console. Monitoring server logs verifies that the bot respects these directives. Most web hosting control panels provide easy access for creating or editing robots.txt files. Remember, robots.txt is a directive and not a security measure; determined crawlers might ignore it.
Comparison of AI Web Crawlers
| Crawler Name | Company | Primary Purpose | User Agent | Training Data Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OAI-SearchBot | OpenAI | ChatGPT Search indexing | OAI-SearchBot | No |
| GPTBot | OpenAI | AI model training | GPTBot | Yes |
| GoogleBot | Search indexing | Googlebot | Limited | |
| Bingbot | Microsoft | Search indexing | Bingbot | Limited |
| CCBot | Common Crawl | Web archiving & datasets | CCBot | Yes |
Each crawler has distinct functions and organizational goals. GoogleBot and Bingbot focus on traditional search engine indexing and have been staples for years; most websites permit them by default. CCBot crawls the web to create datasets widely used for AI company training. GPTBot is specifically collecting data to enrich OpenAI’s models. OAI-SearchBot is the newest addition, focused solely on powering ChatGPT’s search function. The implications of blocking vary significantly. Blocking GoogleBot results in losing Google Search visibility, while blocking OAI-SearchBot results in absence from ChatGPT Search results. Many sites now block CCBot and GPTBot to prevent AI training but keep traditional search bots allowed.
Why OpenAI Created OAI-SearchBot
ChatGPT Search required its own dedicated crawler for several reasons. The feature aims to offer real-time information within ChatGPT conversations, allowing users to search the web directly through ChatGPT without switching to traditional search engines. This need necessitated a fresh, continuously updated index of web content. GPTBot was unsuitable for this purpose as it is designed for training data collection, not search indexing, which mandates different crawling patterns and update frequencies. The bot needs regular visits to pages to capture content changes and new publications. OpenAI’s intent was to allow website owners control over search indexing separate from training data. By maintaining distinct user agents, webmasters can make granular decisions. A site might want ChatGPT Search visibility but not wish for content used in model training. This separation allows OpenAI to optimize each crawler for its role, aligning search indexing with freshness and relevance while training focuses on diversity and quality. This architectural decision adheres to industry standards where various functions employ different crawlers.
Impact on Website Owners and Content Strategy
The emergence of OAI-SearchBot introduces new considerations for content strategy. Website owners must decide if they want a presence in ChatGPT Search results. For news sites and publishers, being indexed can drive new traffic sources, while private databases or paid content sites might prefer blocking. Although the bot’s crawling activity adds to server load, it is usually insignificant. High-traffic sites should still monitor server resources as the bot begins to crawl. SEO professionals must include OAI-SearchBot management in their technical SEO checklists. The robots.txt file becomes more complex as more AI crawlers appear, but some content management systems now include built-in options for managing AI crawler access. WordPress plugins specifically for controlling GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot are available. Web developers should implement logging to track which AI bots visit their sites, helping inform decisions about allowing or blocking specific crawlers. The rise of AI search changes how people find content online; traditional SEO focused on Google and Bing, now ChatGPT Search adds another channel. Content for AI-powered search might need different improvement strategies than traditional SEO. Clear, well-structured information tends to perform well for AI search indexing.
Privacy and Data Considerations
OAI-SearchBot only indexes publicly accessible web pages, maintaining adherence to robots.txt directives and standard web protocols. Once indexed, your content can appear in ChatGPT Search results, with users possibly seeing excerpts or summaries of your content, akin to Google’s snippet presentations in search results. The vital difference lies in how information is presented within an AI conversation. OpenAI does not publicly specify how long indexed content remains in their search database. The crawler processes only the public content of web pages without collecting personal user data. Sites containing sensitive yet public information, such as medical practices, law firms, and financial services, should carefully evaluate their approach. Some organizations block all AI crawlers as precautionary measures, while others welcome the visibility and potential traffic from AI-powered search. There’s no universal right answer; it depends on each unique situation and content type. Regular audits of your robots.txt and crawler access policies are becoming standard practice.
How to Monitor OAI-SearchBot Activity
Tracking OAI-SearchBot visits involves examining web server logs. Most hosting providers provide access to raw server logs or processed analytics. Monitor entries containing “OAI-SearchBot” in the user agent field, indicating when the bot visited, which pages it accessed, and how much data was transferred. Tools for server log analysis can filter and aggregate this data automatically. Free tools like GoAccess or paid solutions like Loggly can parse bot activity. Many website analytics platforms now include bot detection and reporting features. Although Google Analytics filters out most bot traffic by default, you can configure it to track specific bots. Monitoring ensures that your robots.txt rules function correctly. If you notice visits despite a block, there might be an issue with configuration. Unusual crawl patterns or excessive request rates should be investigated, as legitimate crawlers operate at reasonable speeds to avoid overloading servers. Should OAI-SearchBot crawl too aggressively, you can implement server-level rate limiting. Tools like Fail2ban can temporarily block IPs that make excessive requests, but aggressive blocking could prevent legitimate indexing. Aim to strike a balance between server protection and allowing beneficial crawler access.
Future of AI Search Crawlers
The landscape of web crawlers is evolving rapidly alongside AI advancement. More companies will likely launch their own AI search features, each potentially accompanied by a dedicated crawler. Companies like Anthropic or Google could introduce similar bots. Website owners will need sophisticated crawler management strategies. The robots.txt standard might need updates to handle increasing complexity, with industry discussions surrounding more granular control mechanisms. Some proposals suggest allowing sites to specify different rules for various AI use cases. The evolving relationship between content creators and AI companies poses unresolved legal questions about crawling and content use. Some publishers are negotiating direct licensing deals with AI companies, while others prefer blocking AI crawlers entirely to maintain strict content control. Technically, this field will likely advance with improved crawler identification and verification methods. Better tools for managing multiple AI crawlers across large websites are being developed. Content delivery networks and hosting providers are starting to add AI crawler management features. The next few years will shape the coexistence of web content and AI search, urging website owners to stay informed and update policies accordingly.
Conclusion
OAI-SearchBot represents OpenAI’s dedicated crawler for ChatGPT Search indexing. It operates distinctly from GPTBot, which handles training data collection. This distinction matters because blocking one doesn’t affect the other. Website owners control access through robots.txt files using specific user agent directives. The bot respects standard web protocols and crawls publicly accessible content. Understanding this crawler helps you make informed decisions about your content’s presence in ChatGPT Search. Monitor your server logs to track bot activity and verify that your access rules function correctly. The emergence of AI-powered search presents new opportunities and challenges for content visibility. As the AI landscape evolves, staying informed about new crawlers and managing them appropriately becomes increasingly important for web developers and SEO professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I check if OAI-SearchBot has visited my site?
You can check server logs to see visits from OAI-SearchBot. Look for entries containing "OAI-SearchBot" in the user agent field to identify when the bot visited and which pages it accessed.
What happens if I block OAI-SearchBot?
If you block OAI-SearchBot using your robots.txt file, your content will not appear in ChatGPT Search results. This could limit your site's visibility on a platform that may bring in new traffic depending on your content type.
Can I allow OAI-SearchBot to crawl some parts of my site while blocking others?
Yes, you can control OAI-SearchBot's access by specifying which parts of your website to allow or block in your robots.txt file. For example, you can block sensitive areas while permitting access to your public content.
Is OAI-SearchBot different from other crawlers like Googlebot?
Yes, OAI-SearchBot is specifically designed for indexing content for ChatGPT Search, while crawlers like Googlebot focus on traditional search indexing. Each crawler has unique purposes and behaviors, so managing them can differ significantly.
How frequently does OAI-SearchBot crawl websites?
OAI-SearchBot crawls websites at a reasonable rate to avoid server overload, though the exact frequency may vary based on the site's content updates. It's important to monitor your server resources, especially for high-traffic sites.
What should I include in my robots.txt for OAI-SearchBot?
To manage OAI-SearchBot, specify directives in your robots.txt file. For example, use "User-agent: OAI-SearchBot" and either "Disallow: /" to block all access or specify certain paths to allow selective crawling.
How does blocking OAI-SearchBot affect my site's SEO strategy?
Blocking OAI-SearchBot can prevent your content from appearing in AI-specific searches, potentially limiting your reach. You should factor in your overall content visibility strategy and decide based on how important AI traffic is for your site.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.