OpenAI-GPT-User Agent: Blocking & Detection Methods
Learn about OpenAI-GPT-User agent strings, blocking strategies, IP verification methods and alternative approaches for managing AI bot access.
Introduction
The OpenAI-GPT-User agent string is essential for identifying ChatGPT browsing activity on websites. This string, visible in server logs when OpenAI systems access web content, differentiates AI bot traffic from regular visitors. Website owners and developers should understand this identifier to control AI interactions with their content efficiently. Some aim to block OpenAI bots entirely, while others offer selective access, depending on their needs. Recognizing the technical details helps make informed decisions regarding AI bot management. The ChatGPT user agent string works like other bot identifiers, but marks OpenAI’s automated requests specifically.
What is OpenAI-GPT-User Agent
The OpenAI-GPT-User is a user agent string sent in HTTP headers during OpenAI web requests, specifically used for certain user actions in ChatGPT and Custom GPTs. It acts as a digital signature, identifying traffic sources. When ChatGPT browses a website or fetches content, this identifier accompanies the request. In server logs, it typically appears as “Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko; compatible; ChatGPT-User/1.0; +https://openai.com/bot)”. This differs from GPTBot, OpenAI’s web crawler for training data collection, as OpenAI-GPT-User relates to real-time browsing in ChatGPT. The distinction is critical since their purposes diverge: one for training datasets, the other for conversations. These can be managed separately through different strategies.
How OpenAI User Agent Works:
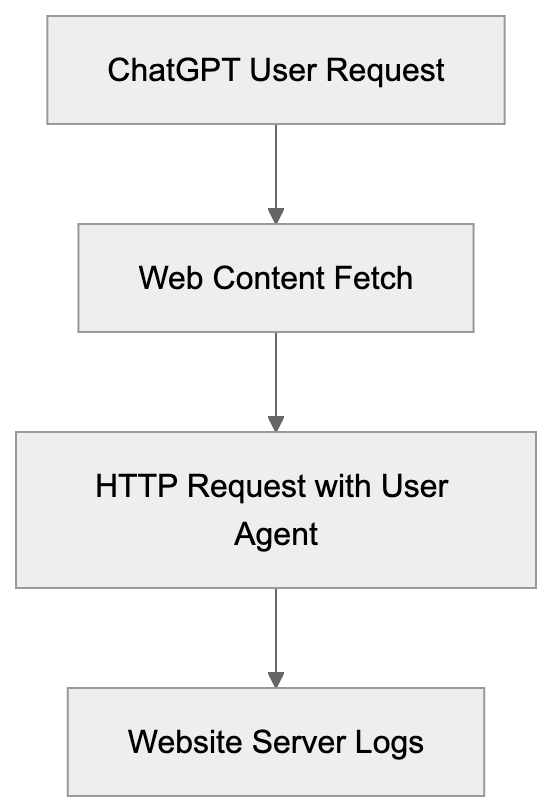
Why OpenAI User Agent Exists
OpenAI developed this user agent to ensure transparency when their systems access websites. It informs website owners of automated visits, serving multiple purposes. It enables AI-generated traffic tracking, allows access control via web protocols, and distinguishes legitimate requests from impersonators. As ChatGPT’s browsing capabilities grew, identification became essential to differentiate AI requests from normal traffic, easing access management. The GPT agent string satisfies compliance and legal standards in some jurisdictions requiring clear automated access identification.
How Companies and Developers Use This Information
Developers and website administrators actively monitor the OpenAI-GPT-User in their server logs. The insights help them understand AI interactions with their content. Some businesses welcome this traffic for visibility through ChatGPT, while others block it to protect exclusive content or save bandwidth. E-commerce sites might allow access to product information but restrict pricing data. Server configurations can filter requests based on user agent strings, with tools like web application firewalls (WAFs) and content delivery networks (CDNs) enhancing control. Analytics teams track AI user agent data separately, revealing content popularity in AI responses.
User Agent Identification Process:

Blocking Strategies for OpenAI-GPT-User
Blocking OpenAI-GPT-User involves technical setup at the server or application level, commonly through web server rules rejecting matching requests. Apache servers might use .htaccess rules, while Nginx employs similar logic in configuration files. Cloudflare and similar services offer user agent blocking through their dashboards, adding strings to a blocklist for CDN enforcement. WordPress can utilize security plugins for bot blocking by adding OpenAI user agent strings to the block list. However, blocking has limitations as agent strings can be spoofed. IP-based blocking enhances security but requires knowledge of OpenAI’s IP ranges.
IP Verification and Advanced Detection Methods
Using IP address verification adds an additional security layer. OpenAI operates from identifiable IP ranges, though these can change over time. Some developers maintain community lists of known OpenAI IPs. Cross-referencing the user agent with the source IP can verify legitimacy. Rate limiting can also protect against excessive requests, balancing accessibility with resource preservation. More sophisticated methods use behavioral analysis to monitor typical AI request patterns or browser fingerprinting to identify inconsistencies, providing better protection against legitimate AI agents and impersonators.
Alternative User Agent Strategies and Variations
Understanding various user agent strategies helps develop comprehensive AI management policies. Companies like Google use identifiable agents for AI services, like “Google-Extended” for training crawlers. Though Anthropic doesn’t publicly document specific strings, they and others like PerplexityBot, have identifiable patterns. Blocking methods are similar across agents, with server configurations including multiple strings in blocklists. User agent spoofing, however, remains a challenge. Multiple verification methods offer better protection than relying solely on user agent strings.
AI Bot Management Flow:
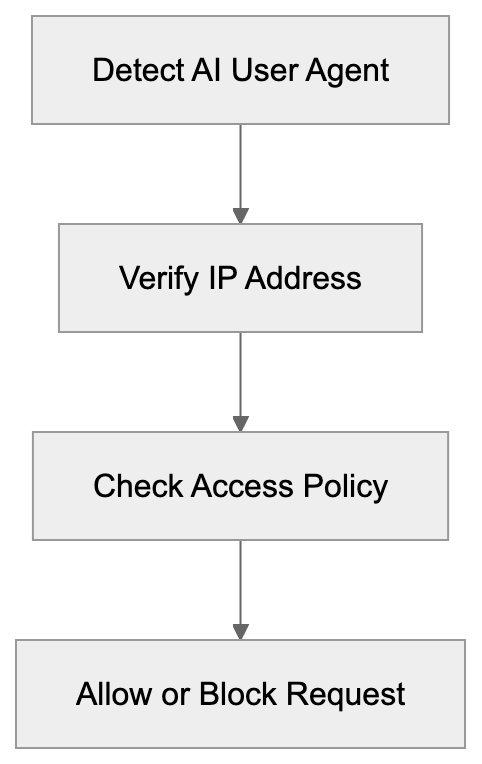
Comparison of Major AI User Agents
Here’s a comparison relevant to website administrators:
| Service | User Agent String | Primary Purpose | Respects robots.txt | Blocking Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI ChatGPT | ChatGPT-User | Real-time browsing | Partially | Medium |
| OpenAI GPTBot | GPTBot | Training data | Yes | Low |
| Google Bard | Google-Extended | Training data | Yes | Low |
| Anthropic Claude | Unknown | Real-time search | Unknown | Medium |
| Perplexity | PerplexityBot | Search indexing | Yes | Low |
Training crawlers better respect robots.txt than real-time browsing agents. Blocking difficulty varies based on agent identification ease. Website owners should evaluate their needs before implementing measures.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Blocking AI agents involves technical and ethical issues. Website owners have the right to regulate content access, yet enforcement is challenging. While some argue for AI companies to consistently respect opt-outs, debates about fair use persist. Commercial sites with proprietary data have stronger justifications for blocking, unlike public information sites. Publishing industries may seek licensing deals over blocking AI access. Regulations like GDPR also require compliance in AI bot management.
Monitoring and Analytics for AI Traffic
Monitoring OpenAI-GPT-User traffic provides strategic insights. Server logs offer raw data necessary for analysis, with tools like Google Analytics segmenting AI traffic by user agent strings. This data reveals which content AI systems most frequently access, indirectly driving new audiences. Businesses might improve such content for AI discoverability, differing from traditional SEO but sharing principles. Regular analysis can address potential abuse or excessive crawling, helping refine AI access policies.
Implementation Best Practices
Effective OpenAI-GPT-User management involves strategic planning. Start with traffic audits to understand AI bot activity, assessing server logs for OpenAI user agent strings. Quantify requests and accessed resources to inform access decisions. Gradually implement blocking rules, monitoring impacts and avoiding disruptions to legitimate integrations. Test configurations in staging environments prior to production and document setups for future reference. Keep updated with AI service developments to maintain effective management.
Future Trends in AI User Agent Management
AI user agent management is evolving as technology advances. As more AI services emerge, scalable approaches are crucial. Industry standards akin to robots.txt could clarify expectations for AI and content owners. Authentication systems could replace simple user agent strings, with API-based access offering enhanced control. The ongoing arms race between blocking and evasion necessitates sophisticated detection methods. Machine learning may identify AI traffic based on behavior, not just explicit identifiers. Privacy regulations will shape AI agent tracking and management, balancing transparency with privacy needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What steps can I take to monitor OpenAI-GPT-User traffic on my website?
You can monitor OpenAI-GPT-User traffic by analyzing your server logs or using analytics tools like Google Analytics. Look for entries that contain the OpenAI-GPT-User string to track this specific traffic. Segmenting this data can help you understand how much AI-driven traffic you receive and which content is most frequently accessed.
How can I block the OpenAI-GPT-User agent from accessing my website?
To block the OpenAI-GPT-User agent, you can set up server rules to reject matching requests. This can be done via .htaccess rules for Apache servers or configuration files for Nginx. Additionally, services like Cloudflare allow you to add the user agent to a blocklist for effective enforcement across your content delivery network.
Is it possible to entirely prevent bot access to my site?
While you can implement strategies to block specific user agents, entirely preventing bot access is challenging. Bots can spoof their user agent strings, making them harder to detect. Combining user agent blocking with IP address verification and behavior analysis can improve your security measures.
What are the legal implications of blocking AI agents?
Blocking AI agents raises legal and ethical considerations, particularly around content access rights. Website owners can regulate what automated systems can access, but compliance with regulations like GDPR is necessary. The enforcement of bans can be challenging, prompting discussions on fair use and licensing between publishers and AI companies.
How can I tell the difference between OpenAI-GPT-User and GPTBot traffic?
The OpenAI-GPT-User agent string is associated with real-time browsing activity within ChatGPT, while the GPTBot is used for training data collection. Analyzing server logs for the specific user agent string can help you differentiate between these two types of traffic. Understanding their distinct purposes informs how you manage access to your content.
What monitoring tools can assist with AI traffic analysis?
Tools like Google Analytics can help segment AI traffic by user agent strings, allowing you to see how AI systems interact with your content. Additionally, server log analyzers can provide insights into the frequency and resources accessed by OpenAI-GPT-User traffic. Regular monitoring of these tools can help refine your AI traffic management strategy.
What are best practices for managing OpenAI-GPT-User effectively?
Best practices include conducting traffic audits to assess AI bot activity, implementing gradual blocking rules, and regularly reviewing impacts on legitimate traffic. Testing configurations in staging environments before applying them can prevent interruptions. Keeping abreast of developments in AI services will also ensure your management strategies remain effective.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.