Understanding Perplexity-User: Real-Time Fetching for AI
Learn about Perplexity-User bot that enhances AI query results through real-time fetching. Explore user-agent strings, blocking, and behavior patterns.
What is Perplexity-User and Why It Matters
Perplexity-User, often referred to as PerplexityBot, is a specialized bot that performs real-time web content fetching for Perplexity AI. It plays a crucial role when users submit AI queries to Perplexity AI by visiting websites to gather current information and provide accurate, up-to-date answers. Unlike traditional search engines that rely on pre-indexed content, Perplexity-User uses real-time fetching to access the latest information available on the web.
The Perplexity bot exists to support Perplexity’s core feature, which is providing AI-powered answers with current data and citations. When you ask Perplexity a question, the service doesn’t rely on stored indexes. Instead, it actively fetches content from relevant websites at that moment. This approach sets Perplexity apart from other AI assistants that might rely solely on training data or cached information.
For website owners and developers, understanding Perplexity-User is important because this bot regularly accesses web content. It affects server resources, analytics data, and content attribution. The bot respects robots.txt files and standard web protocols but differs from traditional search engine web crawlers in frequency and purpose.
How Perplexity-User Works
Real-time Query Process:
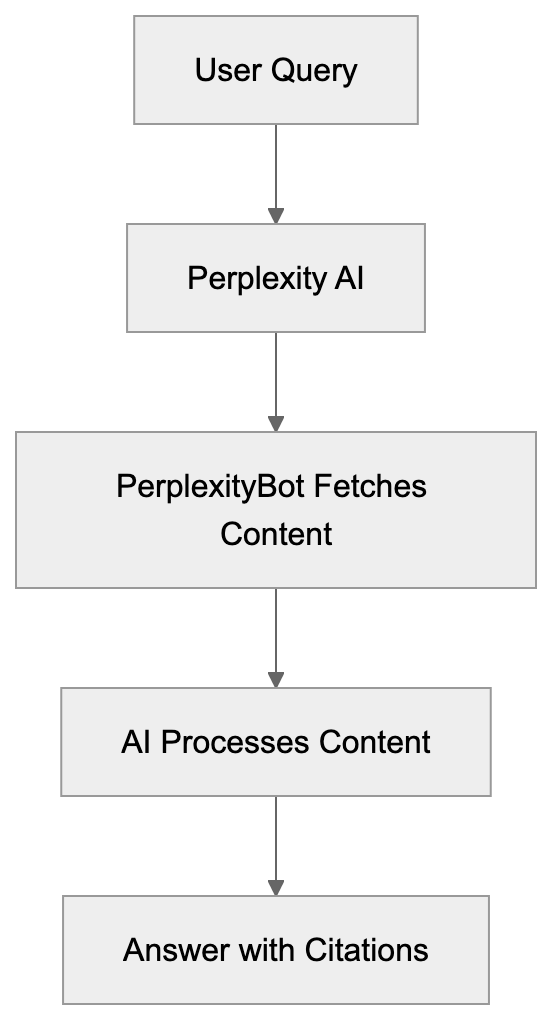
Perplexity-User operates as a real-time content fetcher triggered by user queries. When someone asks Perplexity AI a question, the system determines which websites might contain relevant information. The Perplexity-User bot then visits these sites, extracts content, and feeds it back to the AI model for processing.
The bot identifies itself through a specific user-agent string. Website administrators can detect PerplexityBot in their server logs by looking for this identifier. The user-agent string typically includes “PerplexityBot” in the header information.
This real-time approach means the bot doesn’t follow traditional crawling patterns. It doesn’t systematically index entire websites like Googlebot does. Instead, it makes targeted requests based on active user queries. The frequency of visits depends entirely on how often Perplexity users ask questions that might be answered by content from your site.
Typically, the bot fetches specific pages rather than entire site structures. It looks for content that matches query intent, extracts relevant text, and moves on. This targeted behavior means some pages might receive multiple visits while others might not receive any.
User-Agent String and Technical Details
The Perplexity-User bot announces itself through specific user-agent strings in HTTP requests. Website owners can identify these requests in server logs and analytics tools. The user-agent typically contains identifiers like “PerplexityBot” or variations including version information.
Bot Request Flow:

Here’s what a typical user-agent string looks like:
Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko; compatible; PerplexityBot/1.0; +https://perplexity.ai/bot)The user-agent string serves multiple purposes. It identifies the bot to web servers, provides contact information through the URL, and helps website administrators make informed decisions about access. The included URL typically points to documentation about the bot’s behavior and blocking instructions.
Developers can use this information to create specific rules in robots.txt files or server configurations. Some choose to allow the bot for better visibility in AI search results, while others block it to preserve bandwidth or maintain content exclusivity.
The bot generally respects standard web protocols, including robots.txt directives, crawl-delay settings, and noindex meta tags. However, enforcement depends on proper configuration of these controls on your website.
Blocking Perplexity-User: Methods and Considerations
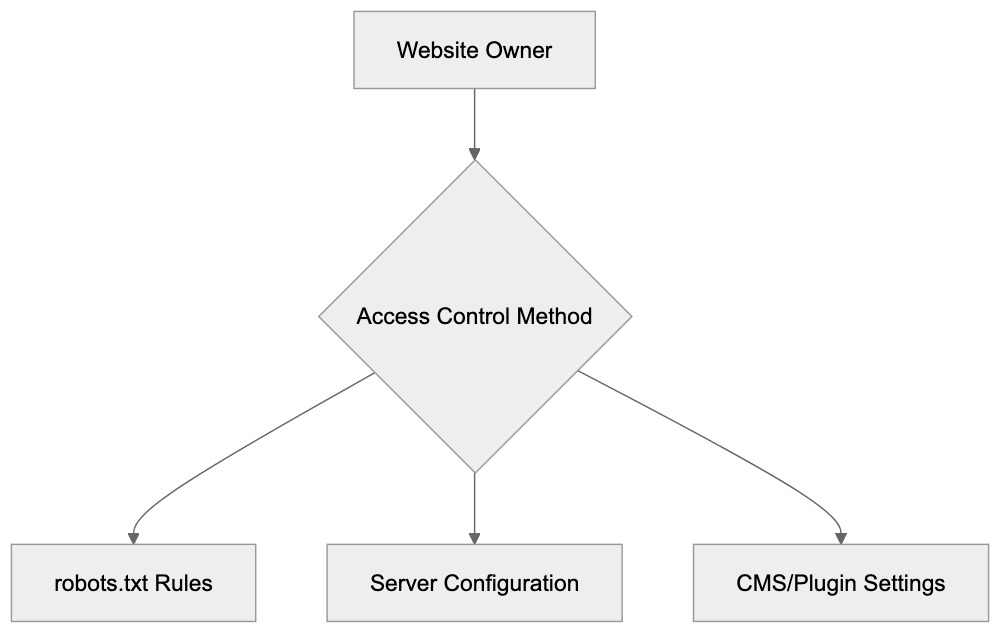
Website owners have several options for controlling Perplexity-User access. The most common method involves adding directives to the robots.txt file. This file tells bots which parts of your site they can or cannot access.
To block PerplexityBot completely, add these lines to your robots.txt file:
User-agent: PerplexityBot
Disallow: /This directive tells the bot not to access any part of your website. Most well-behaved bots respect these instructions, though enforcement isn’t legally guaranteed in all jurisdictions.
Another approach uses server-level configurations. You can configure Apache, Nginx, or other web servers to reject requests from specific user-agents. This method provides stronger control because it blocks requests before they reach your content.
Some content management systems and security plugins offer built-in options for bot management. These tools let you block or allow specific bots through simple interface controls without editing configuration files directly.
Considerations for blocking include potential visibility loss in Perplexity results, reduced traffic from users who find content through Perplexity, and the technical maintenance required to keep blocking rules updated. Some organizations block all AI bots by default, while others selectively allow them based on business goals.
Perplexity-User vs Similar AI Bots
Several AI services use similar real-time fetching bots to gather current information. Understanding how Perplexity-User compares to alternatives helps website administrators make informed access decisions.
| Bot Name | Service | Primary Purpose | Fetching Pattern | Robots.txt Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PerplexityBot | Perplexity AI | Real-time query answering | Query-triggered, targeted | Yes |
| GPTBot | OpenAI | Training data collection | Systematic crawling | Yes |
| Google-Extended | AI training (Bard) | Systematic crawling | Yes | |
| CCBot | Common Crawl | Dataset building | Complete crawling | Yes |
| Anthropic-AI | Anthropic (Claude) | Training and research | Mixed pattern | Yes |
Perplexity-User differs from training-focused bots in its real-time operation. While GPTBot and Google-Extended primarily collect data for future model training, Perplexity-User fetches content to answer immediate user queries. This creates different traffic patterns and resource usage.
Bot Access Control Methods:
 The query-triggered nature means Perplexity-User visits are less predictable than systematic crawlers. You might see bursts of activity when your content becomes relevant to popular queries, followed by quiet periods.
The query-triggered nature means Perplexity-User visits are less predictable than systematic crawlers. You might see bursts of activity when your content becomes relevant to popular queries, followed by quiet periods.
Unlike Common Crawl’s CCBot, which attempts complete web archiving, Perplexity-User focuses on specific content pieces. It doesn’t try to map entire site structures or maintain historical snapshots.
All these bots claim to respect robots.txt, but their business models and data usage differ significantly. Perplexity uses fetched content for immediate answer generation with citations. Training-focused bots incorporate content into models that may or may not attribute sources in outputs.
Business and Developer Use Cases
Website owners and developers interact with Perplexity-User in various scenarios. Understanding these use cases helps determine appropriate access policies.
Content publishers might welcome Perplexity-User because it drives traffic and provides attribution. When Perplexity answers queries using your content, it typically includes citations linking back to source pages. This can generate referral traffic from users who want more detailed information.
News organizations face a complex decision. Real-time fetching means Perplexity can surface breaking news quickly, potentially increasing visibility. However, AI-generated summaries might reduce click-through rates if users get enough information from the answer itself.
E-commerce sites often block AI bots to prevent competitors from easily accessing product information, pricing data, and inventory details. Real-time fetching bots could theoretically monitor price changes or product availability without human intervention.
Developers building APIs or documentation sites generally benefit from Perplexity-User access. When developers search for code examples or API usage instructions, having your documentation appear in Perplexity results increases discoverability.
Marketing professionals need to consider how AI answer engines affect SEO strategy. Traditional search improvement focused on ranking in search results. With AI services providing direct answers, the goal shifts toward being the cited source rather than just ranking high.
Some businesses use analytics data to track Perplexity-User visits and measure their content’s value to AI services. A high visit rate might indicate your content answers common questions in your industry.
Analytics and Monitoring
Tracking Perplexity-User activity provides insight into how AI services use your content. Most web analytics platforms can segment bot traffic for separate analysis.
In Google Analytics, bot traffic appears in user-agent reports. You can create custom segments to isolate Perplexity-User requests and analyze which pages receive the most attention. This data reveals which content AI services find valuable for answering user queries.
Server log analysis offers more detailed information. Logs show exact request patterns, response codes, and bandwidth usage. For high-traffic sites, bot activity can represent significant resource consumption worth monitoring.
Some organizations track referral traffic from Perplexity to measure the bot’s impact on actual user visits. If Perplexity-User fetches content frequently but generates minimal referral traffic, it might indicate your content is being used for answers without driving clicks back to your site.
Monitoring also helps identify unusual patterns that might indicate problems. Sudden spikes in bot activity could suggest your site is answering many trending queries or could indicate technical issues causing excessive requests.
Developers can set up alerts for bot traffic thresholds. If Perplexity-User requests exceed normal levels, automated notifications let you investigate and adjust access controls if needed.
Privacy and Content Attribution
Content attribution remains a key differentiator for Perplexity compared to other AI services. When Perplexity-User fetches your content to answer queries, the service typically provides citations and links to source material.
This citation practice addresses some concerns content creators have about AI services. Rather than simply absorbing content into opaque models, Perplexity shows users where information comes from. This transparency helps users evaluate source credibility and provides traffic opportunities for content owners.
However, attribution doesn’t solve all concerns. Some publishers worry that good summaries reduce the need to visit source sites. If users get sufficient information from AI-generated answers, they might not click through to original content. This affects advertising revenue and engagement metrics.
Privacy considerations differ for Perplexity-User compared to user-facing analytics. The bot doesn’t collect user data from your site; it fetches content. Privacy policies and cookie consent mechanisms don’t typically apply to bot requests.
Website owners should consider whether their content includes sensitive information that shouldn’t appear in AI responses. Even with attribution, having proprietary or confidential information summarized in public AI answers could create issues.
Some content requires human interpretation or context that automated fetching might miss. Medical information, legal advice, and financial guidance need careful handling. Content creators in these fields often implement strict bot controls to prevent misuse or misinterpretation.
Future Considerations and Best Practices
The landscape of AI bots and real-time fetching continues to change. Website administrators need flexible strategies that can adapt to new developments.
Best practices start with clear robots.txt configurations. Maintain an updated file that explicitly states your policies for different bot types. This creates a documented record of your access preferences and helps compliant bots follow your wishes.
Monitor bot traffic regularly to understand patterns and resource impact. Set up dashboards that track requests from Perplexity-User and similar bots. Use this data to make informed decisions about access policies.
Consider implementing rate limiting for bot traffic. Even if you allow access, controlling request frequency prevents resource exhaustion and ensures human visitors get priority for server capacity.
Document your bot policies internally so all team members understand the reasoning. Marketing teams might want maximum visibility in AI results, while infrastructure teams worry about server load. Clear documentation helps balance these concerns.
Stay informed about changes to Perplexity and similar services. Bot behavior, user-agent strings, and access patterns can change as services update their technology. Subscribe to relevant announcements and adjust configurations accordingly.
Test your blocking mechanisms periodically to make sure they work as intended. Robots.txt files can break with site migrations or CMS updates. Regular verification prevents unintended access or blocking.
For content you want to protect, consider technical controls beyond robots.txt. Authentication requirements, JavaScript rendering dependencies, or API-based access can provide stronger protection than relying solely on bot compliance.
End
Perplexity-User represents a new category of web bots focused on real-time content fetching for AI-powered question answering. Unlike traditional search crawlers that build indexes, this bot retrieves specific content on demand to answer active user queries. Website owners and developers need to understand its behavior, user-agent identification, and impact on resources.
The bot respects standard web protocols, including robots.txt directives, giving administrators control over access. Blocking considerations include potential visibility loss in Perplexity results versus bandwidth conservation and content protection. Compared to similar AI bots, Perplexity-User focuses on immediate query answering rather than training data collection, creating distinct traffic patterns.
For businesses and content creators, Perplexity-User presents both opportunities and challenges. Attribution and citation practices offer visibility benefits, but real-time summarization might reduce click-through traffic. Monitoring bot activity through analytics and server logs helps measure impact and inform access policies. As AI services continue to grow, managing bot access becomes an important part of web administration and content strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Perplexity-User differ from traditional search engine crawlers?
Unlike traditional search engine crawlers, which systematically index entire websites, Perplexity-User fetches content in real-time based on user queries. It targets specific pages that match query intent rather than crawling the entire site structure.
What can website owners do to monitor Perplexity-User activity?
Website owners can track Perplexity-User requests through web analytics platforms by filtering bot traffic or reviewing server logs. This allows them to analyze which content is frequently accessed by the bot, revealing how it interacts with their site.
What impact does Perplexity-User have on website traffic and engagement?
Perplexity-User can drive traffic to websites by providing citations in AI-generated answers, which may encourage users to visit the original content. However, if users find sufficient information in the AI answers, it could lead to reduced click-through rates and engagement.
How can I block Perplexity-User from accessing my site?
To block Perplexity-User, you can add specific directives in your robots.txt file to disallow access. Alternatively, server-level configurations can be implemented to reject requests from the bot based on its user-agent string.
What considerations should content creators keep in mind regarding privacy and attribution?
While Perplexity-User provides citations for fetched content, publishers should be cautious about sensitive information being summarized in AI responses. They should also consider the implications of reduced traffic if users receive adequate information without visiting the source.
What are the best practices for managing Perplexity-User access?
Maintaining an updated robots.txt file, monitoring bot traffic, and implementing rate limiting are best practices for managing Perplexity-User access. This helps balance bandwidth conservation with the visibility benefits of AI citation.
How does Perplexity-User support different business goals?
Perplexity-User can support various business goals by driving traffic to content that aligns with user queries. Content publishers may welcome its access for visibility, while e-commerce sites might block it to protect competitive information.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.