PerplexityBot & Perplexity-User: Complete Guide
Learn about PerplexityBot and Perplexity-User crawlers, their differences, how they handle robots.txt, and methods to block them using server configuration.
Introduction
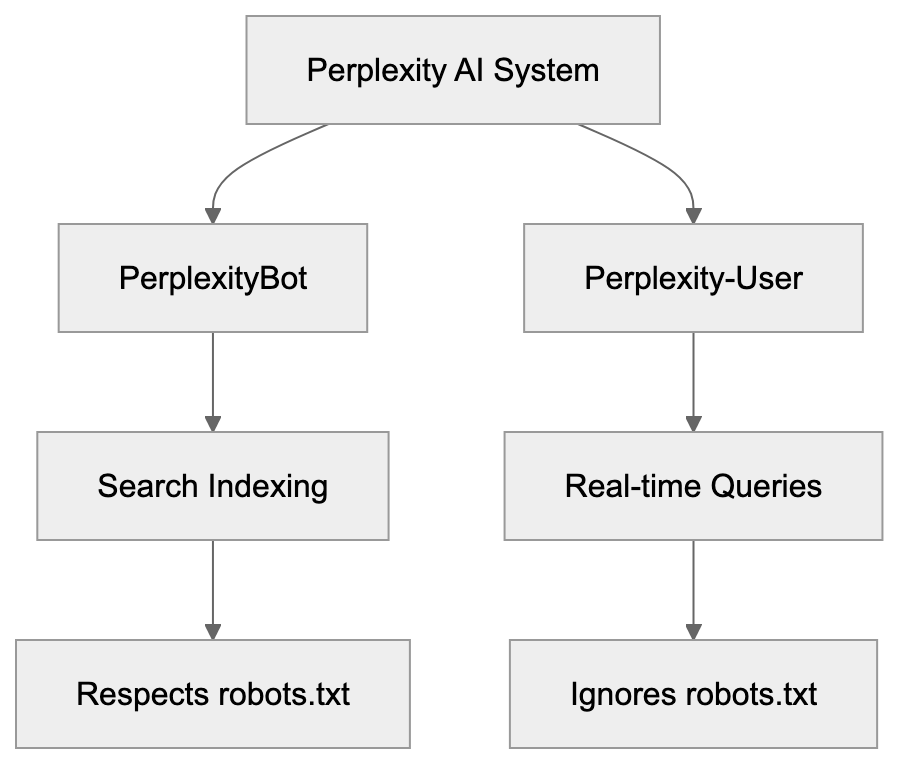
Perplexity AI operates two different crawlers that visit websites: PerplexityBot and Perplexity-User. These bots serve unique purposes and behave differently. Understanding the difference is crucial for website owners and developers who want control over how Perplexity accesses their content. PerplexityBot crawls websites for search indexing purposes and respects robots.txt rules like Google or Bing crawlers. Conversely, Perplexity-User fetches content in real-time when users ask questions and deliberately ignores robots.txt directives.
This creates a challenge because traditional blocking methods don’t work for Perplexity-User. Web developers need to use server-level configurations to block it effectively. The difference in behavior between these two Perplexity crawlers is significant and requires different blocking strategies.
Perplexity Crawler Architecture:
What Are PerplexityBot and Perplexity-User
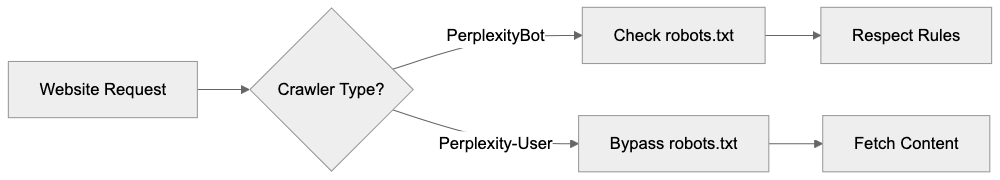
PerplexityBot is the standard web crawler from Perplexity AI, functioning similarly to traditional search engine crawlers. The bot systematically visits web pages to index content for Perplexity’s search database. When PerplexityBot crawls your site, it identifies itself with a specific user agent string. The official user agent for PerplexityBot includes the text “PerplexityBot” in the string. This crawler respects the robots.txt file on your website. If you disallow PerplexityBot in robots.txt, it will stop crawling your site. According to Perplexity’s documentation, PerplexityBot does NOT collect data for foundation model training. Its purpose is purely search indexing.
Perplexity-User serves a different function. This crawler fetches content in real-time when actual users submit queries to Perplexity AI. When someone asks a question on Perplexity, the system retrieves current information from websites. Perplexity-User makes these real-time requests. The crucial difference is that Perplexity-User ignores robots.txt rules by design. Perplexity’s official documentation at docs.perplexity.ai/guides/bots confirms this behavior. The company states that Perplexity-User must bypass robots.txt to provide real-time answers to users. This means standard robots.txt blocking won’t stop Perplexity-User from accessing your content.
Why Perplexity Created Two Different Crawlers
The two-crawler system exists because Perplexity serves two different functions. First, it maintains a search index like traditional search engines. Second, it provides real-time AI-powered answers to user questions. Each function requires different crawling behaviors.
-
PerplexityBot handles the indexing function, crawling websites regularly to build and update Perplexity’s search database. This is similar to how Googlebot or Bingbot work. The crawling happens on a schedule and doesn’t need immediate access to content. Because of this, PerplexityBot can respect robots.txt without harming the user experience.
-
Perplexity-User exists for real-time query fulfillment. When a user asks a question, the AI needs current information. Waiting for the next scheduled crawl isn’t acceptable. The system must fetch content immediately. Perplexity argues that respecting robots.txt for real-time queries would degrade answer quality. If a website blocks crawlers in robots.txt but allows regular browser access, Perplexity-User will still fetch the content. The company treats Perplexity-User more like a browser acting on behalf of a human user than a traditional crawler. This reasoning is controversial among website owners and SEO experts who believe all automated access should respect robots.txt.
Crawler Behavior Comparison:
How Users and Websites Interact With These Crawlers
Website owners encounter these crawlers in their server logs. Both PerplexityBot and Perplexity-User identify themselves through user agent strings. PerplexityBot appears with a user agent containing “PerplexityBot.” Perplexity-User appears with a user agent containing “Perplexity-User.” You can check your web server access logs to see if either crawler has visited your site. The IP addresses used by these crawlers come from specific ranges. Perplexity publishes the IP ranges at perplexity.com/perplexitybot.json. This JSON file contains the current list of IP addresses that Perplexity crawlers use.
Website administrators can use this information to identify and control crawler access. For PerplexityBot, adding a disallow rule in robots.txt is sufficient. You add a line like “User-agent: PerplexityBot” followed by “Disallow: /” to block it completely. For Perplexity-User, you need server-level configuration. This means editing your web server configuration files. Apache users can modify .htaccess or httpd.conf files. Nginx users modify nginx.conf or site-specific configuration files. The server checks the user agent string of incoming requests and blocks those matching Perplexity-User before serving any content.
Blocking PerplexityBot Using robots.txt
Blocking PerplexityBot is straightforward because it respects robots.txt. You need to add specific directives to your robots.txt file. The file should be located at the root of your website domain, for example, yoursite.com/robots.txt. To block PerplexityBot from crawling your entire site, add these lines:
User-agent: PerplexityBot
Disallow: /
This tells PerplexityBot not to crawl any part of your website. If you want to block specific sections only, you can specify paths. For instance, to block only your blog directory:
User-agent: PerplexityBot
Disallow: /blog/
After updating robots.txt, the changes take effect the next time PerplexityBot crawls your site. There is no immediate enforcement. The crawler will see the new rules on its next visit and stop crawling blocked areas. You can verify your robots.txt file is accessible by visiting yoursite.com/robots.txt in a browser. Make sure the file is publicly readable. Remember, robots.txt blocking only works for PerplexityBot. It has zero effect on Perplexity-User.
Blocking Perplexity-User at Server Level
Since Perplexity-User ignores robots.txt, you need server-level blocking. This requires editing web server configuration.
For Apache servers, you can use .htaccess files or the main httpd.conf configuration. Add these lines to block Perplexity-User:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTP_USER_AGENT} Perplexity-User [NC]
RewriteRule .* - [F,L]
This configuration checks incoming requests for the Perplexity-User string in the user agent. If found, it returns a 403 Forbidden response. The [NC] flag makes the match case-insensitive. The [F,L] flags tell Apache to forbid the request and stop processing rules.
For Nginx servers, you add blocking rules to nginx.conf or your site configuration file. The syntax looks like this:
if ($http_user_agent ~* “Perplexity-User”) {
Server-Level Blocking Flow:
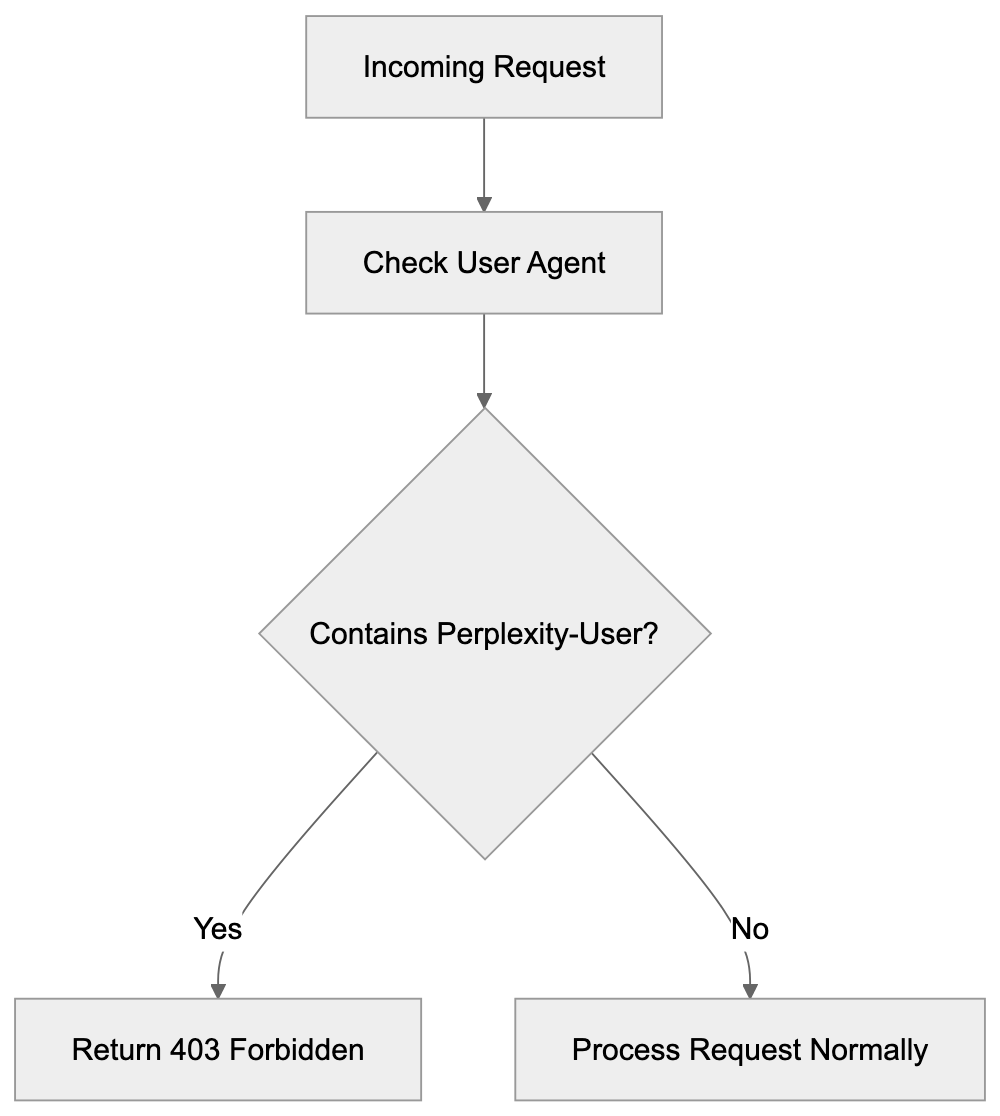 return 403;
return 403;
}
This checks the user agent header and returns a 403 status code if it matches Perplexity-User. The ~* operator makes the comparison case-insensitive. Place this rule inside your server block. After making changes, reload or restart Nginx for the configuration to take effect. You can test blocking by checking server logs after setup. Perplexity-User requests should show 403 status codes instead of 200.
Confirmed Facts and Key Details About Perplexity Crawlers
Perplexity provides official documentation about its crawlers. The IP address ranges are published at perplexity.com/perplexitybot.json. This JSON endpoint updates when Perplexity adds or changes IP addresses. According to official documentation, PerplexityBot explicitly does NOT collect data for foundation model training. Its sole purpose is search indexing. Perplexity-User, by design, ignores robots.txt directives. This is documented at docs.perplexity.ai/guides/bots. The company states this is necessary for real-time query responses.
Both crawlers identify themselves with clear user agent strings. PerplexityBot includes “PerplexityBot” in its user agent. Perplexity-User includes “Perplexity-User” in its user agent. The crawlers do not attempt to hide their identity or spoof other user agents according to official sources. Website owners can reliably identify these crawlers by their user agent strings. The distinction between the two crawlers is important for access control. Standard robots.txt works for one, but not the other.
Comparison With Similar AI Crawlers
Several AI companies operate web crawlers for various purposes. Understanding how Perplexity crawlers compare helps website owners make informed decisions.
| Crawler | Company | Respects Robots.txt | Purpose | Blocking Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PerplexityBot | Perplexity AI | Yes | Search indexing | robots.txt |
| Perplexity-User | Perplexity AI | No | Real-time queries | Server config |
| GPTBot | OpenAI | Yes | Training data | robots.txt |
| GoogleBot-Extended | Yes | AI training | robots.txt | |
| CCBot | Common Crawl | Yes | Dataset building | robots.txt |
| Claude-Web | Anthropic | No | Real-time web access for tool use | Server config |
Perplexity-User stands out as one of the few major AI crawlers that deliberately ignores robots.txt. Most other AI company crawlers respect robots.txt directives. GPTBot from OpenAI respects robots.txt, and website owners can block it using standard methods. GoogleBot-Extended, which Google uses for AI training data, also respects robots.txt. Common Crawl’s CCBot respects robots.txt as well. Anthropic’s Claude-Web follows robots.txt rules.
The key difference is purpose. Most crawlers gather data for model training or dataset creation. These crawlers can respect robots.txt because they don’t need immediate access. Perplexity-User fetches content for real-time user queries. Perplexity argues this requires bypassing robots.txt. Whether this justification is acceptable remains debated in the web development and SEO communities. Many website owners believe all automated access should honor robots.txt regardless of purpose.
Technical Details for Developers
Developers implementing crawler blocking need specific technical information. The user agent string for PerplexityBot typically looks like: “Mozilla/5.0 AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko; compatible; PerplexityBot/1.0; +http://www.perplexity.ai/bot).” The Perplexity-User agent string includes “Perplexity-User,” but the exact format may vary. When writing blocking rules, match on the distinctive part of the string.
IP-based blocking is also possible using the published IP ranges. You can download the JSON file from perplexity.com/perplexitybot.json and extract the IP ranges. Then configure your firewall or web server to block requests from those IPs, but IP-based blocking requires maintenance because the ranges can change. User agent blocking is generally easier to maintain. Combining both methods provides stronger blocking.
For content management systems like WordPress, you can use security plugins that allow user agent blocking. Plugins like Wordfence or iThemes Security include user agent filtering features. You add Perplexity-User to the blocked user agents list. The plugin handles the server-level blocking automatically. This is easier than manually editing server configuration files for users not comfortable with Apache or Nginx syntax.
Privacy and Data Collection Considerations
Website owners care about crawler access for several reasons. Data collection for AI training is a primary concern. Perplexity states that PerplexityBot does not collect data for foundation model training, but Perplexity-User fetches content to answer user queries. Whether this constitutes data collection depends on interpretation. The content is processed to generate answers, but Perplexity has not clearly stated whether query responses are stored or used for training.
Bandwidth usage is another consideration. Aggressive crawling can consume significant server resources. Both PerplexityBot and Perplexity-User generate HTTP requests that use bandwidth. High-traffic websites may want to limit crawler access to manage server load. Blocking or rate-limiting crawlers helps control resource consumption. Some websites choose to block all AI crawlers by default and only allow specific ones.
Content attribution matters to publishers and content creators. When Perplexity uses website content to answer questions, the original source may not receive traffic. Users get answers directly from Perplexity without visiting the source website. This can reduce referral traffic and ad revenue for publishers. Some content creators block AI crawlers to protect their traffic and revenue streams. The decision depends on individual business needs and priorities.
Monitoring and Verification
After implementing blocking rules, you should verify they work correctly. Check your web server access logs for requests from Perplexity crawlers. Look for user agent strings containing PerplexityBot or Perplexity-User. Blocked requests should show 403 Forbidden status codes. If you see 200 OK status codes, the blocking isn’t working properly. Review your configuration syntax and server setup.
You can also monitor the IP addresses making requests. Compare them against the published IP range from perplexity.com/perplexitybot.json. This helps confirm the requests actually come from Perplexity. Be aware that some requests might spoof Perplexity user agents. True Perplexity crawlers will originate from the published IP ranges. Requests claiming to be Perplexity but coming from other IPs are likely fake.
Regular monitoring helps ensure blocking remains effective. Perplexity might update user agent strings or IP ranges. Check the official documentation periodically for changes. Update your blocking rules if needed. Automated monitoring tools can alert you to crawler activity. Log analysis tools can generate reports showing crawler access attempts and blocking effectiveness.
Legal and Ethical Perspectives
The robots.txt protocol has been a web standard since 1994. It’s a voluntary protocol that relies on crawler operators respecting the rules. Most major companies honor robots.txt as a matter of web etiquette and community standards. Perplexity-User’s decision to ignore robots.txt breaks this convention. Some legal experts argue this could violate computer access laws in certain jurisdictions, but enforcement is complex and varies by location.
Website terms of service may prohibit automated access. If a website explicitly forbids scraping or automated collection in its terms, accessing it with Perplexity-User could violate those terms. Whether this creates legal liability depends on specific circumstances and jurisdiction. Website owners who want stronger protection should combine robots.txt with terms of service and technical blocking measures.
The ethical debate centers on balancing user needs with website owner rights. Perplexity argues that users benefit from real-time answers. Website owners argue they should control how their content is accessed and used. Both positions have merit. The web community continues to discuss these issues. Standards organizations may eventually develop new protocols or guidelines for AI crawler behavior.
Impact on SEO and Website Traffic
Blocking Perplexity crawlers has SEO implications. If you block PerplexityBot, your content won’t appear in Perplexity search results. This reduces one potential traffic source, but Perplexity’s market share is much smaller than Google or Bing. The traffic impact from blocking PerplexityBot is likely minimal for most websites. You need to weigh the lost traffic against your reasons for blocking.
Perplexity-User creates different SEO considerations. Since it fetches content for real-time answers, users may not click through to your website. They get information directly from Perplexity. This is similar to how Google featured snippets can reduce click-through rates. Blocking Perplexity-User prevents this zero-click behavior. Your content won’t be used in Perplexity answers, but you also won’t lose potential click-throughs.
Some SEO experts recommend allowing AI crawlers to maintain visibility. Others recommend blocking them to protect traffic and content. The right choice depends on your specific goals. News publishers and content creators often block AI crawlers. Technical documentation sites might allow them. Consider your audience and business model when making this decision.
Conclusion
PerplexityBot and Perplexity-User are two distinct crawlers from Perplexity AI. PerplexityBot respects robots.txt and serves search indexing purposes without collecting training data. Standard robots.txt blocking works effectively for this crawler. Perplexity-User ignores robots.txt by design to fulfill real-time user queries. Website owners must use server-level configuration to block it. Apache and Nginx both support user agent filtering through configuration directives. The distinction between these crawlers is important for effective access control.
Understanding how each crawler works helps developers and website owners make informed decisions. Blocking strategies range from simple robots.txt entries to advanced server configuration. Monitor your setup to make sure blocking rules work as intended. The choice to allow or block these crawlers depends on your specific needs and priorities regarding traffic, content protection, and resource usage.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I identify if Perplexity crawlers have visited my site?
You can check your web server access logs to see requests from the Perplexity crawlers. Look for user agent strings that include "PerplexityBot" or "Perplexity-User." These logs will help you verify which crawler accessed your site and how frequently.
What should I do if I want to block both PerplexityBot and Perplexity-User from accessing my site?
To block PerplexityBot, add specific directives to your robots.txt file. To block Perplexity-User, you will need to implement server-level blocking, which involves editing your web server configuration. Ensure you use the correct directives for your server type (Apache or Nginx) to effectively block both crawlers.
Can blocking PerplexityBot affect my website's search visibility?
Yes, if you block PerplexityBot, your content will not appear in Perplexity's search results, potentially reducing traffic from that source. However, the overall impact may be minimal since Perplexity’s market share is smaller compared to major search engines like Google or Bing.
Why doesn't Perplexity-User respect robots.txt?
Perplexity-User is designed to fetch real-time data when users submit questions, and respecting robots.txt would slow down this process. Perplexity argues that this approach ensures high-quality, immediate answers for users, which they believe justifies ignoring the standard protocol.
What technical skills are needed to block Perplexity-User effectively?
To block Perplexity-User, you will need knowledge of web server configurations, particularly editing .htaccess files for Apache or nginx.conf for Nginx. Understanding user agent strings and how to implement server rules is crucial for ensuring that unauthorized access is prevented.
How often does PerplexityBot crawl my website?
PerplexityBot crawls websites on a schedule to maintain and update the search index. The exact frequency can vary based on several factors, including the website's size, traffic, and content change frequency. Monitoring your server logs can provide insights into how often it visits your site.
Is there a way to monitor the effectiveness of my blocking strategy against Perplexity crawlers?
Yes, you can monitor your web server access logs after implementing your blocking rules. Check for requests from both PerplexityBot and Perplexity-User; blocked requests should return a 403 Forbidden status. Regular monitoring and log analysis can help ensure your blocking measures are functioning as intended.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.