Understanding PetalBot: Huawei's Search & AI Crawler
Complete guide to Huawei's PetalBot crawler. Learn its purpose, user-agent string, crawl behavior, and how to block it from your site.
What is PetalBot
PetalBot, a web crawler managed by Huawei Technologies, plays a crucial role in Huawei’s ecosystem. It’s designed to support Petal Search and AI development projects. This is achieved by crawling websites and collecting data, similar to other search engine bots. As a Huawei AI crawler, PetalBot’s function is similar to other search engine bots, instrumental in indexing web content and gathering data for AI training, as detailed in Huawei’s AI Privacy White Paper.
PetalBot serves multiple purposes. Primarily, it powers Petal Search, Huawei’s alternative search engine, especially in regions where Google services are absent, as reported by PR Newswire. Additionally, this Huawei web crawling capability aids in AI research and the development of machine learning models. If you manage a website, PetalBot has likely appeared in your server logs, as identified by Celia. Understanding its operations enables informed decisions on whether to allow or block PetalBot.
Why PetalBot Exists and Its Purpose
PetalBot Operation Overview:
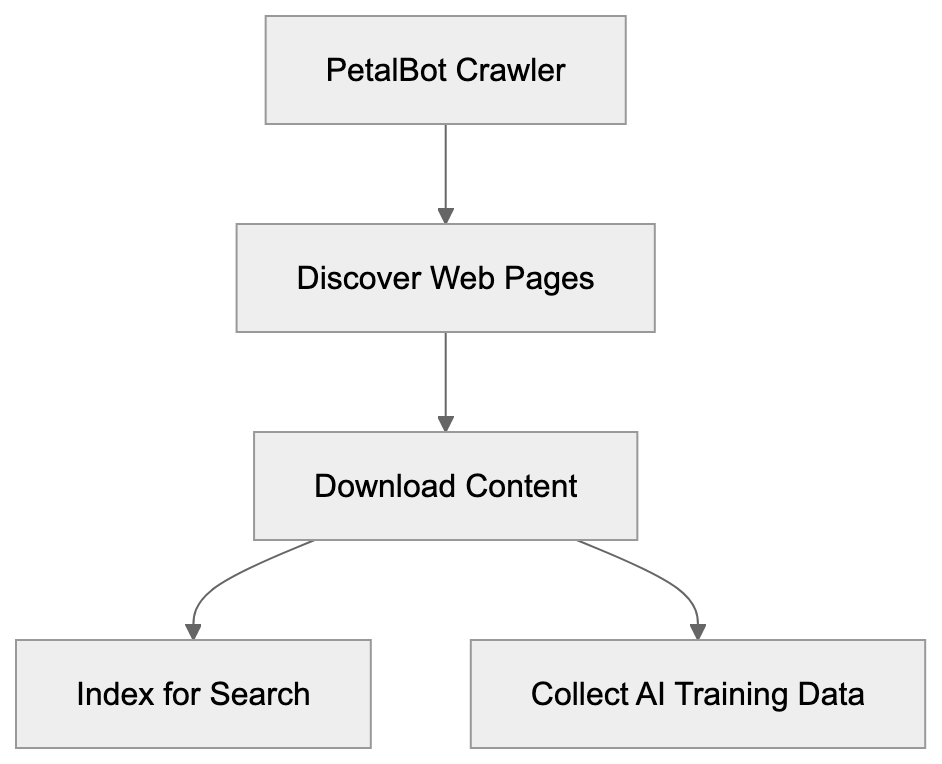
Huawei developed PetalBot to enhance its search engine infrastructure. Following the loss of Google services on new devices, Huawei required an alternative like Petal Search, powered by PetalBot.
The crawler builds and maintains Huawei’s search index. Web crawlers like PetalBot are indispensable, as, without them, search engines wouldn’t know what content is on the web or its ranking. PetalBot downloads web pages, follows links, and processes content to grasp each page’s essence.
Besides search, PetalBot gathers data for AI training. Huawei, like other tech companies, uses this data to train large language and machine learning models. This reflects industry standards, though it raises questions about data usage and website owner consent.
The geographic focus of PetalBot targets markets with strong Huawei presence, including parts of Asia and Europe. Website owners in these regions frequently notice more PetalBot activity.
How PetalBot Operates and Its Crawl Behavior
PetalBot identifies itself via a specific user-agent string when visiting websites. This string, visible in HTTP headers, looks like:
Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 7.0;) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Mobile Safari/537.36 (compatible; PetalBot;+https://webmaster.petalsearch.com/site/petalbot)
This string contains valuable information, such as the bot’s name (PetalBot) and a URL for more details. Such transparency is a common practice among legitimate web crawlers.
PetalBot’s crawl rate varies based on a site’s size and server capacity. Ideally, crawlers adjust their speed to avoid server overload, but some report aggressive behavior from PetalBot, especially during initial site discovery.
The bot adheres to robots.txt protocols—guidelines directing crawlers on accessible content—and responds to crawl-delay directives, allowing website owners to regulate access speed.
PetalBot processes various content types, including HTML, PDFs, and multimedia. Its focus is mainly text content for search indexing, but it also collects multimedia elements for Huawei’s processing and indexing systems.
PetalBot’s Role in Huawei’s AI Ecosystem
Within Huawei’s tech stack, PetalBot plays a significant role. After replacing Google Mobile Services with Huawei Mobile Services (HMS), Petal Search became part of HMS, allowing searches without Google.
Data from PetalBot supports various Huawei services, notably Petal Search and Huawei’s AI research. The data collected contributes to training datasets crucial for tasks like natural language processing and computer vision projects, positioning Huawei as a key player in AI research.
The integration of PetalBot and Huawei services appears tight, with data flowing into indexing systems, aiding Petal Search and possibly AI training pipelines, although Huawei hasn’t detailed these processes.
For developers in the Huawei ecosystem, Petal Search offers valuable search functionality, enabled by PetalBot’s web indexing.
PetalBot Crawling Process:

How to Identify and Control PetalBot Access
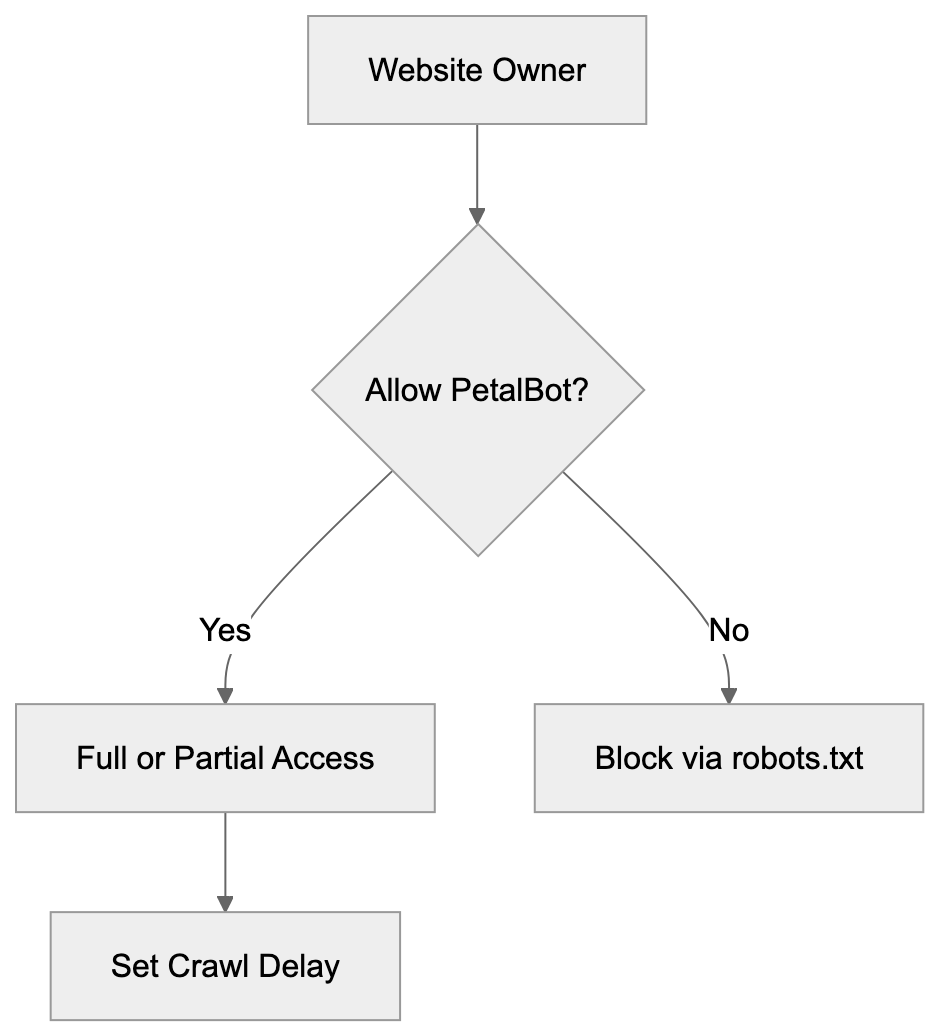
To control PetalBot access, look for the user-agent string in server logs. Most analysis tools allow filtering by user-agent, indicating PetalBot’s visitation frequency.
To block PetalBot, add these lines to your robots.txt:
User-agent: PetalBot
Disallow: /This prevents it from crawling your site. To allow partial access, specify blocked directories and set crawl delays:
User-agent: PetalBot
Disallow: /private/
Disallow: /admin/
Crawl-delay: 10For a more aggressive approach, blocking PetalBot at the server level is possible but requires more technical know-how and doesn’t depend on the bot respecting robots.txt.
Some website owners block PetalBot due to concerns over content use for AI training or lack of perceived value in Petal Search results. Others allow it for broad search visibility. Your decision should align with your audience’s needs and your stance on data collection.
Comparing PetalBot to Other Web Crawlers
PetalBot competes with other web crawlers. Comparison provides context to its operation and behavior.
| Crawler | Owner | Primary Purpose | Respects robots.txt | Known for AI Training |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PetalBot | Huawei | Petal Search, AI research | Yes | Yes |
| Googlebot | Google Search | Yes | Yes | |
| Bingbot | Microsoft | Bing Search | Yes | Yes |
| YandexBot | Yandex | Yandex Search | Yes | Limited |
| Baiduspider | Baidu | Baidu Search | Yes | Limited |
Controlling PetalBot Access:
 | GPTBot | OpenAI | AI training data | Yes | Yes |
| GPTBot | OpenAI | AI training data | Yes | Yes |
Googlebot, with extensive refinement, is the most common crawler. PetalBot is newer and less established, with varied crawling refinement.
Microsoft’s Bingbot, serving Bing Search and AI projects, shows similar politeness and effectiveness. PetalBot follows this model but lacks similar market share.
Regional search engines like YandexBot and Baiduspider focus on specific geographies, and PetalBot’s focus somewhat overlaps in Asian markets.
GPTBot, by OpenAI, focuses solely on AI data collection, unlike dual-purpose crawlers like PetalBot and Googlebot.
PetalBot’s distinction lies in its Huawei ecosystem integration. Its relevance depends on your audience’s use of Huawei devices and Petal Search.
Crawl aggressiveness is a point of contention. Some report PetalBot as more aggressive, though this isn’t universally noted. As Huawei refines its algorithms, expect improvements.
Privacy and Data Usage Considerations
Data collected by PetalBot integrates into Huawei systems, including text, metadata, and potentially images. It’s crucial for privacy-conscious website owners to understand its usage.
Huawei indicates data is used for search indexing and service enhancements. Crawled data informs AI models and search improvement, typical across tech companies.
Unlike user-content platforms, public web content exists in a gray area, accessible without explicit permission. Control is possible via robots.txt, though it relies on crawler compliance.
Concerns about AI data usage can lead to blocking PetalBot. Yet, this reduces your content’s visibility on AI-intensive engines.
Selective blocking—permitting search crawlers while restricting AI-focused ones—requires an updated robots.txt distinguishing different bot intents.
Data usage and retention details remain largely undisclosed, frustrating some website owners conscious of their content’s fate.
Technical Implementation Details
PetalBot aligns with standard crawler practices, featuring distributed crawling from multiple IP addresses, often Huawei’s own infrastructure.
It supports modern web standards, including JavaScript rendering, indexing dynamic sites, though its effectiveness compared to Googlebot isn’t well-documented.
Crawl scheduling targets frequently updated sites, mirroring other crawlers’ resource allocation.
Structured data markup like Schema.org tags is processed, enhancing content understanding, a practice akin to Google’s.
Error handling and retry logic are standard, with persistent errors reducing crawl frequency accordingly.
Making Informed Decisions About PetalBot
Deciding on PetalBot access depends on several factors.
Consider your audience’s geography. Markets with prevalent Huawei device usage might benefit from allowing PetalBot for visibility.
Assess your server capacity. Crawl-delay settings can mitigate performance issues without outright blocking.
Reflect on AI data concerns. If content use for AI training is troublesome, blocking PetalBot, although affecting visibility, might align better with your values.
Analyze your analytics for Petal Search traffic. Blocking removes this channel, impacting reach if significant traffic originates from there.
Organizations should consider policies on crawler permissions, especially regarding security and compliance factors.
Robots.txt provides flexibility, allowing adjustments to PetalBot actions over time. Begin by examining its behavior before enacting blocking.
Conclusion
PetalBot, Huawei’s web crawler, fuels Petal Search and supports AI endeavors. Functioning like major search crawlers, it respects standard protocols like robots.txt.
Serving as part of Huawei’s comprehensive system, it maintains the Petal Search index and collects data for AI. This dual purpose mirrors other tech companies’ crawler strategies.
Allowing PetalBot hinges on audience location, AI data stance, and server capacity considerations. It holds significant relevance for sites targeting markets where Huawei is influential. Understanding PetalBot’s functions aids in deciding its role on your website.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of websites should allow PetalBot?
Websites targeting users in regions where Huawei has a strong presence, such as parts of Asia and Europe, may benefit from allowing PetalBot. This enables visibility on Petal Search, making it easier for users to find relevant content.
How can I monitor PetalBot's activity on my website?
You can monitor PetalBot's activity by checking your server logs for its specific user-agent string. Most web analytics tools offer options to filter traffic based on user agents, helping you keep track of how often PetalBot visits your site.
What should I do if PetalBot’s crawling is affecting my website performance?
If PetalBot is impacting your site performance, consider using a crawl-delay directive in your robots.txt to manage its access speed. This can help mitigate server strain while still allowing it to index your site.
Can I completely block PetalBot from accessing my website?
Yes, you can block PetalBot by adding specific directives in your robots.txt file or by implementing server-level restrictions. However, this will prevent any indexing from PetalBot, which may reduce your site's visibility on Huawei’s search platform.
Does PetalBot comply with the robots.txt file?
Yes, PetalBot adheres to the directives outlined in the robots.txt file, which allows webmasters to control access to their site's content. This compliance is standard for legitimate web crawlers.
Is PetalBot different from other web crawlers?
While PetalBot shares similarities with other crawlers like Googlebot and Bingbot, it is specifically tailored for Huawei's ecosystem to support Petal Search and AI initiatives. Its performance and market share may differ from more established crawlers.
What are the privacy implications of allowing PetalBot?
Allowing PetalBot means that data from your website will be used for search indexing and may contribute to AI training. If you have privacy concerns regarding how your content is used, consider the implications before allowing access.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.