Storebot-Google: The Google Shopping Crawler Explained
Technical guide to Storebot-Google crawler, covering its purpose in e-commerce, feed validation, user-agent string and Merchant Center functionality.
What is Storebot-Google and Why It Matters
Storebot-Google is a specialized e-commerce crawler operated by Google. The primary role of Storebot-Google is to collect product information from online stores and validate product feeds for Google Shopping and Merchant Center. When you run an online store, and aim to have your products appear in Google Shopping results, this Google Shopping crawler will likely visit your website. It checks product pages, verifies pricing info, confirms availability, and makes sure your product data matches what you submitted to Google Merchant Center. The bot operates continuously across millions of e-commerce websites worldwide.
Understanding how this shopping bot functions directly impacts how your products show up in Google Shopping. If the Google bot can’t access your products or discovers mismatches between your feed and actual website data, your listings might be suspended. Therefore, SEO experts and content marketers need to know about Storebot-Google because it significantly affects product visibility and organic shopping traffic.
Understanding What Storebot-Google Actually Does
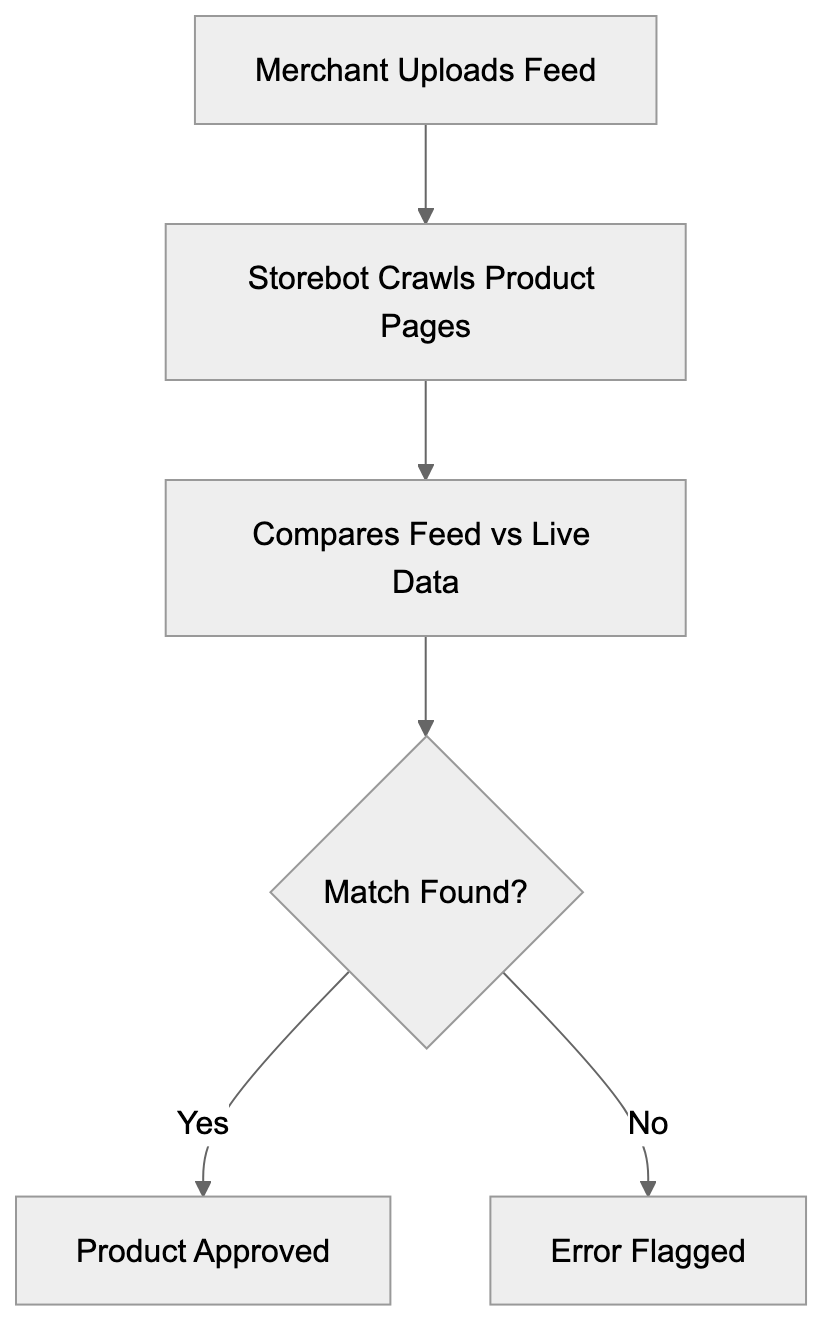
Storebot-Google functions as an automated program visiting e-commerce websites to gather product information. Think of it as Google’s quality control mechanism for shopping listings. Merchants upload product feeds to the Google Merchant Center, detailing price, availability, description, and images. However, Google doesn’t just trust this data blindly.
That’s where Storebot comes in. The product data crawler visits actual product pages on your website, comparing live data against your submitted feed. This verification process helps Google maintain accuracy in Shopping results and prevents merchants from submitting misleading information. Storebot-Google crawls product URLs, extracts structured data, checks Schema markup, and validates the information. It looks for discrepancies in pricing, stock status, and product details. For instance, if your website shows a product costs $50 but the feed says $30, Storebot will flag this mismatch. The crawler also respects robots.txt files and crawl rate limits, though it’s generally less aggressive than the Google bot for regular search indexing.
Storebot-Google Verification Process:
The Technical Details Behind Storebot-Google
The user-agent string for Storebot-Google typically appears as “Storebot-Google” in server logs. The full string might look like: Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Storebot-Google/1.0). When analyzing your web server logs or analytics, search for this identifier to track when the bot visits your site.
The crawler mainly focuses on product pages rather than category pages or blog content. It follows links from your product feed and might also locate products through on-site navigation. Storebot supports standard web technologies, including JavaScript rendering, which means it can manage changing content loaded via JS frameworks. But developers should make sure product data loads quickly and reliably. The bot’s timeout settings are generally generous but not infinite. Response times over 10 seconds might cause crawl issues.
From a technical perspective, Storebot verifies structured data markup like Schema.org Product markup, checks meta tags, and evaluates microdata or JSON-LD formatting. Web developers should implement proper structured data to help the crawler accurately understand product information. The bot also checks for HTTPS connections and secure checkout processes as part of Google’s quality requirements for Merchant Center participants.
How Businesses and Merchants Work With This Crawler
Online retailers primarily interact with Storebot-Google through the Google Merchant Center. After creating a Merchant Center account, businesses upload product feeds in XML or TXT format. These feeds contain product IDs, titles, descriptions, prices, stock availability, image URLs, and other attributes.
Once the feed is uploaded, Google processes it and Storebot begins verification crawls. The e-commerce crawler visits product pages to ensure the feed data aligns with reality. For small business owners, maintaining synchronization between your website and feed is crucial. If you change a price on your website, update your feed too. Many e-commerce platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, and BigCommerce offer plugins that automatically sync product data with the Merchant Center. This automation minimizes manual work and reduces discrepancies Storebot might flag.
Product Data Validation Flow:

Marketing professionals must monitor the Merchant Center for warnings and errors resulting from Storebot-Google crawls. Common issues include mismatched prices, out-of-stock products listed as available, or missing return policy information. Google provides diagnostic reports detailing what Storebot found during its crawls. Addressing these issues promptly prevents listing suspensions and helps maintain your Shopping ad performance.
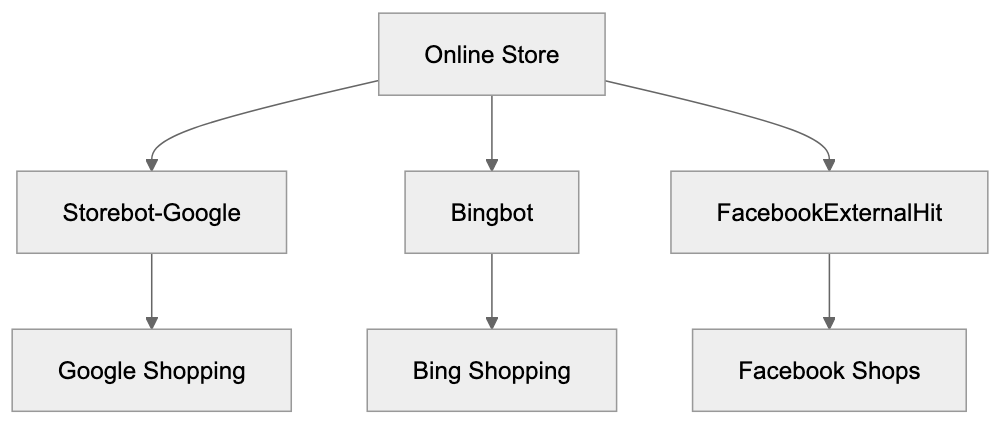
Comparing Storebot-Google to Other E-commerce Crawlers
Storebot-Google isn’t the only e-commerce crawler examining websites. Several platforms operate similar bots for their shopping and marketplace features. Understanding these differences can help website owners optimize for multiple channels.
| Crawler Name | Platform | Primary Purpose | Crawl Frequency | Special Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storebot-Google | Google Shopping | Product feed validation and verification | Daily to weekly | Structured data, HTTPS, fast load times |
| Bingbot | Microsoft Shopping | Product indexing for Bing Shopping | Weekly | Bing Webmaster Tools verification |
| FacebookExternalHit | Facebook/Instagram Shopping | Product catalog validation | As needed | Facebook Business Manager setup |
| Amazonbot | Amazon | Web content discovery and analysis | Variable | Standard robots.txt compliance |
| PinterestBot | Pinterest Shopping | Product pin validation | Weekly | Rich Pins metadata |
Storebot-Google tends to be more strict about data accuracy compared to some alternatives. Google maintains detailed quality guidelines and actively suspends accounts for policy violations. The bot checks not just product info but also landing page experience, shipping cost display, and mobile usability. Compared to Bingbot, Storebot crawls more frequently and has a lower tolerance for mismatches. FacebookExternalHit mainly focuses on Open Graph tags and catalog feed validation but doesn’t conduct as deep verification of on-page pricing. On the other hand, Amazonbot serves different purposes since Amazon primarily uses it for general web indexing rather than third-party merchant validation.
For web developers managing multiple shopping channels, meeting the requirements for all these crawlers simultaneously can be a challenge. The good news is that implementing proper structured data and maintaining accurate product information benefits all platforms.
Feed Validation Behavior and Error Handling
When Storebot-Google finds issues during its crawls, the consequences appear in the Merchant Center. The platform categorizes problems into warnings and errors. Errors prevent products from showing in Shopping results until fixed. Warnings don’t block listings immediately but should still be addressed.
Common errors include price mismatches, where the website displays different pricing than the feed, availability conflicts when products marked in-stock are actually unavailable, and missing required attributes like GTIN or brand. The crawler also checks for policy violations such as prohibited products, misleading claims, or restricted content.
Feed validation occurs in stages. First, Google processes your uploaded feed for formatting and syntax errors. Then Storebot crawls the actual product pages for verification. This two-step process means you might get initial approval but face issues later when the crawler visits your site. Content marketers should note that product titles and descriptions also undergo validation. Keyword stuffing, excessive capitalization, or promotional language can trigger warnings. The crawler compares your feed content against on-page content to ensure consistency.
For developers troubleshooting crawl issues, check your server logs for Storebot requests that returned errors. A 404 response means the product URL is broken. A 503 suggests server overload during bot visits. Timeout errors indicate slow page loads that need improvement.
Managing Crawl Rate and Server Resources
Storebot-Google generally crawls at reasonable rates that shouldn’t overload most servers, but large catalogs with thousands of products can experience significant bot traffic. Website owners can influence crawl behavior through several methods.
The robots.txt file allows you to control which URLs Storebot can access, though blocking product pages will prevent verification. A better approach is using crawl-delay directives if your server struggles with bot traffic. In Google Merchant Center settings, you can adjust how often your feed gets processed, which indirectly affects crawl frequency. Smaller catalogs might see crawls every few days, while huge catalogs get crawled more continuously.
Server resources matter because Storebot expects reasonably fast responses. If your hosting can’t handle concurrent bot requests alongside regular user traffic, consider upgrading or implementing caching. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) help by serving product images and static assets quickly. Page caching plugins reduce server load for repeat bot visits. For WordPress and WooCommerce sites, improving database queries enhances response times when the crawler requests product data.
Monitor your server logs to identify patterns in Storebot visits. Some merchants notice increased crawl activity after uploading new feeds or making bulk product updates. This makes sense as Google wants to verify changes quickly.
E-commerce Crawler Ecosystem:
Best Practices for Storebot-Google Optimization
To ensure smooth interactions with Storebot-Google, follow these proven strategies:
- Implement complete structured data using Schema.org Product markup. Include all relevant properties like price, availability, image, description, and identifiers. Use JSON-LD format, which is easiest for both the crawler and developers.
- Maintain perfect synchronization between your product feed and website. Automated feed generation tools eliminate manual errors and keep data current.
- Ensure fast page load times, especially for product pages. Aim for under 3 seconds on mobile devices. Compress images, minimize JavaScript, and use browser caching.
- Provide clear pricing, including any additional fees or taxes. Hidden costs discovered by the crawler can trigger policy violations.
- Display accurate stock status. If a product is out of stock, mark it correctly in both your feed and on the page.
- Use HTTPS across your entire site. Google requires secure connections for Merchant Center participants.
- Create mobile-friendly product pages as Google prioritizes the mobile experience. Test your pages with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
- Monitor Merchant Center diagnostics regularly. Address warnings before they escalate to errors. Set up email notifications for feed issues so you can respond swiftly.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Merchants frequently encounter specific problems with Storebot-Google crawls. Price mismatches are the most common issue. This occurs when sale prices on your website don’t match feed prices or when currency formatting differs. Solution: Use consistent price formatting and update feeds immediately when running sales.
Availability problems occur when products show as in stock on your site, but the feed says out of stock, or vice versa. Solution: Implement real-time inventory sync between your e-commerce platform and feed.
Missing return policy information causes warnings for many merchants. Solution: Add clear return policy details to product pages and include the link in your Merchant Center settings.
Image quality issues arise when product images are too small, too large, or low resolution. Solution: Use high-quality images at recommended dimensions, typically at least 800x800 pixels.
Landing page issues happen when the product URL in your feed goes to a category page instead of the specific product. Solution: Verify each product URL leads directly to that individual product page.
Schema markup errors occur when structured data contains syntax mistakes or missing required fields. Solution: Validate your markup using Google’s Rich Results Test tool.
Crawl timeout problems suggest your pages load too slowly for the bot. Solution: Improve server performance, enable caching, and reduce page weight.
The Relationship Between Storebot and Google Merchant Center
Google Merchant Center acts as the control panel for all interactions with Storebot-Google. When you upload a product feed to the Merchant Center, you’re essentially providing Storebot a roadmap of products to verify. The platform processes your feed, validates formatting, and then dispatches Storebot to check actual product pages.
Merchant Center displays crawl results through diagnostic reports. These reports highlight disapproved products, warnings requiring attention, and successfully verified items. The dashboard includes metrics on feed processing status, product performance, and policy compliance.
SEO experts should understand that Merchant Center approval doesn’t guarantee Shopping ad visibility. Products must also meet quality scores and bid requirements, but Storebot’s verification is the foundation everything else builds on. Without passing crawler validation, products never make it to the auction.
The Merchant Center also manages supplemental feeds, which allow you to update product attributes without altering your main feed. Storebot validates these supplements during regular crawls. For international sellers, Merchant Center manages feeds for different countries. Storebot crawls product pages appropriate to each target market, checking language, currency, and local requirements.
How Storebot Impacts Your Shopping Performance
The efficiency of Storebot-Google directly affects your e-commerce success on Google Shopping. Products that pass validation appear in Shopping results and can run as Shopping ads. Products that fail validation get suspended and generate no traffic.
The crawler’s assessment of your landing page quality influences your Quality Score, which affects ad costs and positioning. Faster crawls and clean validations mean quicker time-to-market for new products. When you add items to your catalog, effective Storebot processing gets them live in Shopping results within days rather than weeks. Conversely, crawl errors delay product launches, costing potential sales.
Marketing professionals track metrics like the approval rate (percentage of products passing validation), average time from feed upload to approval, and error resolution time. These metrics indicate how well your technical setup works with Storebot. Higher approval rates and faster processing correlate with better Shopping campaign performance.
For content marketers managing product descriptions, understanding Storebot’s text analysis helps improve content. The crawler evaluates description quality, keyword relevance, and policy compliance. Well-written, accurate descriptions pass validation smoothly, while misleading or low-quality content triggers reviews.
Future Developments and Crawler Evolution
Google continues updating Storebot-Google’s capabilities as e-commerce technology evolves. Recent changes include enhanced JavaScript rendering support, improved mobile crawling, and improved structured data validation.
The crawler now handles single-page applications more effectively, which is important for modern web frameworks like React and Vue. Machine learning processes help Storebot identify suspicious patterns like artificial price inflation or fake availability claims. These AI-powered checks make it harder to game the system with misleading feed data.
Google has also improved crawl efficiency, allowing the bot to verify more products in less time. For developers, this means staying current with Google’s technical requirements. What worked last year might not meet today’s standards. Regular reviews of Merchant Center documentation and staying informed about Shopping policy updates helps maintain compliance.
The trend toward stricter quality requirements continues. Google wants Shopping results to provide an excellent user experience, which means higher standards for merchants. Expect Storebot to become more sophisticated in detecting low-quality pages, poor mobile experiences, and policy violations.
End and Key Takeaways
Storebot-Google is the verification engine behind Google Shopping and Merchant Center. This specialized e-commerce crawler visits websites to validate product information, check pricing accuracy, and ensure merchants comply with quality guidelines. For online retailers, understanding how Storebot works is crucial for maintaining active Shopping listings.
The crawler compares your product feed against actual website data, flagging any discrepancies or policy violations. Technical improvement is vital, with proper structured data, fast page loads, and accurate product information forming the foundation for successful validation.
Web developers should implement Schema markup, ensure mobile compatibility, and monitor server performance to support effective crawling. Marketing professionals need to track Merchant Center diagnostics, resolve errors quickly, and maintain synchronized data across all platforms.
Compared to other e-commerce crawlers, Storebot-Google operates with higher frequency and stricter validation standards. The investment in improvements pays off through better product visibility, lower ad costs, and increased shopping traffic.
As Google continues improving crawler capabilities, staying informed about updates and maintaining technical best practices ensures your products remain competitive in Shopping results.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I ensure that my product data is compliant with Storebot-Google?
To ensure compliance, implement complete structured data using Schema.org Product markup that includes all relevant properties like price, availability, and descriptions. Regularly check your Merchant Center diagnostics to resolve any warnings or errors quickly.
What should I do if I receive a warning or error from Storebot-Google?
Warnings and errors should be addressed promptly. Focus on fixing common issues such as price mismatches, stock availability errors, and missing required attributes. Use the diagnostic reports in the Merchant Center to pinpoint and resolve specific problems.
How often does Storebot-Google crawl my website?
The crawl frequency can vary based on the size of your product catalog and other factors. Typically, smaller catalogs may be crawled every few days, while larger catalogs could experience continuous crawls for updates.
What can impact Storebot-Google's ability to crawl my site?
Factors that can impact crawling include slow page load times, server overload during peak traffic, and incorrect robots.txt settings that prevent the crawler from accessing product pages. Ensure your site is optimized for speed and that your server can handle simultaneous requests.
What kind of structured data does Storebot-Google check?
Storebot-Google checks for structured data markup like Schema.org Product markup, validating that all required fields are present and correctly formatted. It also looks for meta tags and microdata, ensuring that your product information is accurate and up-to-date.
Does Storebot-Google respect the robots.txt file?
Yes, Storebot-Google respects the robots.txt file, but blocking access to product pages can prevent proper verification. Instead, consider using crawl-delay directives to manage traffic if necessary.
How can I improve my product's visibility on Google Shopping?
To improve visibility, ensure your product listings are fully compliant with Storebot-Google's requirements by using structured data, maintaining accurate pricing and stock status, and monitoring your Merchant Center for issues. Fast loading times and mobile-friendly pages also enhance visibility.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.