Complete Guide to YandexBot: Russia's Premier Search Crawler
Learn about YandexBot, the web crawler from Russia's largest search engine. Covers user-agent strings, robots.txt handling, and AI training usage.
What is YandexBot
YandexBot is a web crawler operated by Yandex, the largest search engine and tech company in Russia. As a Russian search bot, YandexBot scans websites across the internet to index their content, which powers search results when users enter queries in the Yandex search engine. Understanding how YandexBot works is crucial for website owners and developers, as it determines a site’s visibility in Yandex search results.
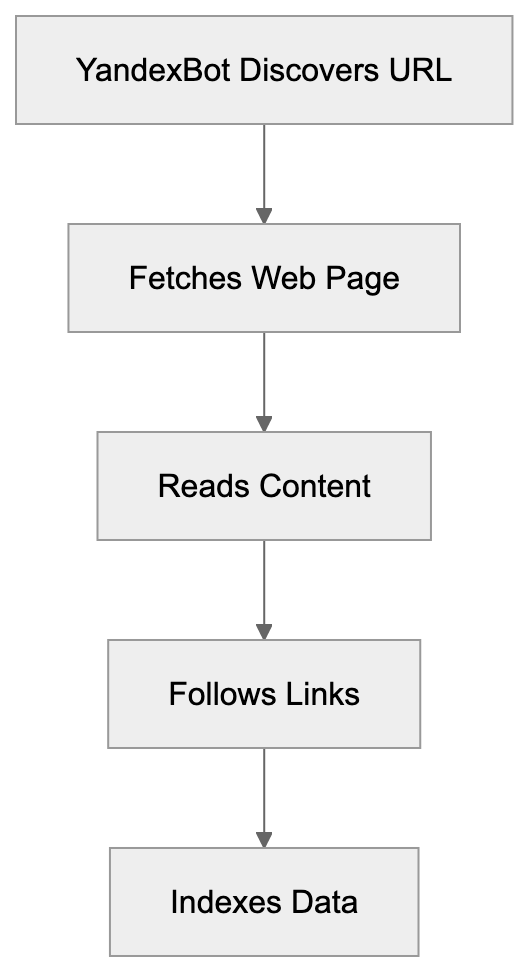
YandexBot visits web pages, reads their content, and follows links to discover new pages, similar to how Googlebot operates for Google. Yandex, serving millions mainly in Russia and nearby regions, also uses this data for AI development, making YandexBot essential in today’s AI landscape.
YandexBot Crawling Process:
Understanding Yandex as a Company
Yandex, the dominant search engine in Russia, commands roughly 60% market share in the region. Established in 1997, it has expanded into a significant tech conglomerate. Beyond search, Yandex offers services like email, maps, cloud storage, ride-sharing, and e-commerce.
The company develops machine learning technologies and natural language processing systems, which enhance features such as search ranking and translation services. YandexBot’s web crawling supplies the necessary training data for these AI systems.
Yandex maintains data centers in multiple countries. Thousands of its engineers and researchers focus on search technology and artificial intelligence. For businesses targeting Russian markets or Eastern European users, proper YandexBot indexing can enhance online visibility.
How YandexBot Works and Its User-Agent Strings
YandexBot identifies itself through specific user-agent strings when visiting websites, allowing server logs to track its activity. The primary user-agent string is:
Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; YandexBot/3.0; +http://yandex.com/bots)
Yandex operates various specialized crawlers, each with unique user-agent identifiers:
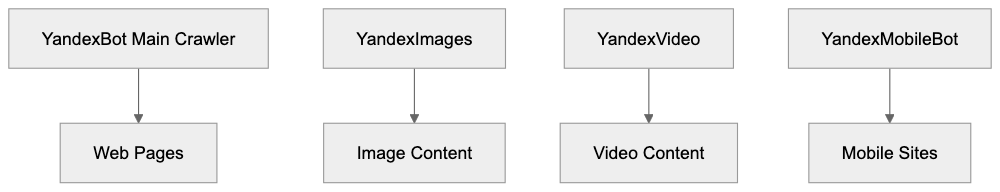
- YandexBot - main web crawler for search indexing
- YandexImages - image crawling
- YandexVideo - video content crawling
- YandexMedia - media file handling
- YandexBlogs - blog content focus
- YandexNews - news websites crawling
- YandexMobileBot - mobile-optimized crawling
YandexBot Specialized Crawlers:
These crawlers adhere to web protocols such as robots.txt files and meta robots tags, allowing website administrators to determine YandexBot’s access and activity.
Controlling YandexBot Through Robots.txt
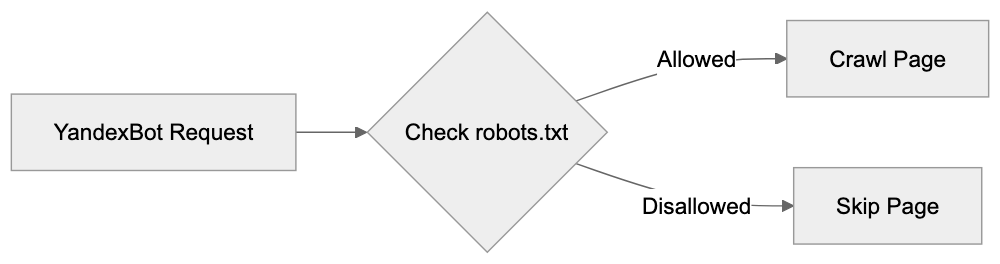
The robots.txt file allows managing how YandexBot interacts with your site. Place this text file in your site’s root directory to instruct web crawlers.
To block YandexBot entirely:
User-agent: YandexBot
Disallow: /To allow YandexBot but block specific directories:
User-agent: YandexBot
Disallow: /private/
Disallow: /admin/
Allow: /Robots.txt Control Flow:
For server load management, set a crawl-delay:
User-agent: YandexBot
Crawl-delay: 5This setting instructs the bot to wait 5 seconds between requests. Remember not to block YandexBot if you wish for your site to appear in Yandex search results.
YandexBot and AI Training Data Collection
Yandex uses crawled web content to train AI models, with data from YandexBot feeding machine learning systems for various applications. Content accessible by YandexBot may be incorporated into AI training datasets. No separate opt-out exists for AI training, so blocking YandexBot also removes search indexing.
YandexBot crawls billions of web pages, forming a vast data foundation for sophisticated AI systems. While details about training data usage are often proprietary, the impact on AI development is significant.
Comparing YandexBot to Other Search Crawlers
Different search engines operate distinct crawlers, each with varying behaviors. Understanding these aids website administrators in improving crawler management strategies.
| Crawler | Company | Market Focus | Crawl Frequency | AI Training Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YandexBot | Yandex | Russia, CIS countries | Medium-High | Yes |
| Googlebot | Global | High | Yes | |
| Bingbot | Microsoft | Global, English-focused | Medium | Yes |
| Baiduspider | Baidu | China | High (for Chinese sites) | Yes |
| DuckDuckBot | DuckDuckGo | Global, privacy-focused | Low-Medium | Limited |
YandexBot aggressively targets Russian-language content. Comparing crawler frequency, Googlebot often has the highest rate, with Bingbot improving significantly.
Technical Specifications and Crawling Behavior
Operating from IP addresses owned by Yandex, YandexBot requests can be verified through reverse DNS lookups. Legitimate requests originate from domains ending in .yandex.ru or .yandex.net.
Respecting standard HTTP status codes, YandexBot supports JavaScript rendering, though server-side or static HTML still offers the most reliable indexing. It respects hreflang tags for internationalization.
Managing Server Load from YandexBot
Web crawlers like the Yandex crawler can affect server performance. Monitor your logs for YandexBot activity patterns. If performance degrades, you have multiple strategies:
- Use the Crawl-delay directive in robots.txt for basic rate limiting.
- Configure your server for more granular rate-limiting.
- Implement caching strategies to reduce processing load.
- Leverage Content Delivery Networks for geographic load distribution.
Privacy and Data Considerations
YandexBot collects publicly accessible content and does not bypass authentication systems. The robots.txt file remains the primary tool for controlling YandexBot’s access, with trade-offs between visibility and data privacy.
Some websites only allow specific verified crawlers or block all bots from certain regions, a complex but effective strategy.
YandexBot Impact on SEO Strategy
For Russian-speaking audiences, optimizing for YandexBot is vital. Yandex values user engagement metrics and links from Russian websites.
Utilize Yandex Webmaster Tools for insights into YandexBot’s view of your site, where crawl errors and indexing status can be monitored.
Structured data markup, supported by Yandex, aids the crawler in understanding your content better.
Future Developments and Trends
Crawling technology evolves as AI training needs grow. YandexBot will likely enhance its JavaScript rendering and mobile crawling capabilities. As content creators and search engines interact, restrictions, policies, and technological improvements will continue shaping YandexBot and other crawlers’ roles in the industry.
End
YandexBot acts as Yandex’s primary web crawler, pivotal for search indexing and AI training data collection. Website owners use robots.txt and web protocols to manage YandexBot’s access. Understanding YandexBot’s intricacies is crucial for enhancing visibility in Yandex search results and managing content usage in AI development.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I check if my website is being crawled by YandexBot?
You can check your server logs for requests originating from Yandex's IP addresses or examine the user-agent string in your log files. The primary user-agent for YandexBot is 'Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; YandexBot/3.0; +http://yandex.com/bots)'. Monitoring these will help you track YandexBot's activity on your site.
What should I do if YandexBot is affecting my server's performance?
If YandexBot's activity degrades your server performance, you can use the 'Crawl-delay' directive in your robots.txt file to limit its request rate. Additionally, consider optimizing your server configuration for rate limits, implementing caching strategies, or utilizing a Content Delivery Network (CDN) for load management.
How can I ensure my site is well-indexed by YandexBot?
To enhance your site's indexing by YandexBot, ensure your content is structured properly and accessible without authentication barriers. Utilize Yandex Webmaster Tools to monitor crawl errors and indexing status, and consider employing structured data markup to help YandexBot understand your content better.
Can I block YandexBot from crawling my website?
Yes, you can block YandexBot by adding specific directives to your robots.txt file. For example, including 'User-agent: YandexBot' followed by 'Disallow: /' will prevent YandexBot from accessing your site. However, blocking it also means your site will not appear in Yandex search results.
What are the implications of YandexBot collecting data for AI training?
YandexBot collects data from crawled content to train its AI systems, and there's no separate opt-out option for this process. If you choose to block YandexBot, your content will be excluded from both search indexing and AI training datasets, limiting its visibility and potential usage within Yandex's AI products.
How do YandexBot's crawling rules differ from other web crawlers?
Each web crawler has its own behaviors and rules, such as crawl frequency and the types of content they prioritize. For instance, YandexBot specifically targets Russian-language content and has different priorities compared to Googlebot or Baiduspider, which may have broader or different focuses based on their respective market strategies.
What type of content does YandexBot prioritize?
YandexBot focuses on Russian-language content but also crawls diverse types including images, videos, and news articles through its specialized crawlers. Engaging content with quality backlinks and user engagement metrics is highly valued, influencing how well your site ranks in Yandex search results.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.