Elasticsearch Guide: Open Source AI Search Engine Explained
Learn how Elasticsearch works as an AI-powered search engine, its vector search capabilities, and how it compares to Algolia and Solr.
What is Elasticsearch?
Elasticsearch is an open-source search engine built on Apache Lucene, designed to help companies efficiently search through large datasets. This versatile tool can perform searches across text, numbers, dates, and vectors for AI search tasks. Businesses utilize it for powering website search boxes, analyzing logs, and enhancing machine learning initiatives.
Notably fast, Elasticsearch allows real-time searchability of new data immediately upon entry, making it highly effective in managing millions of records. Globally recognized enterprises such as Wikipedia, Netflix, and LinkedIn rely on Elasticsearch for their search engine needs.
Launched by Elastic NV, the company behind Elasticsearch, in 2010, the search engine has become widely adopted, with over half of Fortune 500 companies using it. The basic version is free and open-source.
Main Features and Benefits
Elasticsearch offers numerous powerful features that contribute to its popularity:
- Fast Search Speed: Capable of searching millions of documents in milliseconds.
- **Vector Search:** Enhances AI and machine learning applications with vector operations.
- Real-time Results: Displays new data immediately upon addition.
- Easy Scaling: Scalability from a single computer to multiple servers.
- REST API: Streamlined integration with various software platforms.
Elasticsearch Architecture Overview:
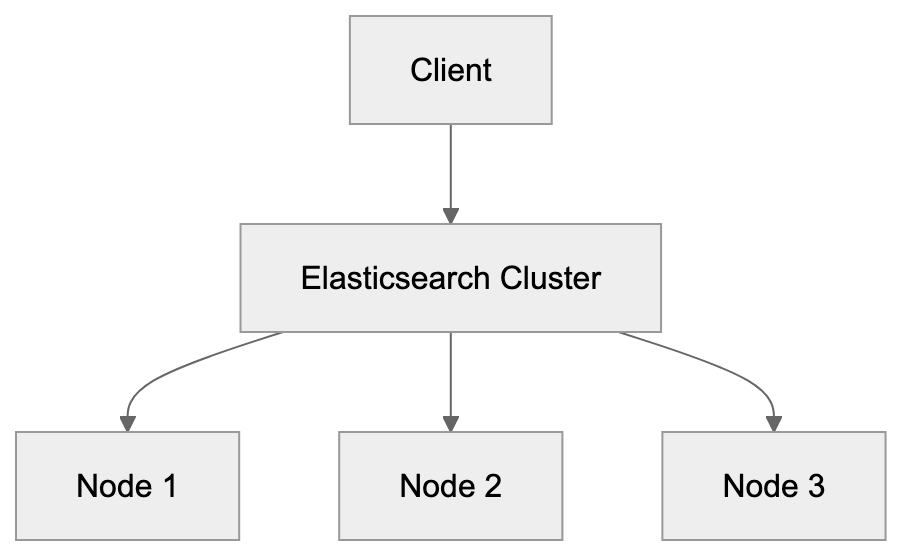
- Text Analysis: Sophisticated text search capabilities that correct typos.
- Aggregations: Efficient data grouping and counting.
Elasticsearch is adaptable for various data types:
- Website content
- Product catalogs
- Log files
- Business data
- Scientific data
- Customer records
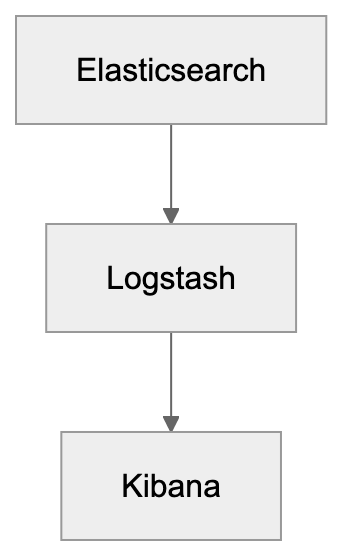
The ELK Stack
Elasticsearch functions as a core component of the ELK Stack, which includes:
- Elasticsearch: The primary search engine.
- Logstash: Responsible for data collection and [processing.
- Kibana: For visualizing data through charts and graphs](https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch).
Key Features of the ELK Stack:
Many companies employ the full ELK Stack to diagnose system issues, monitor application performance, secure networks, understand user behavior, and inform business decisions.
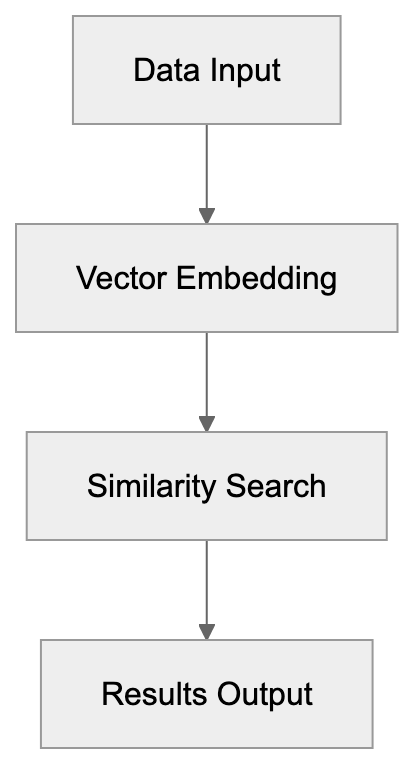
Vector Search for AI
Elasticsearch’s support for vector search is vital for AI and machine learning. Unlike traditional searches, vector search identifies similar items instead of just exact matches.
Vector search applications include:
- Identifying similar images
- Matching related products
- Finding semantically similar words
- Grouping analogous customer behaviors
These vector features integrate with:
- Neural search
- Semantic search
- Image similarity
- Recommendation systems
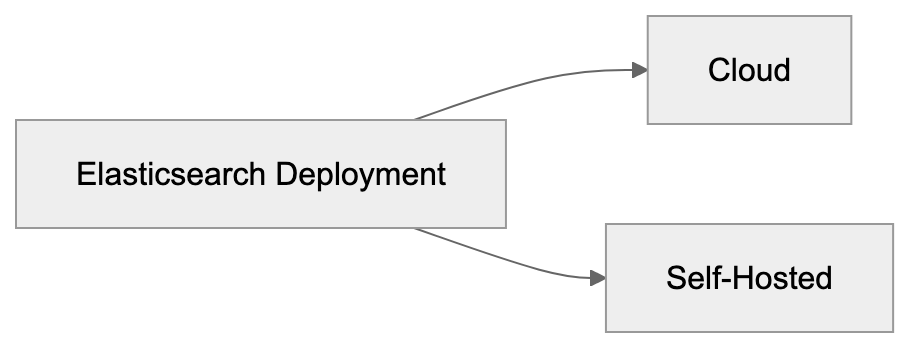
Cloud vs Self-Hosted Options
Elasticsearch can be deployed via two main methods:
- Cloud Service:
- Elastic Cloud (official service)
Vector Search Process:
- AWS Elasticsearch
- Google Cloud Elasticsearch
- Azure Elasticsearch
- Self-Hosted:
- Personal servers
- Local machines
- Private cloud environments
Both options offer distinct advantages:
Cloud Benefits:
- Simplified initiation
- Automated updates
- Reduced management workload
- Integrated security features
Self-Hosted Benefits:
- Full operational control
- Cost-effective for large-scale use
- Data remains in-house
- Customizable configurations
Cloud vs Self-Hosted Deployment:
Comparison with Other Search Tools
Here’s a comparison of Elasticsearch with similar tools:
Elasticsearch vs Algolia:
- Elasticsearch: Offers greater flexibility but requires more complex setup.
- Algolia: User-friendly but more expensive.
Elasticsearch vs Solr:
- Elasticsearch: Preferred for new projects due to simpler API.
- Solr: More established, excellent for text search.
Key differences:
-
Setup Time:
- Algolia: Minutes
- Elasticsearch: Hours to days
- Solr: Days
-
Cost:
- Algolia: Subscription-based
- Elasticsearch: Free with optional paid support
- Solr: Free
-
Ease of Use:
- Algolia: Very user-friendly
- Elasticsearch: Moderate complexity
- Solr: More complex
Licensing Changes
In 2021, Elasticsearch altered its licensing, with key changes including:
- Basic features remain free.
- Certain new features now require a paid license.
- Older versions retain the Apache 2.0 license.
- Companies can continue to use it free of charge.
- Paid features encompass advanced AI tools.
This licensing transformation has sparked the emergence of alternative open-source solutions and a variety of cloud providers with different pricing frameworks.
Getting Started Tips
To commence with Elasticsearch:
-
Choose your setup:
- Opt for a cloud service for convenience.
- Install locally for educational purposes.
- Use Docker for experimentation.
-
Learn basic concepts:
- Indices
- Documents
- Queries
- Mappings
-
Try simple operations:
- Add data
- Search text
- Filter results
- Sort items
-
Utilize these tools:
- Kibana for data visualization
- REST API for integration
- Client libraries
Conclusion
Elasticsearch stands out as a dynamic search tool, continually evolving. It excels in both straightforward searches and advanced AI tasks. Its blend of free and premium features allows companies to start modestly and expand as needed.
Key takeaways:
- Fast, reliable search engine.
- Effective for AI and conventional search.
- Versatile across various data types.
- Multiple deployment options available.
- Robust support from the Elastic company.
Whether you require basic search capabilities or advanced AI features, Elasticsearch offers a comprehensive solution. Its open-source foundation combined with business features makes it suitable for a broad range of applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of queries can Elasticsearch handle?
Elasticsearch can manage a variety of query types, including full-text searches, structured searches on numerical and date data, and vector searches designed for AI applications. This allows users to perform complex analyses across different data formats seamlessly.
How do I choose between cloud and self-hosted Elasticsearch?
Your choice depends on your specific needs. If you prefer a hassle-free setup and management, a cloud service might be ideal. However, if data privacy and customization are critical, consider self-hosting.
Can I integrate Elasticsearch with other software?
Yes, Elasticsearch provides a REST API that facilitates integration with various platforms and applications. This enables users to easily connect Elasticsearch with other software tools for enhanced data management and searching capabilities.
What is the ELK Stack, and how is it related to Elasticsearch?
The ELK Stack comprises Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana. While Elasticsearch acts as the primary search engine, Logstash is used for data collection and processing, and Kibana provides visualization tools, making it easier to analyze and interpret data.
How has the licensing for Elasticsearch changed?
In 2021, Elasticsearch changed its licensing model to include paid features while maintaining free access to basic functionalities. This shift encourages users to explore premium capabilities while allowing ongoing free usage of earlier versions.
What are some common use cases for Elasticsearch?
Common use cases include website search functionalities, log file analysis, business intelligence, data monitoring, and powering AI applications. Its versatile capabilities make it suitable for a broad range of fields and applications.
How can I get started with Elasticsearch?
Begin by selecting your deployment option, either cloud or self-hosted. Familiarize yourself with key concepts such as indices, documents, and queries, and then try simple operations like adding data and performing searches to build your understanding.
Track Your AI Visibility
See how AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity discover and recommend your brand.